Abstract
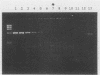
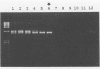
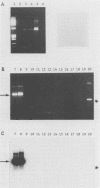
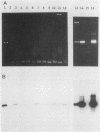
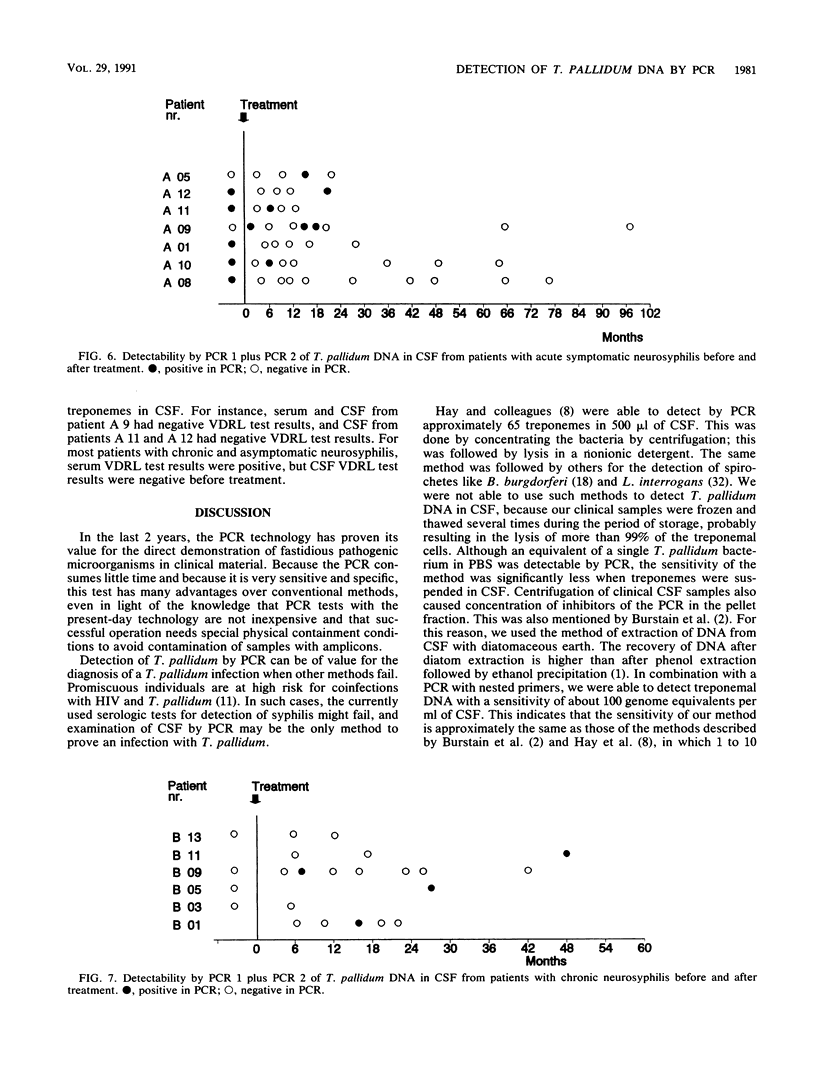
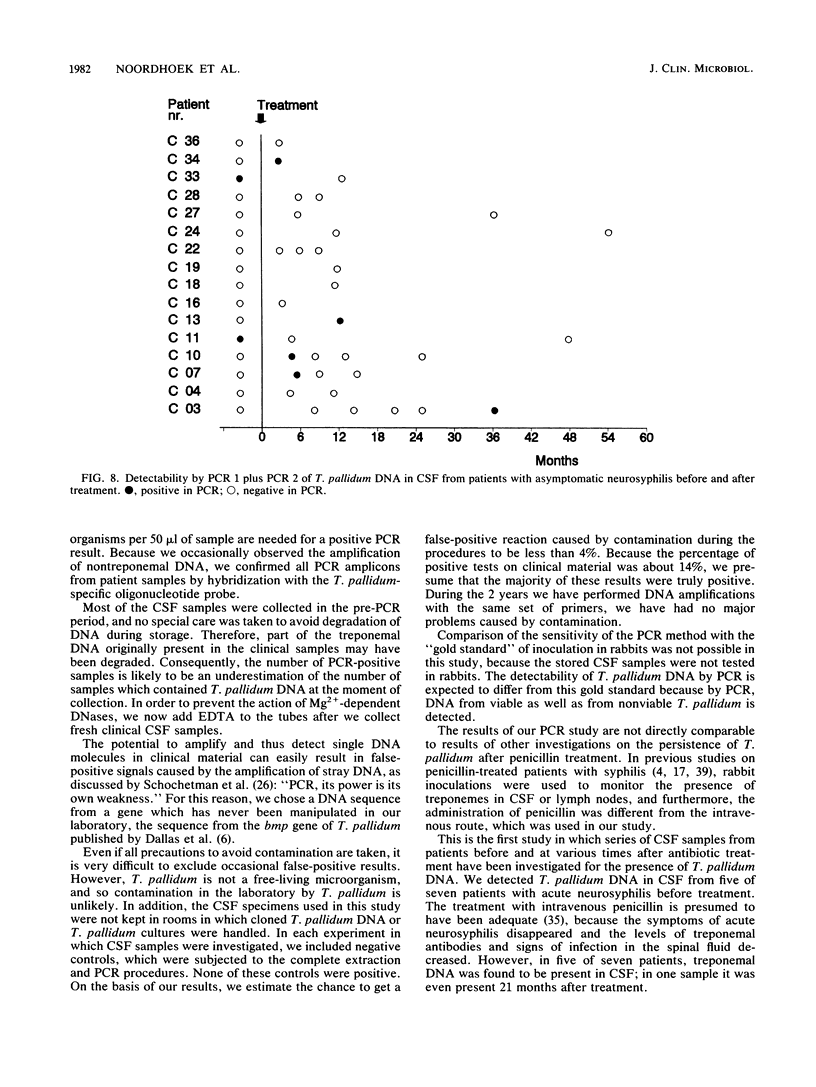
A polymerase chain reaction with nested primer pairs based on the DNA sequence of the 39-kDa bmp gene of Treponema pallidum subsp. pallidum is described. The method allowed the detection of purified T. pallidum DNA equivalent to the amount of DNA in a single bacterium and was specific for T. pallidum subspecies. After concentration of DNA, using diatomaceous earth, it was possible to detect about 100 treponemes in 1 ml of cerebrospinal fluid. Cerebrospinal fluid samples from a total of 29 symptomatic and asymptomatic patients with neurosyphilis were tested for the presence of treponemal DNA before and at various intervals after intravenous treatment with penicillin. Prior to the penicillin treatment, we detected T. pallidum DNA in 5 of 7 patients with acute symptomatic neurosyphilis, in none of the 4 patients with chronic symptomatic neurosyphilis tested before treatment, and in 2 of 16 patients with asymptomatic neurosyphilis. Unexpectedly, T. pallidum DNA was also often detected in cerebrospinal fluid long after intervenous treatment with penicillin, sometimes up to 3 years after therapy.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boom R., Sol C. J., Salimans M. M., Jansen C. L., Wertheim-van Dillen P. M., van der Noordaa J. Rapid and simple method for purification of nucleic acids. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Mar;28(3):495–503. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.3.495-503.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burstain J. M., Grimprel E., Lukehart S. A., Norgard M. V., Radolf J. D. Sensitive detection of Treponema pallidum by using the polymerase chain reaction. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Jan;29(1):62–69. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.1.62-69.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COLLART P., BOREL L. J., DUREL P. SIGNIFICANCE OF SPIRAL ORGANISMS FOUND, AFTER TREATMENT, IN LATE HUMAN AND EXPERIMENTAL SYPHILIS. Br J Vener Dis. 1964 Jun;40:81–89. doi: 10.1136/sti.40.2.81. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins F. M. Mycobacterial disease, immunosuppression, and acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1989 Oct;2(4):360–377. doi: 10.1128/cmr.2.4.360. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dallas W. S., Ray P. H., Leong J., Benedict C. D., Stamm L. V., Bassford P. J., Jr Identification and purification of a recombinant Treponema pallidum basic membrane protein antigen expressed in Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1987 May;55(5):1106–1115. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.5.1106-1115.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harries A. D. Tuberculosis and human immunodeficiency virus infection in developing countries. Lancet. 1990 Feb 17;335(8686):387–390. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)90216-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hay P. E., Clarke J. R., Strugnell R. A., Taylor-Robinson D., Goldmeier D. Use of the polymerase chain reaction to detect DNA sequences specific to pathogenic treponemes in cerebrospinal fluid. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1990 Mar 15;56(3):233–238. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1990.tb13943.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hay P. E., Clarke J. R., Taylor-Robinson D., Goldmeier D. Detection of treponemal DNA in the CSF of patients with syphilis and HIV infection using the polymerase chain reaction. Genitourin Med. 1990 Dec;66(6):428–432. doi: 10.1136/sti.66.6.428. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hicks C. B., Benson P. M., Lupton G. P., Tramont E. C. Seronegative secondary syphilis in a patient infected with the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) with Kaposi sarcoma. A diagnostic dilemma. Ann Intern Med. 1987 Oct;107(4):492–495. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-107-4-492. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hook E. W., 3rd Syphilis and HIV infection. J Infect Dis. 1989 Sep;160(3):530–534. doi: 10.1093/infdis/160.3.530. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johns D. R., Tierney M., Felsenstein D. Alteration in the natural history of neurosyphilis by concurrent infection with the human immunodeficiency virus. N Engl J Med. 1987 Jun 18;316(25):1569–1572. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198706183162503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz D. A., Berger J. R. Neurosyphilis in acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Arch Neurol. 1989 Aug;46(8):895–898. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1989.00520440085024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krawetz S. A., Pon R. T., Dixon G. H. Increased efficiency of the Taq polymerase catalyzed polymerase chain reaction. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jan 25;17(2):819–819. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.2.819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwok S., Higuchi R. Avoiding false positives with PCR. Nature. 1989 May 18;339(6221):237–238. doi: 10.1038/339237a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lukehart S. A., Hook E. W., 3rd, Baker-Zander S. A., Collier A. C., Critchlow C. W., Handsfield H. H. Invasion of the central nervous system by Treponema pallidum: implications for diagnosis and treatment. Ann Intern Med. 1988 Dec 1;109(11):855–862. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-109-11-855. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malloy D. C., Nauman R. K., Paxton H. Detection of Borrelia burgdorferi using the polymerase chain reaction. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Jun;28(6):1089–1093. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.6.1089-1093.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noordhoek G. T., Hermans P. W., Paul A. N., Schouls L. M., van der Sluis J. J., van Embden J. D. Treponema pallidum subspecies pallidum (Nichols) and Treponema pallidum subspecies pertenue (CDC 2575) differ in at least one nucleotide: comparison of two homologous antigens. Microb Pathog. 1989 Jan;6(1):29–42. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(89)90005-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noordhoek G. T., Wieles B., van der Sluis J. J., van Embden J. D. Polymerase chain reaction and synthetic DNA probes: a means of distinguishing the causative agents of syphilis and yaws? Infect Immun. 1990 Jun;58(6):2011–2013. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.6.2011-2013.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noordhoek G. T., van Embden J. D. Yaws, an endemic treponematosis reconsidered in the HIV era. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1991 Jan;10(1):4–5. doi: 10.1007/BF01967089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polnikorn N., Witoonpanich R., Vorachit M., Vejjajiva S., Vejjajiva A. Penicillin concentrations in cerebrospinal fluid after different treatment regimens for syphilis. Br J Vener Dis. 1980 Dec;56(6):363–367. doi: 10.1136/sti.56.6.363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rufli T. Syphilis and HIV infection. Dermatologica. 