Abstract
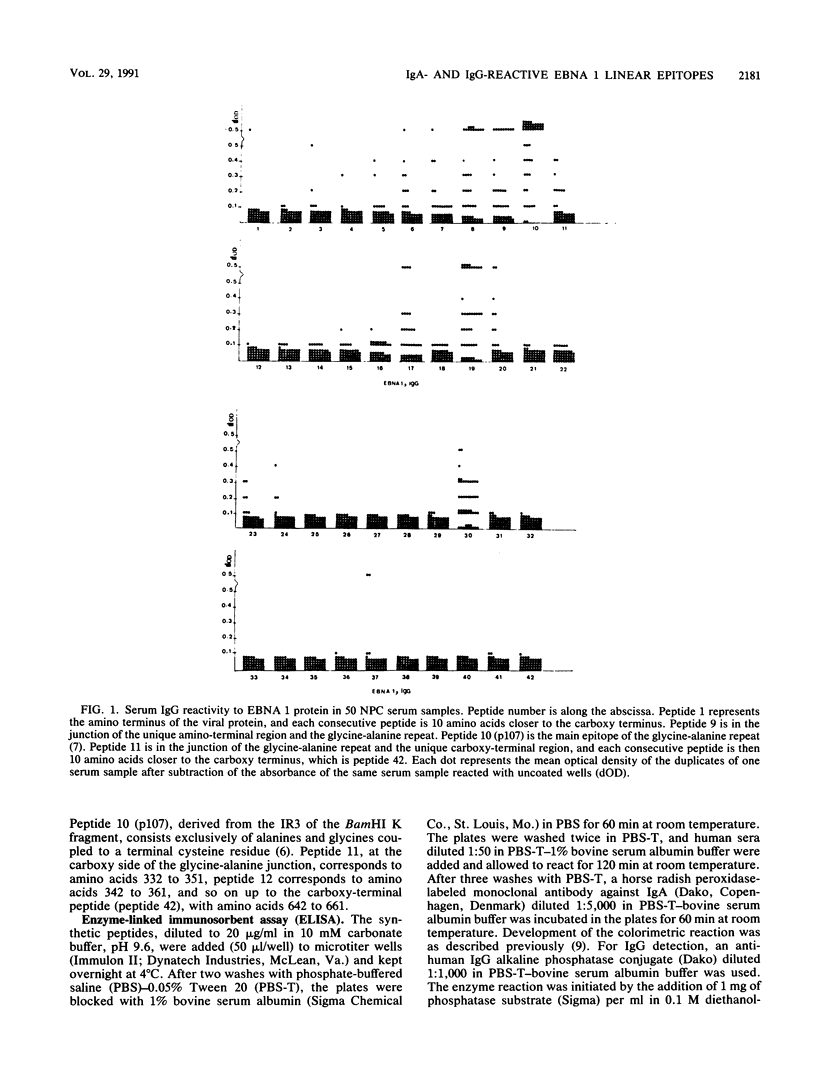
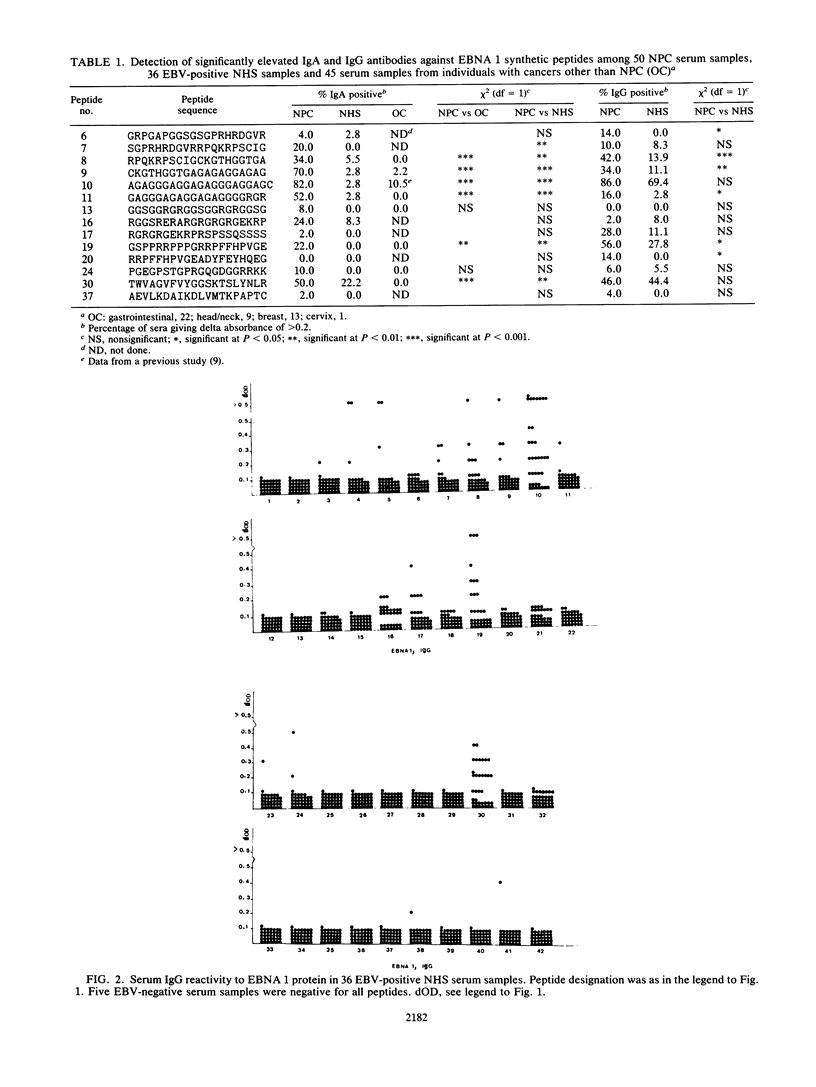
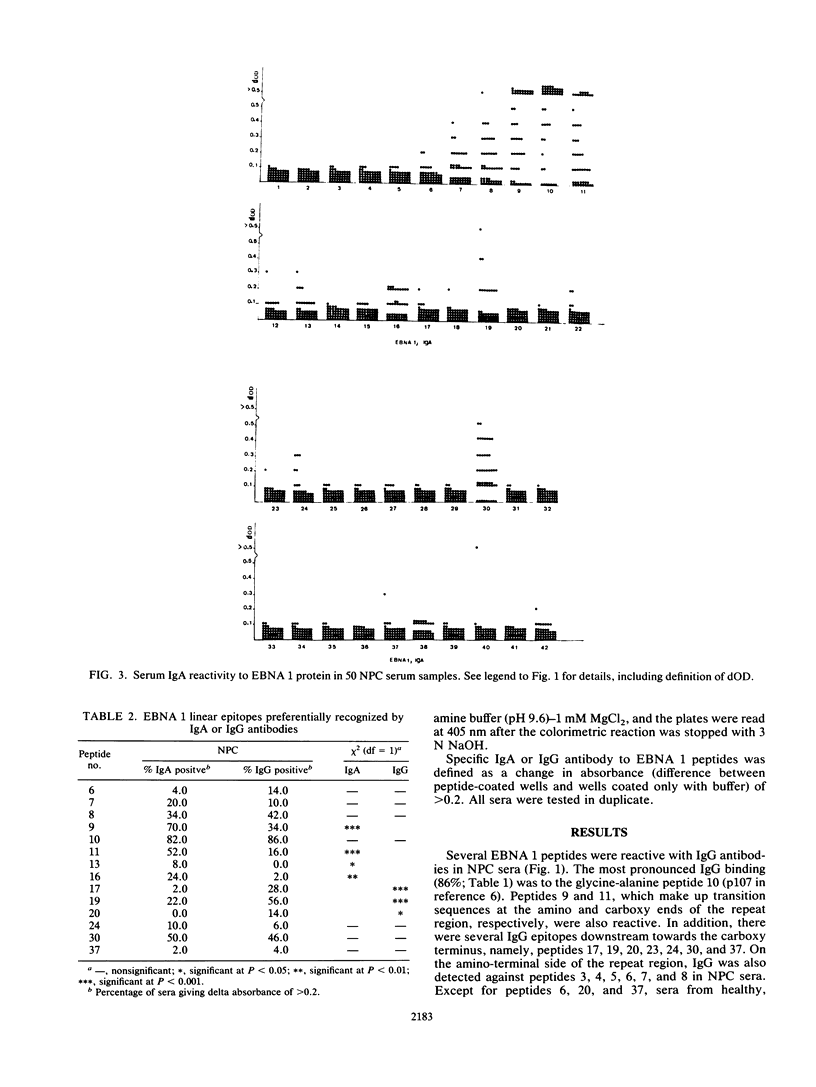
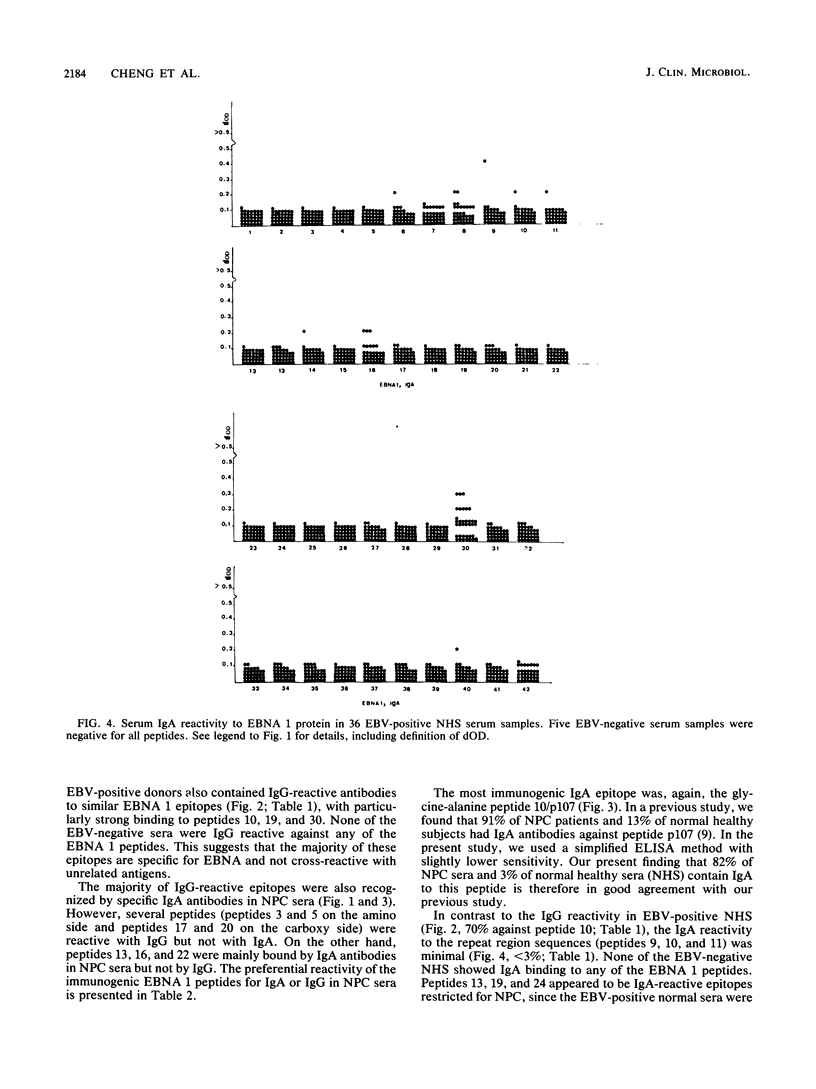
The entire amino acid sequence of the unique region of the EBNA 1 protein was synthesized as a set of 41 20-residue peptides with an overlap of 10 amino acids. The peptides were tested in the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for reactivity with immunoglobulin A (IgA) and IgG in sera from 50 patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) as compared with 36 serum samples from healthy Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-seropositive donors and 5 serum samples from EBV-negative donors. The most immunoreactive peptide for both IgA and IgG binding was localized to the glycine-alanine repeat domain of the antigen. In the unique regions, 16 immunoreactive peptides were found. Of these, four were reactive with IgG but not IgA and three peptides were reactive with IgA but not IgG in NPC sera. In addition, several IgA and IgG epitopes on the carboxy-terminal region were specifically reactive with NPC sera, but unreactive with sera from healthy EBV-positive donors. The results suggest that EBV serology specific for individual epitopes may provide additional useful information not available by conventional serology with whole antigens or the EBNA complex.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baer R., Bankier A. T., Biggin M. D., Deininger P. L., Farrell P. J., Gibson T. J., Hatfull G., Hudson G. S., Satchwell S. C., Séguin C. DNA sequence and expression of the B95-8 Epstein-Barr virus genome. Nature. 1984 Jul 19;310(5974):207–211. doi: 10.1038/310207a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen J. Y., Chen C. J., Liu M. Y., Cho S. M., Hsu M. M., Lynn T. C., Shieh T., Tu S. M., Lee H. H., Kuo S. L. Antibodies to Epstein-Barr virus-specific DNase in patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma and control groups. J Med Virol. 1987 Sep;23(1):11–21. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890230103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dillner J., Dillner L., Robb J., Willems J., Jones I., Lancaster W., Smith R., Lerner R. A synthetic peptide defines a serologic IgA response to a human papillomavirus-encoded nuclear antigen expressed in virus-carrying cervical neoplasia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(10):3838–3841. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.10.3838. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dillner J., Dillner L., Utter G., Eklund C., Rotola A., Costa S., DiLuca D. Mapping of linear epitopes of human papillomavirus type 16: the L1 and L2 open reading frames. Int J Cancer. 1990 Mar 15;45(3):529–535. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910450326. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dillner J., Kallin B. The Epstein-Barr virus proteins. Adv Cancer Res. 1988;50:95–158. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60436-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dillner J., Sternås L., Kallin B., Alexander H., Ehlin-Henriksson B., Jörnvall H., Klein G., Lerner R. Antibodies against a synthetic peptide identify the Epstein-Barr virus-determined nuclear antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(15):4652–4656. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.15.4652. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dillner J., Szigeti R., Henle W., Henle G., Lerner R. A., Klein G. Cellular and humoral immune responses to synthetic peptides deduced from the amino-acid sequences of Epstein-Barr virus-encoded proteins in EBV-transformed cells. Int J Cancer. 1987 Oct 15;40(4):455–460. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910400404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foong Y. T., Cheng H. M., Sam C. K., Dillner J., Hinderer W., Prasad U. Serum and salivary IgA antibodies against a defined epitope of the Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen (EBNA) are elevated in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Int J Cancer. 1990 Jun 15;45(6):1061–1064. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910450614. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fåhraeus R., Fu H. L., Ernberg I., Finke J., Rowe M., Klein G., Falk K., Nilsson E., Yadav M., Busson P. Expression of Epstein-Barr virus-encoded proteins in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Int J Cancer. 