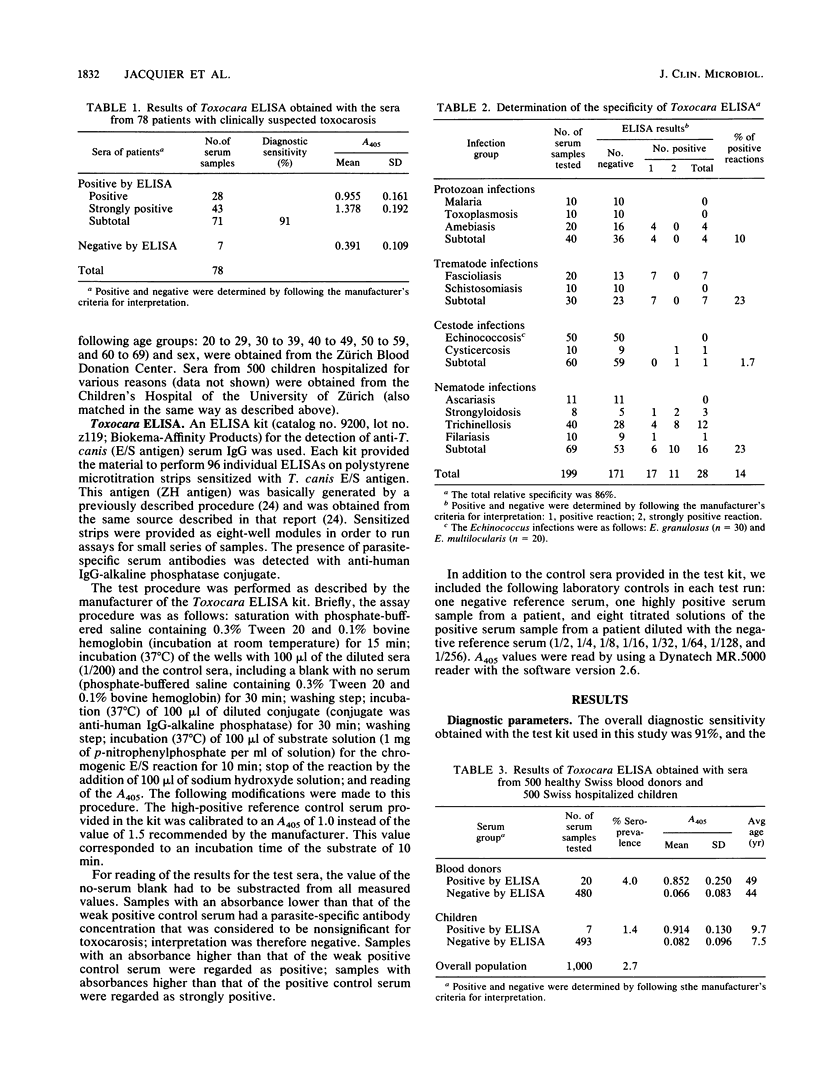
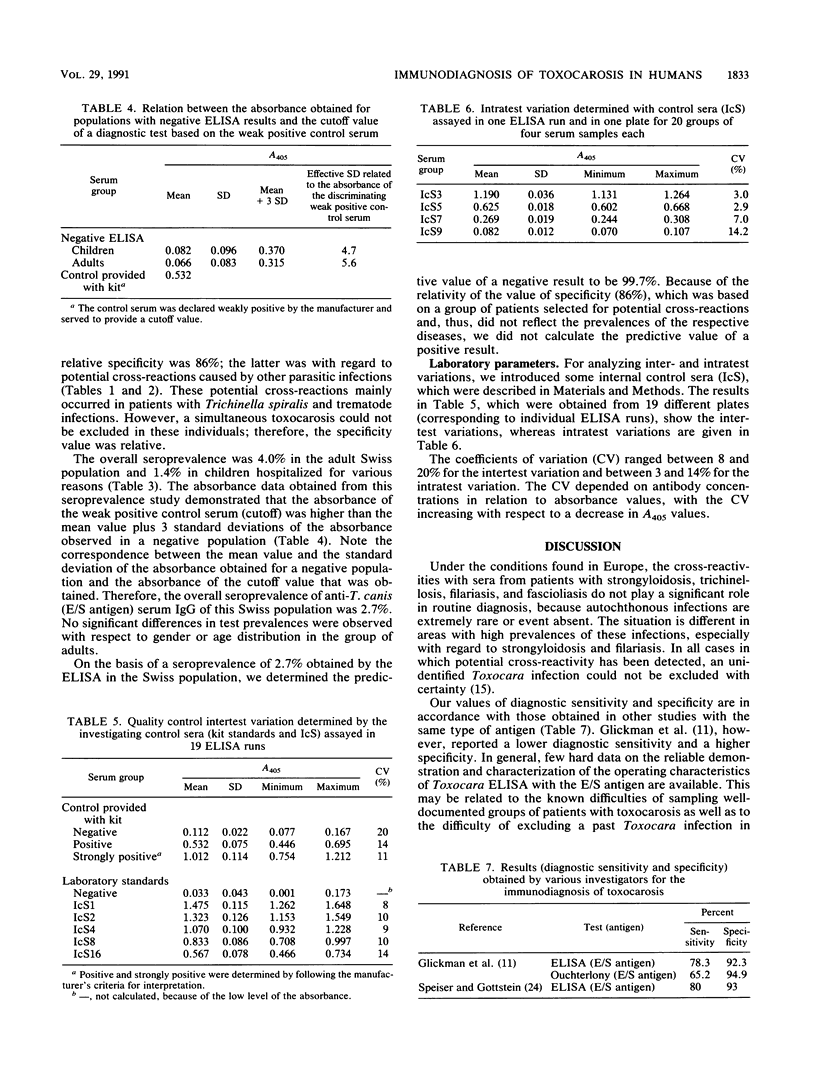
Abstract
Excretory/secretory (E/S) antigen derived from second-stage larvae of Toxocara canis maintained in defined medium in vitro has been well established worldwide for the immunodiagnosis of human toxocarosis by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Such an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, based on the detection of human anti-T. canis (E/S antigen) serum immunoglobulin G, has recently been commercialized by Biokema-Affinity Products (Crissier-Lausanne, Switzerland). This commercial test kit was evaluated with regard to its application in a routine diagnostic laboratory and the reliability of the results. Of 78 patients with suspected clinical toxocarosis, 71 had anti-T. canis antibodies (positive serological result) corresponding to a diagnostic sensitivity of 91%; 14% of serum samples (n = 199) from patients with protozoan or with helminthic infections also showed positive reactions mainly related to infections with Trichinella, Strongyloides, and Fasciola species. An epidemiological study with 1,000 serum samples from randomly selected healthy blood donors and children in Switzerland demonstrated a seroprevalence of 2.7%. The test kit under evaluation had an overall diagnostic sensitivity of 91% and a relative specificity of 86%, the latter being related to some protozoan and helminthic infections. Because of the scarcity of such infections, potential cross-reactivity does not play a major role under the conditions found in the middle part of Europe. In conclusion, the application of the test kit provided for use in this study can be recommended for routine diagnostic use.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barriga O. O. A critical look at the importance, prevalence and control of toxocariasis and the possibilities of immunological control. Vet Parasitol. 1988 Sep;29(2-3):195–234. doi: 10.1016/0304-4017(88)90126-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaver P. C. The nature of visceral larva migrans. J Parasitol. 1969 Feb;55(1):3–12. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyce W. M., Branstetter B. A., Kazacos K. R. Comparative analysis of larval excretory-secretory antigens of Baylisascaris procyonis, Toxocara canis and Ascaris suum by Western blotting and enzyme immunoassay. Int J Parasitol. 1988 Feb;18(1):109–113. doi: 10.1016/0020-7519(88)90044-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillespie S. H. The epidemiology of Toxocara canis. Parasitol Today. 1988 Jun;4(6):180–182. doi: 10.1016/0169-4758(88)90156-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glickman L. T., Chaudry I. U., Costantino J., Clack F. B., Cypess R. H., Winslow L. Pica patterns, toxocariasis, and elevated blood lead in children. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1981 Jan;30(1):77–80. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1981.30.77. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glickman L. T., Magnaval J. F., Domanski L. M., Shofer F. S., Lauria S. S., Gottstein B., Brochier B. Visceral larva migrans in French adults: a new disease syndrome? Am J Epidemiol. 1987 Jun;125(6):1019–1034. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a114618. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glickman L. T., Schantz P. M. Epidemiology and pathogenesis of zoonotic toxocariasis. Epidemiol Rev. 1981;3:230–250. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.epirev.a036235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glickman L., Schantz P., Dombroske R., Cypess R. Evaluation of serodiagnostic tests for visceral larva migrans. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1978 May;27(3):492–498. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1978.27.492. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottstein B. Purification and characterization of a specific antigen from Echinococcus multilocularis. Parasite Immunol. 1985 May;7(3):201–212. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3024.1985.tb00070.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kassai T., Cordero del Campillo M., Euzeby J., Gaafar S., Hiepe T., Himonas C. A. Standardized nomenclature of animal parasitic diseases (SNOAPAD). Vet Parasitol. 1988 Oct;29(4):299–326. doi: 10.1016/0304-4017(88)90148-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynch N. R., Eddy K., Hodgen A. N., Lopez R. I., Turner K. J. Seroprevalence of Toxocara canis infection in tropical Venezuela. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1988;82(2):275–281. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(88)90446-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynch N. R., Wilkes L. K., Hodgen A. N., Turner K. J. Specificity of Toxocara ELISA in tropical populations. Parasite Immunol. 1988 May;10(3):323–337. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3024.1988.tb00224.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumura K., Endo R. Seroepidemiological study on toxocaral infection in man by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. J Hyg (Lond) 1983 Feb;90(1):61–65. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400063841. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meghji M., Maizels R. M. Biochemical properties of larval excretory-secretory glycoproteins of the parasitic nematode Toxocara canis. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1986 Feb;18(2):155–170. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(86)90035-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller N., Gottstein B., Vogel M., Flury K., Seebeck T. Application of a recombinant Echinococcus multilocularis antigen in an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for immunodiagnosis of human alveolar echinococcosis. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1989 Sep;36(2):151–159. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(89)90187-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholas W. L., Stewart A. C., Walker J. C. Toxocariasis: a serological survey of blood donors in the Australian Capital Territory together with observations on the risks of infection. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1986;80(2):217–221. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(86)90015-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsons J. C., Bowman D. D., Grieve R. B. Tissue localization of excretory-secretory antigens of larval Toxocara canis in acute and chronic murine toxocariasis. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1986 Sep;35(5):974–981. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1986.35.974. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savigny D. H. In vitro maintenance of Toxocara canis larvae and a simple method for the production of Toxocara ES antigen for use in serodiagnostic tests for visceral larva migrans. J Parasitol. 1975 Aug;61(4):781–782. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scaglia M., Gatti S., Bruno A., Cevini C., Chichino G., Magnani B., Brustia R. Larva migrans viscérale et oculaire: étude épidémiologique, clinique et immunologique portant sur 20 cas, adultes et enfants. Bull Soc Pathol Exot Filiales. 1989;82(3):410–421. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schantz P. M. Toxocara larva migrans now. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1989 Sep;41(3 Suppl):21–34. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1989.41.21. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speiser F., Gottstein B. A collaborative study on larval excretory/secretory antigens of Toxocara canis for the immunodiagnosis of human toxocariasis with ELISA. Acta Trop. 1984 Dec;41(4):361–372. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stürchler D., Bruppacher R., Speiser F. Epidemiologische Aspekte der Toxokariasis in der Schweiz. Schweiz Med Wochenschr. 1986 Aug 16;116(33):1088–1093. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stürchler D., Schubarth P., Gualzata M., Gottstein B., Oettli A. Thiabendazole vs. albendazole in treatment of toxocariasis: a clinical trial. Ann Trop Med Parasitol. 1989 Oct;83(5):473–478. doi: 10.1080/00034983.1989.11812374. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodruff A. W., Salih S. Y., de Savigny D., Baya E. I., Shah A. I., Dafalla A. A. Toxocariasis in the Sudan. Ann Trop Med Parasitol. 1981 Oct;75(5):559–561. doi: 10.1080/00034983.1981.11687481. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Savigny D. H., Voller A., Woodruff A. W. Toxocariasis: serological diagnosis by enzyme immunoassay. J Clin Pathol. 1979 Mar;32(3):284–288. doi: 10.1136/jcp.32.3.284. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Knapen F., van Leusden J., Polderman A. M., Franchimont J. H. Visceral larva migrans: examinations by means of enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay of human sera for antibodies to excretory-secretory antigens of the second-stage larvae of Toxocara canis. Z Parasitenkd. 1983;69(1):113–118. doi: 10.1007/BF00934015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



