Abstract
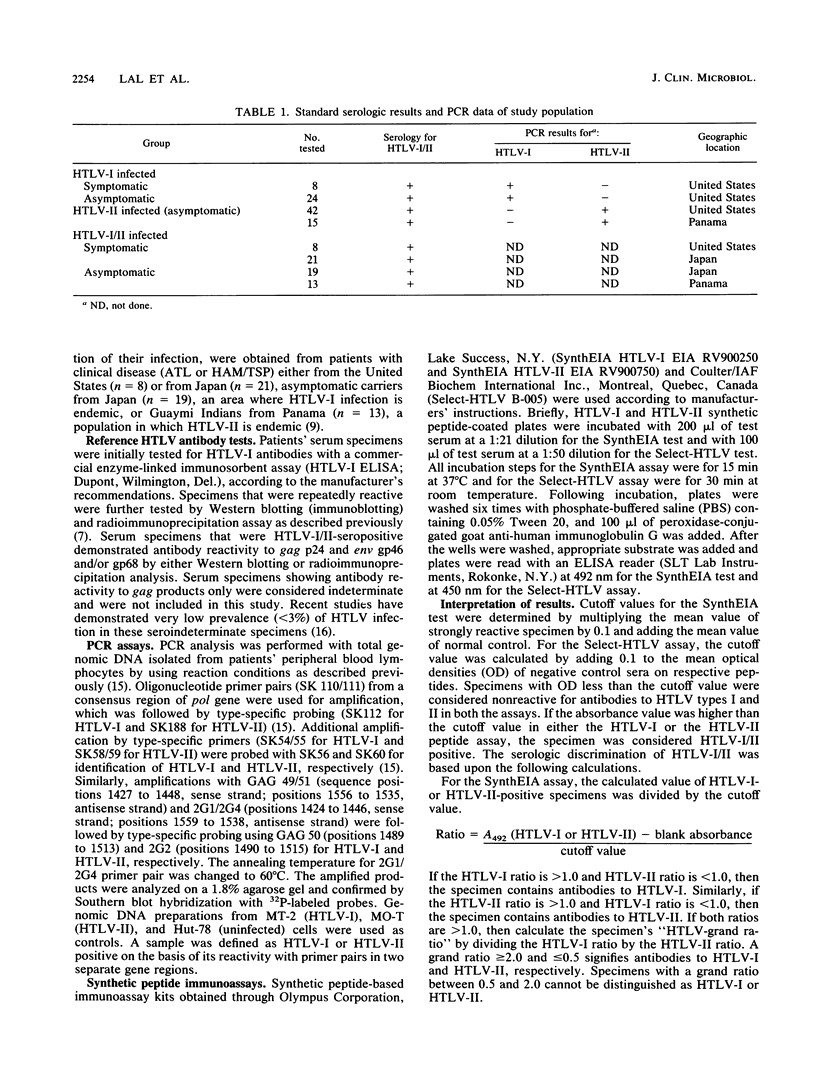
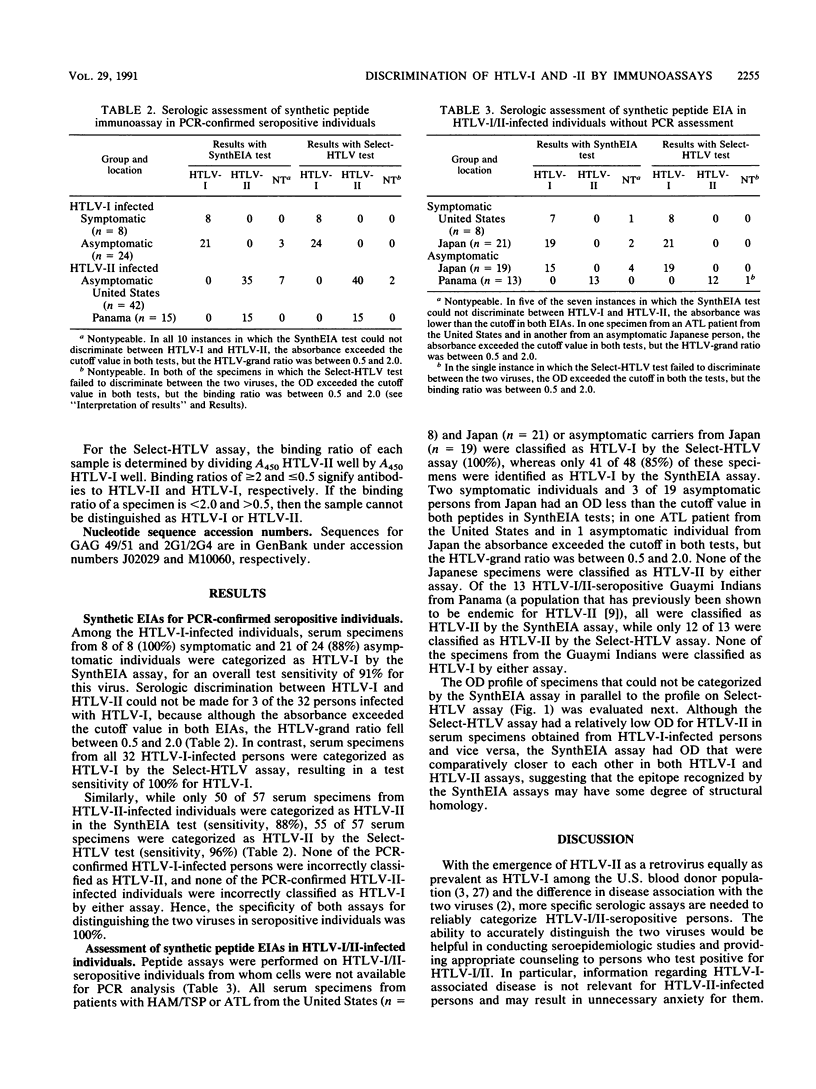
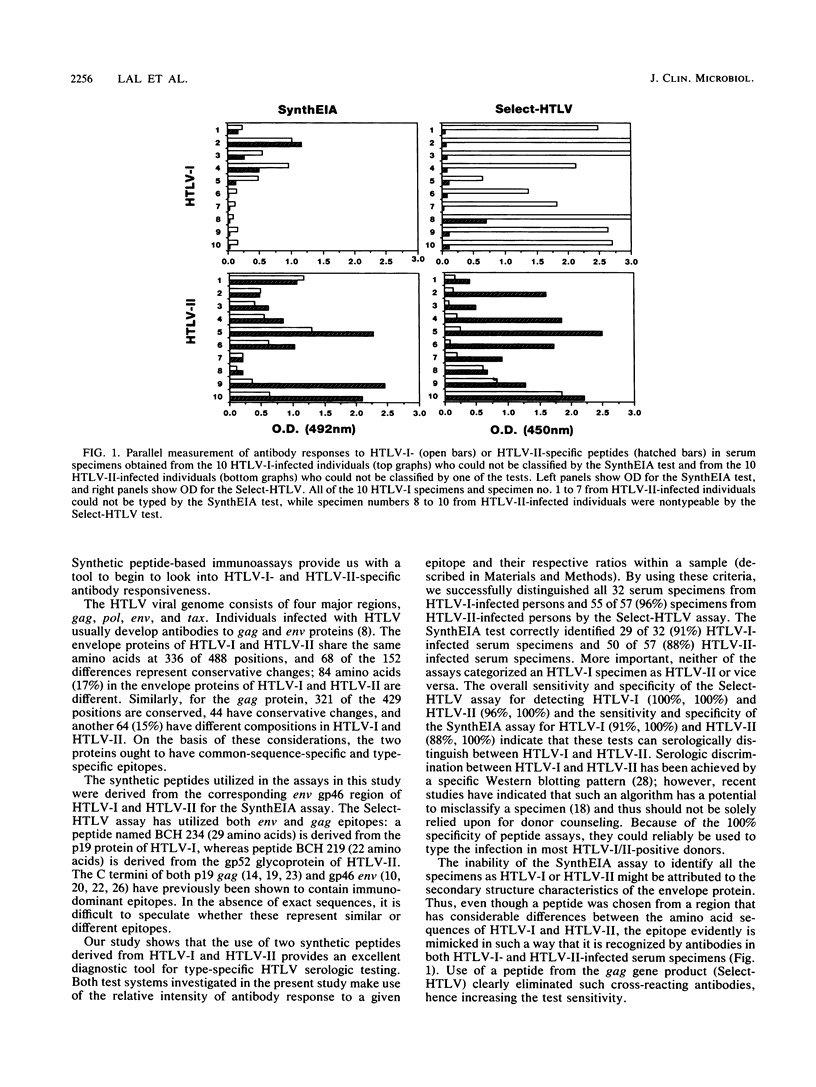
Until now, serologic tests that distinguish the closely related human T-cell lymphotropic virus types I (HTLV-I) and II (HTLV-II) infections have not been available. Synthetic peptide assays, employing peptides derived from the core and envelope proteins of HTLV-I and HTLV-II (SynthEIA and Select-HTLV tests), were evaluated for the ability to serologically discriminate HTLV-I and HTLV-II infections. Of 32 HTLV-I- and 57 HTLV-II-positive serum specimens from individuals whose infections were confirmed by polymerase chain reaction, the SynthEIA test categorized 29 (91%) as HTLV-I and 50 (88%) as HTLV-II, and 10 (11%) were nontypeable. In contrast, the Select-HTLV test categorized 32 (100%) as HTLV-I and 55 (96%) as HTLV-II, and 2 (2%) were nontypeable. The specificity of both the assays in seropositive serum specimens was 100% in that none of the specimens were incorrectly classified. Additional serum specimens obtained from clinically diseased patients from the United States (n = 8) and asymptomatic carriers and patients from Japan (an endemic population for HTLV-I; n = 40) were categorized as HTLV-I by at least one of the assays, while serum specimens from Guaymi Indians from Panama (an endemic population for HTLV-II; n = 13) were categorized as HTLV-II. Thus, peptide enzyme immunoassays appear to represent a simple technique employing chemically synthesized antigens for discrimination between antibodies of HTLV-I and HTLV-II.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson D. W., Epstein J. S., Lee T. H., Lairmore M. D., Saxinger C., Kalyanaraman V. S., Slamon D., Parks W., Poiesz B. J., Pierik L. T. Serological confirmation of human T-lymphotropic virus type I infection in healthy blood and plasma donors. Blood. 1989 Nov 15;74(7):2585–2591. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Y. M., Lee T. H., Wiktor S. Z., Shaw G. M., Murphy E. L., Blattner W. A., Essex M. Type-specific antigens for serological discrimination of HTLV-I and HTLV-II infection. Lancet. 1990 Nov 10;336(8724):1153–1155. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)92769-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coates S. R., Harris A. J., Parkes D. L., Smith C. M., Liu H. L., Akita R. W., Ferrer M. M., Sampson E. K., Brandis J. W., Sliwkowski M. X. Serological evaluation of Escherichia coli-expressed human T-cell leukemia virus type I env, gag p24, and tax proteins. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Jun;28(6):1139–1142. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.6.1139-1142.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gnann J. W., Jr, McCormick J. B., Mitchell S., Nelson J. A., Oldstone M. B. Synthetic peptide immunoassay distinguishes HIV type 1 and HIV type 2 infections. Science. 1987 Sep 11;237(4820):1346–1349. doi: 10.1126/science.2888192. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartley T. M., Khabbaz R. F., Cannon R. O., Kaplan J. E., Lairmore M. D. Characterization of antibody reactivity to human T-cell lymphotropic virus types I and II using immunoblot and radioimmunoprecipitation assays. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Apr;28(4):646–650. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.4.646-650.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haseltine W. A., Sodroski J. G., Patarca R. Structure and function of the genome of HTLV. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1985;115:177–209. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-70113-9_12. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heneine W., Kaplan J. E., Gracia F., Lal R., Roberts B., Levine P. H., Reeves W. C. HTLV-II endemicity among Guaymi Indians in Panama. N Engl J Med. 1991 Feb 21;324(8):565–565. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199102213240815. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horal P., Hall W. W., Svennerholm B., Lycke J., Jeansson S., Rymo L., Kaplan M. H., Vahlne A. Identification of type-specific linear epitopes in the glycoproteins gp46 and gp21 of human T-cell leukemia viruses type I and type II using synthetic peptides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 1;88(13):5754–5758. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.13.5754. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan J. E., Khabbaz R. F. HTLV-I: newest addition to blood donor screening. Am Fam Physician. 1989 Aug;40(2):189–195. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khabbaz R. F., Darrow W. W., Hartley T. M., Witte J., Cohen J. B., French J., Gill P. S., Potterat J., Sikes R. K., Reich R. Seroprevalence and risk factors for HTLV-I/II infection among female prostitutes in the United States. JAMA. 1990 Jan 5;263(1):60–64. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khabbaz R. F., Douglas J. M., Jr, Judson F. N., Spiegel R. A., St Louis M. E., Whittington W., Hartley T. M., Lairmore M., Kaplan J. E. Seroprevalence of human T-lymphotropic virus type I or II in sexually transmitted disease clinic patients in the USA. J Infect Dis. 1990 Jul;162(1):241–244. doi: 10.1093/infdis/162.1.241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuroda N., Washitani Y., Shiraki H., Kiyokawa H., Ohno M., Sato H., Maeda Y. Detection of antibodies to human T-lymphotropic virus type I by using synthetic peptides. Int J Cancer. 1990 May 15;45(5):865–868. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910450514. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwok S., Kellogg D., Ehrlich G., Poiesz B., Bhagavati S., Sninsky J. J. Characterization of a sequence of human T cell leukemia virus type I from a patient with chronic progressive myelopathy. J Infect Dis. 1988 Dec;158(6):1193–1197. doi: 10.1093/infdis/158.6.1193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwok S., Lipka J. J., McKinney N., Kellogg D. E., Poiesz B., Foung S. K., Sninsky J. J. Low incidence of HTLV infections in random blood donors with indeterminate western blot patterns. Transfusion. 1990 Jul-Aug;30(6):491–494. doi: 10.1046/j.1537-2995.1990.30690333477.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lairmore M. D., Jacobson S., Gracia F., De B. K., Castillo L., Larreategui M., Roberts B. D., Levine P. H., Blattner W. A., Kaplan J. E. Isolation of human T-cell lymphotropic virus type 2 from Guaymi Indians in Panama. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(22):8840–8844. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.22.8840. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lal R. B., Rudolph D. L., Griffis K. P., Kitamura K., Honda M., Coligan J. E., Folks T. M. Characterization of immunodominant epitopes of gag and pol gene-encoded proteins of human T-cell lymphotropic virus type I. J Virol. 1991 Apr;65(4):1870–1876. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.4.1870-1876.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lal R. B., Rudolph D. L., Lairmore M. D., Khabbaz R. F., Garfield M., Coligan J. E., Folks T. M. Serologic discrimination of human T cell lymphotropic virus infection by using a synthetic peptide-based enzyme immunoassay. J Infect Dis. 1991 Jan;163(1):41–46. doi: 10.1093/infdis/163.1.41. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee H., Swanson P., Shorty V. S., Zack J. A., Rosenblatt J. D., Chen I. S. High rate of HTLV-II infection in seropositive i.v. drug abusers in New Orleans. Science. 