Abstract
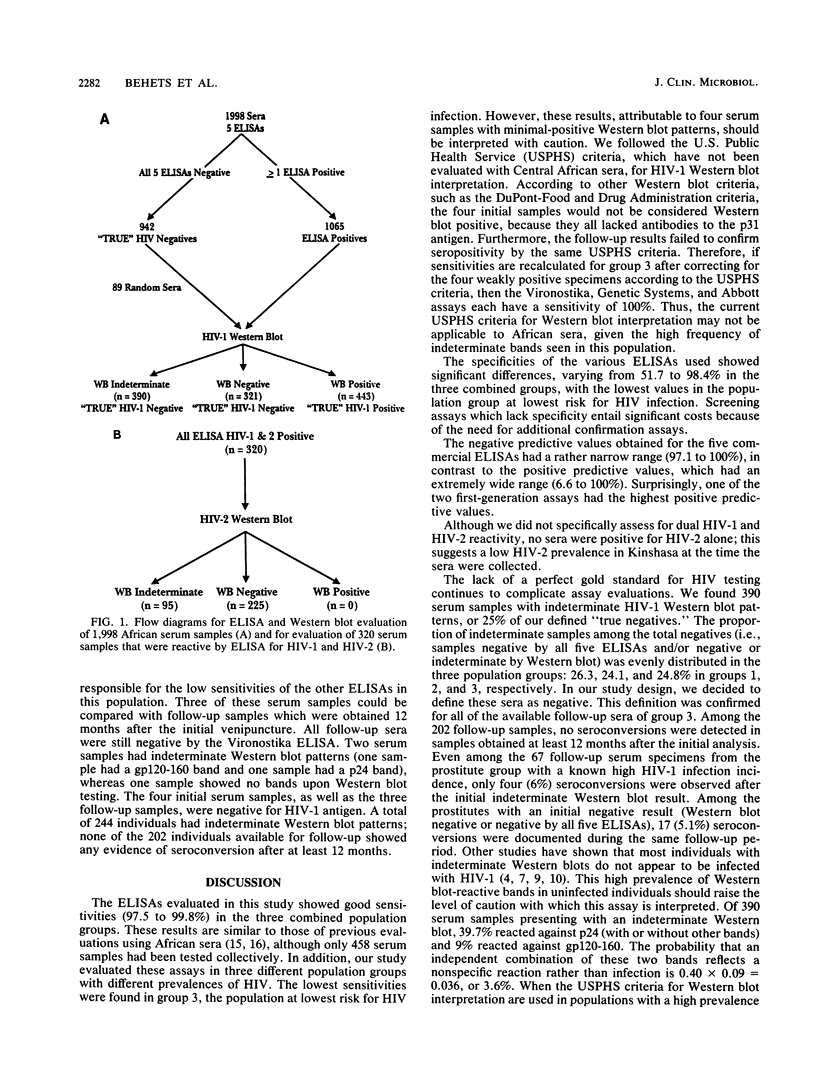
Detection by five different enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISAs) of antibody to human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) in sera from three Zairian populations consisting of 1,998 individuals with various risks for HIV infection was evaluated. Sera that were reactive by at least one assay and 10% of the nonreactive serum samples were analyzed by Western blot (immunoblot) by using U.S. Public Health Service interpretation criteria. Sera which were positive by ELISA for detection of antibody to HIV-1 and HIV-2 and negative or indeterminate by HIV-1 Western blot were also analyzed by HIV-2 Western blot. Overall, 443 (22.2%) serum specimens were HIV-1 Western blot positive, 390 (19.5%) had indeterminate HIV-1 Western blot patterns, and no samples were HIV-2 Western blot positive. The sensitivity of the ELISAs ranged from 97.5 to 99.8%, and the specificity ranged from 51.7 to 98.4%. By population group, the negative predictive value ranged from 97.1 to 100%, in contrast to the positive predictive value, which varied from 6.6 to 100%. Follow-up results for sera which were indeterminate for antibody to HIV-1 documented only four seroconversions (6.0%) among 67 individuals at high risk for HIV-1 infection and no seroconversions among 202 individuals at relatively low risk for HIV-1 infection. This study demonstrates the importance of evaluating commercial ELISAs with sera from appropriate geographical regions in order to select the most cost-effective and practical assay for use in that region. Furthermore, the high frequency of indeterminate Western blots for African sera emphasizes the continual need for improved confirmatory assays and interpretation criteria.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bredberg-Rådén U., Kiango J., Mhalu F., Biberfeld G. Evaluation of commercial enzyme immunoassays for anti-HIV-1 using East African sera. AIDS. 1988 Aug;2(4):281–285. doi: 10.1097/00002030-198808000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burkhardt U., Mertens T., Eggers H. J. Comparison of two commercially available anti-HIV ELISAs: Abbott HTLV III EIA and Du Pont HTLV III-ELISA. J Med Virol. 1987 Nov;23(3):217–224. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890230303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Constantine N. T., Fox E., Abbatte E. A., Woody J. N. Diagnostic usefulness of five screening assays for HIV in an east African city where prevalence of infection is low. AIDS. 1989 May;3(5):313–317. doi: 10.1097/00002030-198905000-00012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deinhardt F., Eberle J., Gürtler L. Sensitivity and specificity of eight commercial and one recombinant anti-HIV ELISA tests. Lancet. 1987 Jan 3;1(8523):40–40. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)90726-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Genesca J., Shih J. W., Jett B. W., Hewlett I. K., Epstein J. S., Alter H. J. What do western blot indeterminate patterns for human immunodeficiency virus mean in EIA-negative blood donors? Lancet. 1989 Oct 28;2(8670):1023–1025. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)91027-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gürtler L. G., Eberle J., Lorbeer B., Deinhardt F. Sensitivity and specificity of commercial ELISA kits for screening anti-LAV/HTLV III. J Virol Methods. 1987 Jan;15(1):11–23. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(87)90044-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson J. B., MacDonald K. L., Cadwell J., Sullivan C., Kline W. E., Hanson M., Sannerud K. J., Stramer S. L., Fildes N. J., Kwok S. Y. Absence of HIV infection in blood donors with indeterminate western blot tests for antibody to HIV-1. N Engl J Med. 1990 Jan 25;322(4):217–222. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199001253220402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lantin J. P., Graf I., Frei P. C. Serological diagnosis of HIV infection: incidence, outcome and significance of partial reactions found in western blot analysis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1989 Jun;76(3):332–336. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maskill W. J., Crofts N., Waldman E., Healey D. S., Howard T. S., Silvester C., Gust I. D. An evaluation of competitive and second generation ELISA screening tests for antibody to HIV. J Virol Methods. 1988 Oct;22(1):61–73. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(88)90088-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozanne G., Fauvel M. Performance and reliability of five commercial enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay kits in screening for anti-human immunodeficiency virus antibody in high-risk subjects. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Aug;26(8):1496–1500. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.8.1496-1500.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parry J. V., McAlpine L., Avillez M. F. Sensitivity of six commercial enzyme immunoassay kits that detect both anti-HIV-1 and anti-HIV-2. AIDS. 1990 Apr;4(4):355–360. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199004000-00012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reesink H. W., Lelie P. N., Huisman J. G., Schaasberg W., Gonsalves M., Aaij C., Winkel I. N., van der Does J. A., Hekker A. C., Desmyter J. Evaluation of six enzyme immunoassays for antibody against human immunodeficiency virus. Lancet. 1986 Aug 30;2(8505):483–486. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)90358-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van de Perre P., Nzaramba D., Allen S., Riggin C. H., Sprecher-Goldberger S., Butzler J. P. Comparison of six serological assays for human immunodeficiency virus antibody detection in developing countries. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Mar;26(3):552–556. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.3.552-556.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vercauteren G., van der Groen G., Piot P. Comparison of enzyme immunoassays and an immunofluorescence test for detection of antibody to human immunodeficiency virus in African sera. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Apr;6(2):132–135. doi: 10.1007/BF02018193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


