Abstract
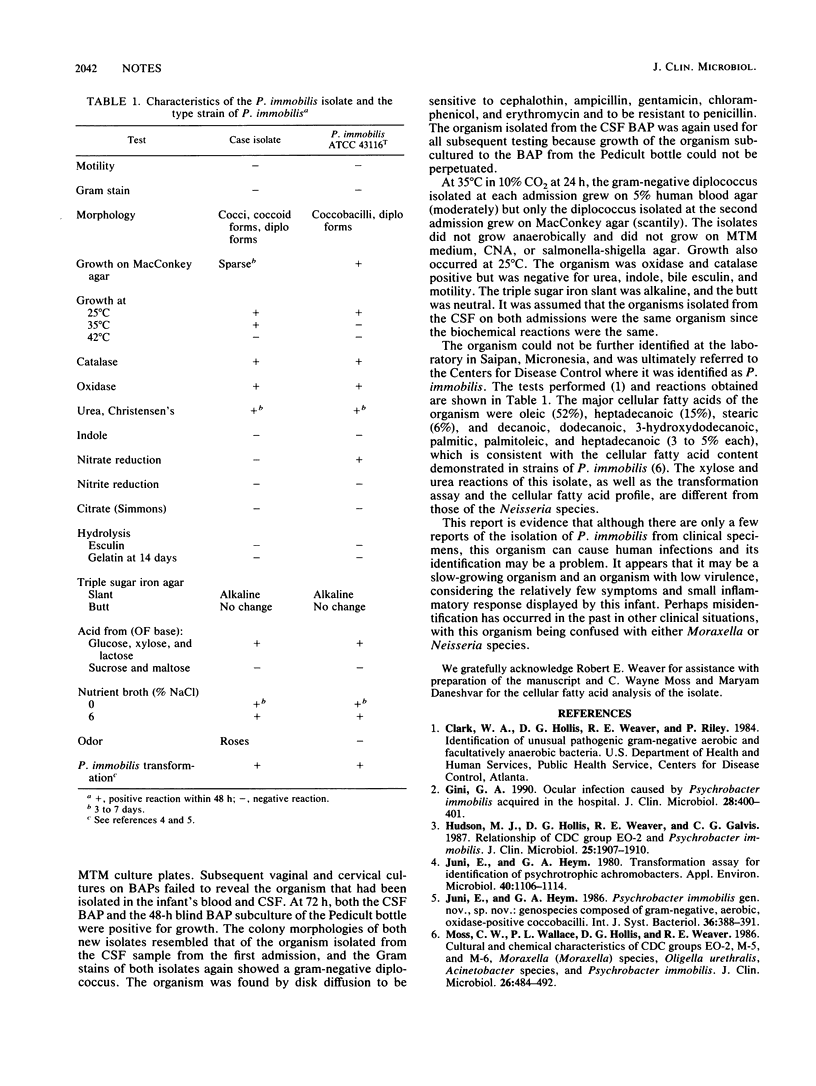
Psychrobacter immobilis was isolated from the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and blood of a 2-day-old infant who appeared well except for a fever and a full anterior fontanelle. The infant was treated with antibiotics intravenously. After 48 h, he became afebrile and CSF and blood cultures were negative; he was then discharged. After 96 h of incubation, CSF and blood cultures yielded a gram-negative organism, P. immobilis. The child was readmitted to the hospital, and the same organism was again isolated from his blood and CSF.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Gini G. A. Ocular infection caused by Psychrobacter immobilis acquired in the hospital. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Feb;28(2):400–401. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.2.400-401.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudson M. J., Hollis D. G., Weaver R. E., Galvis C. G. Relationship of CDC group EO-2 and psychrobacter immobilis. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Oct;25(10):1907–1910. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.10.1907-1910.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Juni E., Heym G. A. Transformation assay for identification of psychrotrophic achromobacters. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Dec;40(6):1106–1114. doi: 10.1128/aem.40.6.1106-1114.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss C. W., Wallace P. L., Hollis D. G., Weaver R. E. Cultural and chemical characterization of CDC groups EO-2, M-5, and M-6, Moraxella (Moraxella) species, Oligella urethralis, Acinetobacter species, and Psychrobacter immobilis. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Mar;26(3):484–492. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.3.484-492.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