1989 Apr 28;244(4903):471–475. doi: 10.1126/science.2655084. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipka J. J., Bui K., Reyes G. R., Moeckli R., Wiktor S. Z., Blattner W. A., Murphy E. L., Shaw G. M., Hanson C. V., Sninsky J. J. Determination of a unique and immunodominant epitope of human T cell lymphotropic virus type I. J Infect Dis. 1990 Aug;162(2):353–357. doi: 10.1093/infdis/162.2.353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palker T. J., Scearce R. M., Copeland T. D., Oroszlan S., Haynes B. F. C-terminal region of human T cell lymphotropic virus type I (HTLVI) p19 core protein is immunogenic in humans and contains an HTLVI-specific epitope. J Immunol. 1986 Apr 1;136(7):2393–2397. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenblatt J. D., Chen I. S., Wachsman W. Infection with HTLV-I and HTLV-II: evolving concepts. Semin Hematol. 1988 Jul;25(3):230–246. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuel K. P., Lautenberger J. A., Jorcyk C. L., Josephs S., Wong-Staal F., Papas T. S. Diagnostic potential for human malignancies of bacterially produced HTLV-I envelope protein. Science. 1984 Nov 30;226(4678):1094–1097. doi: 10.1126/science.6208612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandler S. G., Fang C., Williams A. Retroviral infections transmitted by blood transfusion. Yale J Biol Med. 1990 Sep-Oct;63(5):353–360. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiktor S. Z., Alexander S. S., Shaw G. M., Weiss S. H., Murphy E. L., Wilks R. J., Shortly V. J., Hanchard B., Blattner W. A. Distinguishing between HTLV-I and HTLV-II by western blot. Lancet. 1990 Jun 23;335(8704):1533–1533. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)93078-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams A. E., Fang C. T., Slamon D. J., Poiesz B. J., Sandler S. G., Darr W. F., 2nd, Shulman G., McGowan E. I., Douglas D. K., Bowman R. J. Seroprevalence and epidemiological correlates of HTLV-I infection in U.S. blood donors. Science. 1988 Apr 29;240(4852):643–646. doi: 10.1126/science.2896386. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanagihara R., Jenkins C. L., Ajdukiewicz A. B., Lal R. B. Serological discrimination of HTLV I and II infection in Melanesia. Lancet. 1991 Mar 9;337(8741):617–618. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(91)91684-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



