Abstract
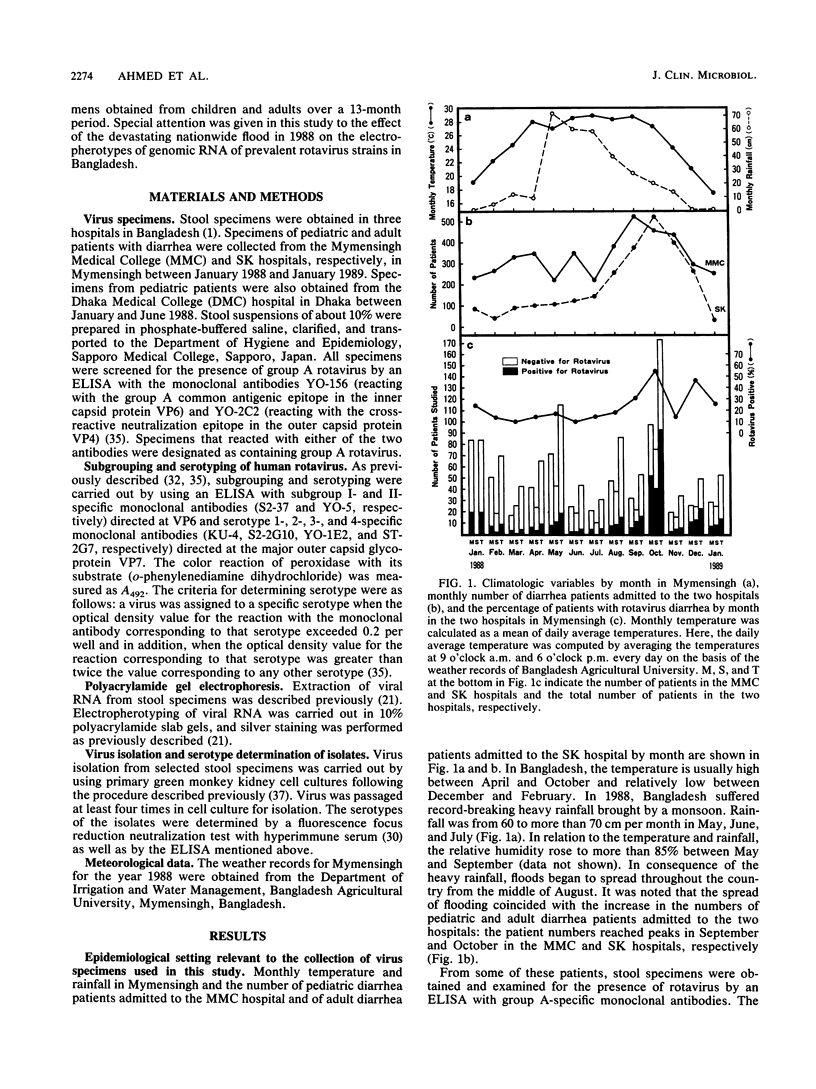
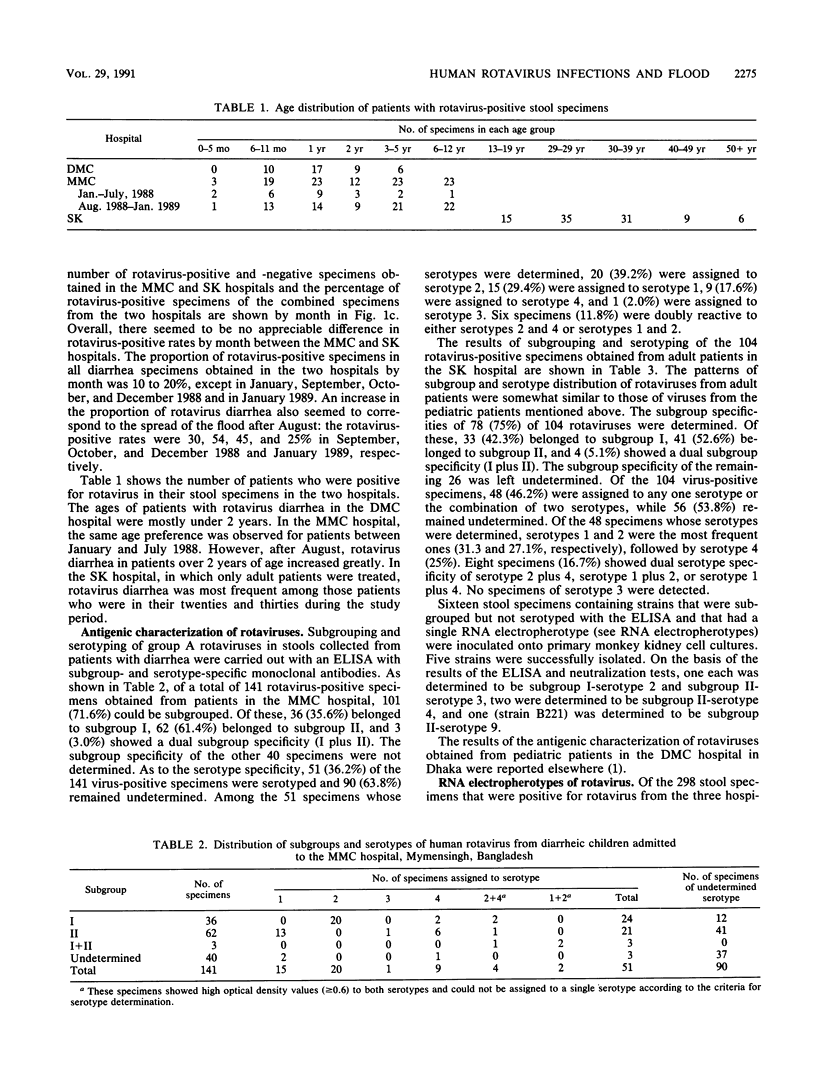
The virologic character of human rotavirus strains prevailing in Bangladesh was investigated in relation to the devastating nationwide floods brought by the 1988 monsoon. Human rotaviruses contained in stool specimens that were collected from inpatients with infantile and adult diarrhea in two hospitals in Mymensingh over a 13-month period (January 1988 to January 1989) and in one hospital in Dhaka over a 3-month period (February to April 1988) were examined for their subgroup, VP7 serotype, and RNA electropherotype. In concurrence with the spread of the flood (from the middle of August 1988), the number of infantile and adult diarrhea patients increased greatly. At the same time, the proportion of rotavirus-positive specimens in all diarrhea cases also increased remarkably, reaching 54 and 45% in September and October, respectively. An electrophoretic analysis of viral RNA revealed 17 distinct patterns of viral RNA (14 long and 3 short electropherotypes) and a considerable number of mixed electropherotypes, suggesting the simultaneous infection of some patients with more than two rotavirus strains. It was noteworthy that electropherotypes of rotavirus strains prevailing in the community changed considerably after the spreading of the flood and that the frequency of virus specimens showing mixed electropherotypes increased significantly during the flood period. These results suggest that sudden environmental change caused by the devastating floods seriously affected the epidemiology of rotavirus infections by increasing the opportunity of transmission of the virus and by reducing the resistance of the host to infection. In both pediatric and adult patient groups, serotypes 1 and 2 were the most frequent ones detected, followed by serotype 4.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF
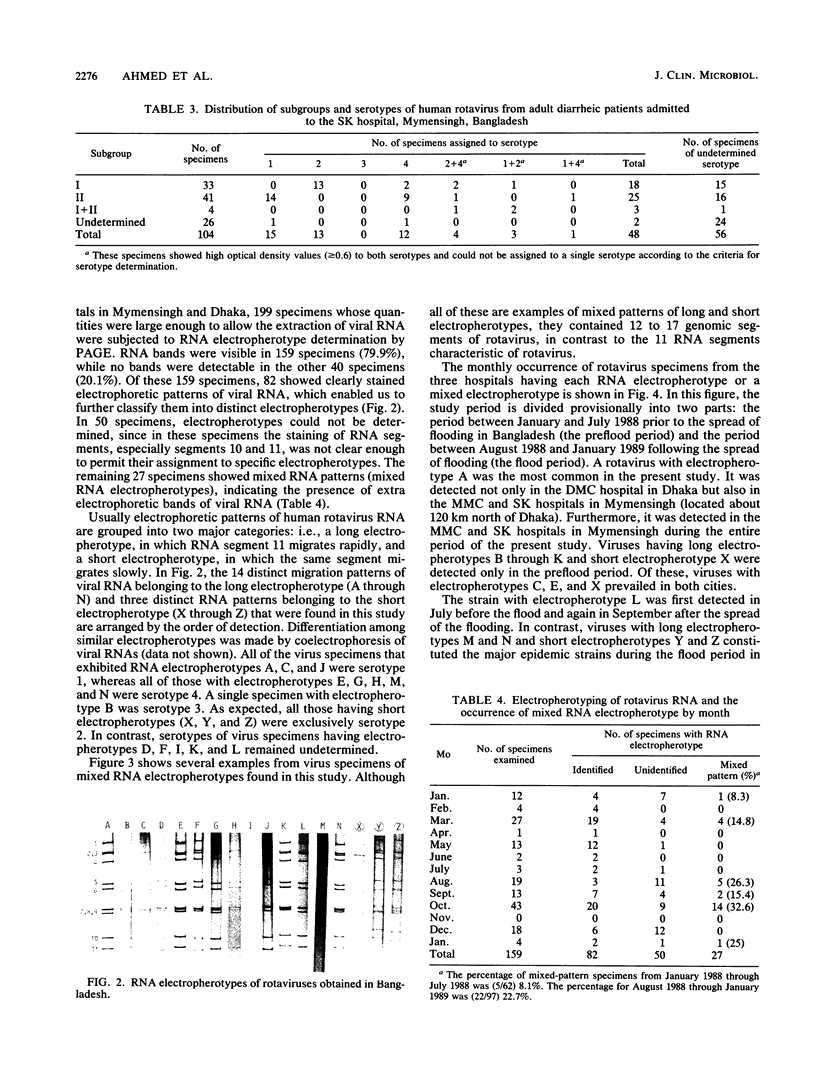
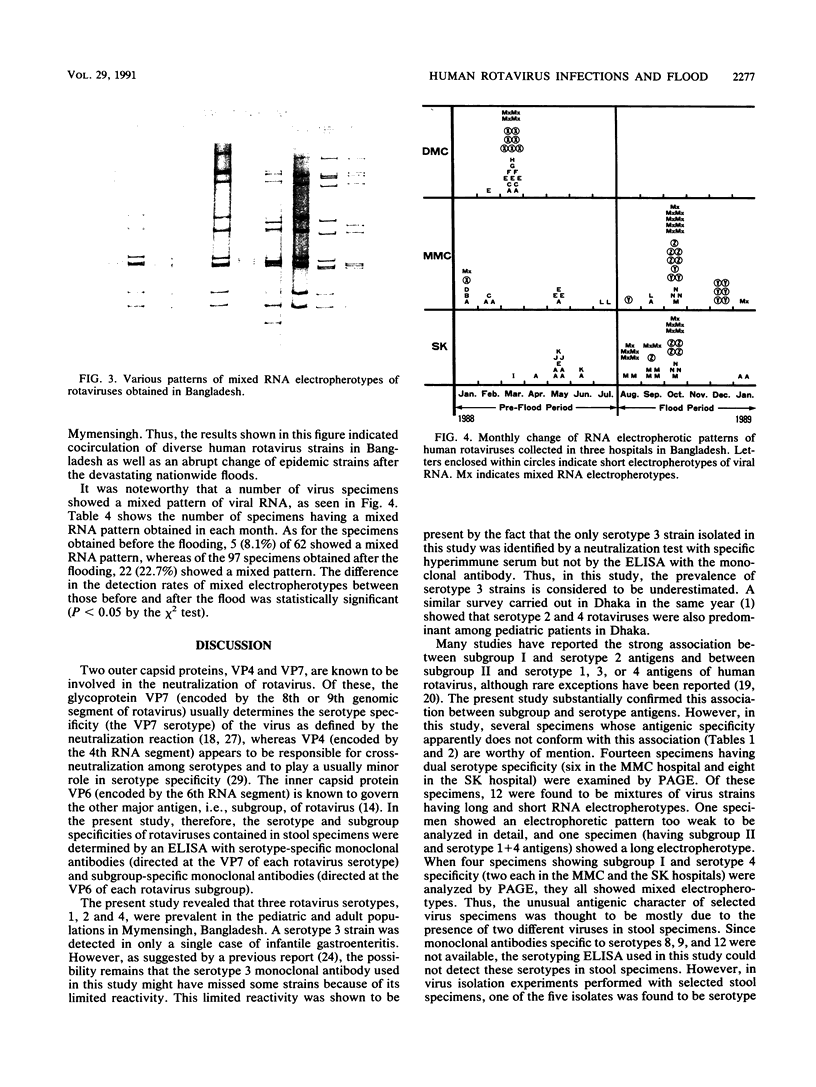


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahmed M. U., Taniguchi K., Kobayashi N., Urasawa T., Wakasugi F., Islam M., Shaikh H., Urasawa S. Characterization by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay using subgroup- and serotype-specific monoclonal antibodies of human rotavirus obtained from diarrheic patients in Bangladesh. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Jul;27(7):1678–1681. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.7.1678-1681.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Albert M. J., Unicomb L. E., Bishop R. F. Cultivation and characterization of human rotaviruses with "super short" RNA patterns. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Jan;25(1):183–185. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.1.183-185.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beards G. M. Polymorphism of genomic RNAs within rotavirus serotypes and subgroups. Arch Virol. 1982;74(1):65–70. doi: 10.1007/BF01320783. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birch C. J., Heath R. L., Gust I. D. Use of serotype-specific monoclonal antibodies to study the epidemiology of rotavirus infection. J Med Virol. 1988 Jan;24(1):45–53. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890240107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black R. E., Brown K. H., Becker S., Alim A. R., Huq I. Longitudinal studies of infectious diseases and physical growth of children in rural Bangladesh. II. Incidence of diarrhea and association with known pathogens. Am J Epidemiol. 1982 Mar;115(3):315–324. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a113308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiba Y., Miyazaki C., Makino Y., Mutanda L. N., Kibue A., Lichenga E. O., Tukei P. M. Rotavirus infection of young children in two districts of Kenya from 1982 to 1983 as analyzed by electrophoresis of genomic RNA. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 May;19(5):579–582. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.5.579-582.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark H. F., Hoshino Y., Bell L. M., Groff J., Hess G., Bachman P., Offit P. A. Rotavirus isolate WI61 representing a presumptive new human serotype. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Sep;25(9):1757–1762. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.9.1757-1762.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Estes M. K., Graham D. Y., Dimitrov D. H. The molecular epidemiology of rotavirus gastroenteritis. Prog Med Virol. 1984;29:1–22. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Follett E. A., Sanders R. C., Beards G. M., Hundley F., Desselberger U. Molecular epidemiology of human rotaviruses. Analysis of outbreaks of acute gastroenteritis in Glasgow and the west of Scotland 1981/82 and 1982/83. J Hyg (Lond) 1984 Apr;92(2):209–222. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400064238. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Georges-Courbot M. C., Beraud A. M., Beards G. M., Campbell A. D., Gonzalez J. P., Georges A. J., Flewett T. H. Subgroups, serotypes, and electrophoretypes of rotavirus isolated from children in Bangui, Central African Republic. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Apr;26(4):668–671. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.4.668-671.