1989;179(3):113–117. doi: 10.1159/000248335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schochetman G., Ou C. Y., Jones W. K. Polymerase chain reaction. J Infect Dis. 1988 Dec;158(6):1154–1157. doi: 10.1093/infdis/158.6.1154. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoth P. E., Wolters E. C. Penicillin concentrations in serum and CSF during high-dose intravenous treatment for neurosyphilis. Neurology. 1987 Jul;37(7):1214–1216. doi: 10.1212/wnl.37.7.1214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. L., Israel C. W. Treponemes in aqueous humor in late seronegative syphilis. Trans Am Acad Ophthalmol Otolaryngol. 1968 Jan-Feb;72(1):63–75. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snijders P. J., van den Brule A. J., Schrijnemakers H. F., Snow G., Meijer C. J., Walboomers J. M. The use of general primers in the polymerase chain reaction permits the detection of a broad spectrum of human papillomavirus genotypes. J Gen Virol. 1990 Jan;71(Pt 1):173–181. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-71-1-173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Eys G. J., Gravekamp C., Gerritsen M. J., Quint W., Cornelissen M. T., Schegget J. T., Terpstra W. J. Detection of leptospires in urine by polymerase chain reaction. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Oct;27(10):2258–2262. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.10.2258-2262.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolters E. C., Hische E. A., Tutuarima J. A., van Trotsenburg L., van Eijk R. V., Bos J. D., Starink T. M., Emsbroek L. J., van der Helm H. J. Central nervous system involvement in early and late syphilis: the problem of asymptomatic neurosyphilis. J Neurol Sci. 1988 Dec;88(1-3):229–239. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(88)90220-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolters E. C. Neurosyphilis: a changing diagnostic problem? Eur Neurol. 1987;26(1):23–28. doi: 10.1159/000116306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolters E. C. Treatment of neurosyphilis. Clin Neuropharmacol. 1987 Apr;10(2):143–154. doi: 10.1097/00002826-198704000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods S. A., Cole S. T. A rapid method for the detection of potentially viable Mycobacterium leprae in human biopsies: a novel application of PCR. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1989 Dec;53(3):305–309. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(89)90235-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yobs A. R., Clark J. W., Jr, Mothershed S. E., Bullard J. C., Artley C. W. Further observations on the persistence of Treponema pallidum after treatment in rabbits and humans. Br J Vener Dis. 1968 Jun;44(2):116–130. doi: 10.1136/sti.44.2.116. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zenker P. N., Rolfs R. T. Treatment of syphilis, 1989. Rev Infect Dis. 1990 Jul-Aug;12 (Suppl 6):S590–S609. doi: 10.1093/clinids/12.supplement_6.s590. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Embden J. D., van der Donk H. J., van Eijk R. V., van der Heide H. G., de Jong J. A., van Olderen M. F., Osterhaus A. B., Schouls L. M. Molecular cloning and expression of Treponema pallidum DNA in Escherichia coli K-12. Infect Immun. 1983 Oct;42(1):187–196. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.1.187-196.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Valk P. G., Kraai E. J., van Voorst Vader P. C., Haaxma-Reiche H., Snijder J. A. Penicillin concentrations in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) during repository treatment regimen for syphilis. Genitourin Med. 1988 Aug;64(4):223–225. doi: 10.1136/sti.64.4.223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]