1988 Sep 15;42(3):329–338. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910420305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginsburg M. Antibodies against the large subunit of the EBV-encoded ribonucleotide reductase in patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Int J Cancer. 1990 Jun 15;45(6):1048–1053. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910450612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hearing J. C., Levine A. J. The Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen (BamHI K antigen) is a single-stranded DNA binding phosphoprotein. Virology. 1985 Aug;145(1):105–116. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90205-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heller M., Henderson A., Kieff E. Repeat array in Epstein-Barr virus DNA is related to cell DNA sequences interspersed on human chromosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(19):5916–5920. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.19.5916. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henle G., Henle W. Epstein-Barr virus-specific IgA serum antibodies as an outstanding feature of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Int J Cancer. 1976 Jan 15;17(1):1–7. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910170102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hennessy K., Kieff E. One of two Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigens contains a glycine-alanine copolymer domain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Sep;80(18):5665–5669. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.18.5665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houghten R. A. General method for the rapid solid-phase synthesis of large numbers of peptides: specificity of antigen-antibody interaction at the level of individual amino acids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(15):5131–5135. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.15.5131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein G., Giovanella B. C., Lindahl T., Fialkow P. J., Singh S., Stehlin J. S. Direct evidence for the presence of Epstein-Barr virus DNA and nuclear antigen in malignant epithelial cells from patients with poorly differentiated carcinoma of the nasopharynx. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Dec;71(12):4737–4741. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.12.4737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linde A., Kallin B., Dillner J., Andersson J., Jägdahl L., Lindvall A., Wahren B. Evaluation of enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays with two synthetic peptides of Epstein-Barr virus for diagnosis of infectious mononucleosis. J Infect Dis. 1990 May;161(5):903–909. doi: 10.1093/infdis/161.5.903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Littler E., Newman W., Arrand J. R. Immunological response of nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients to the Epstein-Barr-virus-coded thymidine kinase expressed in Escherichia coli. Int J Cancer. 1990 Jun 15;45(6):1028–1032. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910450608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu M. Y., Chou W. H., Nutter L., Hsu M. M., Chen J. Y., Yang C. S. Antibody against Epstein-Barr virus DNA polymerase activity in sera of patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma. J Med Virol. 1989 Jun;28(2):101–105. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890280209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luka J., Kreofsky T., Pearson G. R., Hennessy K., Kieff E. Identification and characterization of a cellular protein that cross-reacts with the Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen. J Virol. 1984 Dec;52(3):833–838. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.3.833-838.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milman G., Scott A. L., Cho M. S., Hartman S. C., Ades D. K., Hayward G. S., Ki P. F., August J. T., Hayward S. D. Carboxyl-terminal domain of the Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen is highly immunogenic in man. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(18):6300–6304. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.18.6300. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norrby E., Mufson M. A., Alexander H., Houghten R. A., Lerner R. A. Site-directed serology with synthetic peptides representing the large glycoprotein G of respiratory syncytial virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Sep;84(18):6572–6576. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.18.6572. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reedman B. M., Klein G. Cellular localization of an Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-associated complement-fixing antigen in producer and non-producer lymphoblastoid cell lines. Int J Cancer. 1973 May;11(3):499–520. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910110302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ricksten A., Kallin B., Alexander H., Dillner J., Fåhraeus R., Klein G., Lerner R., Rymo L. BamHI E region of the Epstein-Barr virus genome encodes three transformation-associated nuclear proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(4):995–999. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.4.995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rumpold H., Rhodes G. H., Bloch P. L., Carson D. A., Vaughan J. H. The glycine-alanine repeating region is the major epitope of the Epstein-Barr nuclear antigen-1 (EBNA-1). J Immunol. 1987 Jan 15;138(2):593–599. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz A. M., Henderson L. E., Oroszlan S., Garber E. A., Hanafusa H. Amino terminal myristylation of the protein kinase p60src, a retroviral transforming protein. Science. 1985 Jan 25;227(4685):427–429. doi: 10.1126/science.3917576. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. S., Naso R. B., Rosen J., Whalley A., Hom Y. L., Hoey K., Kennedy C. J., McCutchan J. A., Spector S. A., Richman D. D. Antibody to a synthetic oligopeptide in subjects at risk for human immunodeficiency virus infection. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Aug;25(8):1498–1504. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.8.1498-1504.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yates J. L., Warren N., Sugden B. Stable replication of plasmids derived from Epstein-Barr virus in various mammalian cells. 1985 Feb 28-Mar 6Nature. 313(6005):812–815. doi: 10.1038/313812a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