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gombold J. L., Ramig R. F. Analysis of reassortment of genome segments in mice mixedly infected with rotaviruses SA11 and RRV. J Virol. 1986 Jan;57(1):110–116. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.1.110-116.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorziglia M., Larralde G., Kapikian A. Z., Chanock R. M. Antigenic relationships among human rotaviruses as determined by outer capsid protein VP4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Sep;87(18):7155–7159. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.18.7155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gouvea V., Ho M. S., Glass R., Woods P., Forrester B., Robinson C., Ashley R., Riepenhoff-Talty M., Clark H. F., Taniguchi K. Serotypes and electropherotypes of human rotavirus in the USA: 1987-1989. J Infect Dis. 1990 Aug;162(2):362–367. doi: 10.1093/infdis/162.2.362. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg H. B., Kalica A. R., Wyatt R. G., Jones R. W., Kapikian A. Z., Chanock R. M. Rescue of noncultivatable human rotavirus by gene reassortment during mixed infection with ts mutants of a cultivatable bovine rotavirus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jan;78(1):420–424. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.1.420. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoshino Y., Wyatt R. G., Greenberg H. B., Flores J., Kapikian A. Z. Serotypic similarity and diversity of rotaviruses of mammalian and avian origin as studied by plaque-reduction neutralization. J Infect Dis. 1984 May;149(5):694–702. doi: 10.1093/infdis/149.5.694. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalica A. R., Greenberg H. B., Espejo R. T., Flores J., Wyatt R. G., Kapikian A. Z., Chanock R. M. Distinctive ribonucleic acid patterns of human rotavirus subgroups 1 and 2. Infect Immun. 1981 Sep;33(3):958–961. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.3.958-961.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalica A. R., Greenberg H. B., Wyatt R. G., Flores J., Sereno M. M., Kapikian A. Z., Chanock R. M. Genes of human (strain Wa) and bovine (strain UK) rotaviruses that code for neutralization and subgroup antigens. Virology. 1981 Jul 30;112(2):385–390. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90285-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitaoka S., Nakagomi T., Fukuhara N., Hoshino Y., Suzuki H., Nakagomi O., Kapikian A. Z., Ebina T., Konno T., Ishida N. Serologic characteristics of a human rotavirus isolate, AU-1, which has a "long" RNA pattern and subgroup I specificity. J Med Virol. 1987 Dec;23(4):351–357. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890230407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi N., Lintag I. C., Urasawa T., Taniguchi K., Saniel M. C., Urasawa S. Unusual human rotavirus strains having subgroup I specificity and "long" RNA electropherotype. Arch Virol. 1989;109(1-2):11–23. doi: 10.1007/BF01310514. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matson D. O., Estes M. K., Burns J. W., Greenberg H. B., Taniguchi K., Urasawa S. Serotype variation of human group A rotaviruses in two regions of the USA. J Infect Dis. 1990 Sep;162(3):605–614. doi: 10.1093/infdis/162.3.605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuno S., Hasegawa A., Mukoyama A., Inouye S. A candidate for a new serotype of human rotavirus. J Virol. 1985 May;54(2):623–624. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.2.623-624.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishikawa K., Hoshino Y., Taniguchi K., Green K. Y., Greenberg H. B., Kapikian A. Z., Chanock R. M., Gorziglia M. Rotavirus VP7 neutralization epitopes of serotype 3 strains. Virology. 1989 Aug;171(2):503–515. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90620-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodger S. M., Bishop R. F., Birch C., McLean B., Holmes I. H. Molecular epidemiology of human rotaviruses in Melbourne, Australia, from 1973 to 1979, as determined by electrophoresis of genome ribonucleic acid. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Feb;13(2):272–278. doi: 10.1128/jcm.13.2.272-278.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnagl R. D., Rodger S. M., Holmes I. H. Variation in human rotavirus electropherotypes occurring between rotavirus gastroenteritis epidemics in central Australia. Infect Immun. 1981 Jul;33(1):17–21. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.1.17-21.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M. L., Lazdins I., Holmes I. H. Coding assignments of double-stranded RNA segments of SA 11 rotavirus established by in vitro translation. J Virol. 1980 Mar;33(3):976–982. doi: 10.1128/jvi.33.3.976-982.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki H., Sato T., Kitaoka S., Tazawa F., Konno T., Amano Y., Alava Alprecht A., Gutiérrez Vera E., Lopez Villalta J., Numazaki Y. Epidemiology of rotavirus in Guayaquil, Ecuador. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1986 Mar;35(2):372–375. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1986.35.372. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taniguchi K., Morita Y., Urasawa T., Urasawa S. Cross-reactive neutralization epitopes on VP3 of human rotavirus: analysis with monoclonal antibodies and antigenic variants. J Virol. 1987 May;61(5):1726–1730. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.5.1726-1730.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taniguchi K., Urasawa S., Urasawa T. Preparation and characterization of neutralizing monoclonal antibodies with different reactivity patterns to human rotaviruses. J Gen Virol. 1985 May;66(Pt 5):1045–1053. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-66-5-1045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taniguchi K., Urasawa T., Kobayashi N., Gorziglia M., Urasawa S. Nucleotide sequence of VP4 and VP7 genes of human rotaviruses with subgroup I specificity and long RNA pattern: implication for new G serotype specificity. J Virol. 1990 Nov;64(11):5640–5644. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.11.5640-5644.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taniguchi K., Urasawa T., Morita Y., Greenberg H. B., Urasawa S. Direct serotyping of human rotavirus in stools by an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay using serotype 1-, 2-, 3-, and 4-specific monoclonal antibodies to VP7. J Infect Dis. 1987 Jun;155(6):1159–1166. doi: 10.1093/infdis/155.6.1159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urasawa S., Urasawa T., Taniguchi K. Genetic reassortment between two human rotaviruses having different serotype and subgroup specificities. J Gen Virol. 1986 Aug;67(Pt 8):1551–1559. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-8-1551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urasawa S., Urasawa T., Taniguchi K., Morita Y., Sakurada N., Saeki Y., Morita O., Hasegawa S. Validity of an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay with serotype-specific monoclonal antibodies for serotyping human rotavirus in stool specimens. Microbiol Immunol. 1988;32(7):699–708. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1988.tb01431.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urasawa S., Urasawa T., Taniguchi K., Wakasugi F., Kobayashi N., Chiba S., Sakurada N., Morita M., Morita O., Tokieda M. Survey of human rotavirus serotypes in different locales in Japan by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay with monoclonal antibodies. J Infect Dis. 1989 Jul;160(1):44–51. doi: 10.1093/infdis/160.1.44. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urasawa S., Urasawa T., Wakasugi F., Kobayashi N., Taniguchi K., Lintag I. C., Saniel M. C., Goto H. Presumptive seventh serotype of human rotavirus. Arch Virol. 1990;113(3-4):279–282. doi: 10.1007/BF01316680. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urasawa T., Urasawa S., Taniguchi K. Sequential passages of human rotavirus in MA-104 cells. Microbiol Immunol. 1981;25(10):1025–1035. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1981.tb00109.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]