Abstract
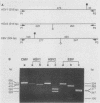
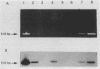
A single pair of oligonucleotide primers selected within a highly conserved region of the DNA polymerase gene of the herpesviruses was designed to amplify related viral genomes, i.e., herpes simplex virus type 1, herpes simplex virus type 2, Epstein-Barr virus, and cytomegalovirus, by the polymerase chain reaction. A simple restriction enzyme analysis of these amplified products allowed accurate characterization of the herpesvirus type. Ninety-nine cerebrospinal fluid samples from 36 patients (including newborns, children, and adults) with acute encephalitis were tested for the presence and identification of herpesvirus DNA by this approach. High levels of viral DNA, which were readily visualized by simple ethidium bromide staining, were found in all these patients from the first days of the disease and, in some cases, until the third week following the onset of acute encephalitis. The herpesvirus type was rapidly identified by enzymatic digestion in 33 patients' samples and by hybridization and direct sequencing in the last 3 patients' samples. Our results show that the polymerase chain reaction provides a highly sensitive and specific technique for the identification of herpesviruses DNA in cerebrospinal fluid that should be of value for early and rapid diagnosis, therapeutic decisions, prognostic evaluation, and epidemiological studies.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aurelius E., Johansson B., Sköldenberg B., Staland A., Forsgren M. Rapid diagnosis of herpes simplex encephalitis by nested polymerase chain reaction assay of cerebrospinal fluid. Lancet. 1991 Jan 26;337(8735):189–192. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(91)92155-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corey L., Whitley R. J., Stone E. F., Mohan K. Difference between herpes simplex virus type 1 and type 2 neonatal encephalitis in neurological outcome. Lancet. 1988 Jan 2;1(8575-6):1–4. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)90997-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Digard P., Coen D. M. A novel functional domain of an alpha-like DNA polymerase. The binding site on the herpes simplex virus polymerase for the viral UL42 protein. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 15;265(29):17393–17396. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gyllensten U. B., Erlich H. A. Generation of single-stranded DNA by the polymerase chain reaction and its application to direct sequencing of the HLA-DQA locus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(20):7652–7656. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.20.7652. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahlon J., Chatterjee S., Lakeman F. D., Lee F., Nahmias A. J., Whitley R. J. Detection of antibodies to herpes simplex virus in the cerebrospinal fluid of patients with herpes simplex encephalitis. J Infect Dis. 1987 Jan;155(1):38–44. doi: 10.1093/infdis/155.1.38. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klapper P. E., Cleator G. M., Dennett C., Lewis A. G. Diagnosis of herpes encephalitis via Southern blotting of cerebrospinal fluid DNA amplified by polymerase chain reaction. J Med Virol. 1990 Dec;32(4):261–264. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890320413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koenig H., Rabinowitz S. G., Day E., Miller V. Post-infectious encephalomyelitis after successful treatment of herpes simplex encephalitis with adenine arabinoside: ultrastructural observations. N Engl J Med. 1979 May 10;300(19):1089–1093. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197905103001906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kouzarides T., Bankier A. T., Satchwell S. C., Weston K., Tomlinson P., Barrell B. G. Sequence and transcription analysis of the human cytomegalovirus DNA polymerase gene. J Virol. 1987 Jan;61(1):125–133. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.1.125-133.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lakeman F. D., Koga J., Whitley R. J. Detection of antigen to herpes simplex virus in cerebrospinal fluid from patients with herpes simplex encephalitis. J Infect Dis. 1987 Jun;155(6):1172–1178. doi: 10.1093/infdis/155.6.1172. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larder B. A., Kemp S. D., Darby G. Related functional domains in virus DNA polymerases. EMBO J. 1987 Jan;6(1):169–175. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04735.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lebon P., Boutin B., Dulac O., Ponsot G., Arthuis M. Interferon gamma in acute and subacute encephalitis. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1988 Jan 2;296(6614):9–11. doi: 10.1136/bmj.296.6614.9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lebon P., Ponsot G., Aicardi J., Goutières F., Arthuis M. Early intrathecal synthesis of interferon in herpes encephalitis. Biomedicine. 1979 Dec;31(9-10):267–271. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lonsdale D. M. A rapid technique for distinguishing herpes-simplex virus type 1 from type 2 by restriction-enzyme technology. Lancet. 1979 Apr 21;1(8121):849–852. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(79)91265-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews J. T., Carroll R. D., Stevens J. T., Haffey M. L. In vitro mutagenesis of the herpes simplex virus type 1 DNA polymerase gene results in altered drug sensitivity of the enzyme. J Virol. 1989 Nov;63(11):4913–4918. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.11.4913-4918.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puchhammer-Stöckl E., Popow-Kraupp T., Heinz F. X., Mandl C. W., Kunz C. Establishment of PCR for the early diagnosis of herpes simplex encephalitis. J Med Virol. 1990 Oct;32(2):77–82. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890320202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotbart H. A. Diagnosis of enteroviral meningitis with the polymerase chain reaction. J Pediatr. 1990 Jul;117(1 Pt 1):85–89. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(05)82451-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowley A. H., Whitley R. J., Lakeman F. D., Wolinsky S. M. Rapid detection of herpes-simplex-virus DNA in cerebrospinal fluid of patients with herpes simplex encephalitis. Lancet. 1990 Feb 24;335(8687):440–441. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)90667-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Scharf S., Faloona F., Mullis K. B., Horn G. T., Erlich H. A., Arnheim N. Enzymatic amplification of beta-globin genomic sequences and restriction site analysis for diagnosis of sickle cell anemia. Science. 1985 Dec 20;230(4732):1350–1354. doi: 10.1126/science.2999980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaunak S., Albright R. E., Klotman M. E., Henry S. C., Bartlett J. A., Hamilton J. D. Amplification of HIV-1 provirus from cerebrospinal fluid and its correlation with neurologic disease. J Infect Dis. 1990 Jun;161(6):1068–1072. doi: 10.1093/infdis/161.6.1068. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsurumi T., Maeno K., Nishiyama Y. Nucleotide sequence of the DNA polymerase gene of herpes simplex virus type 2 and comparison with the type 1 counterpart. Gene. 1987;52(2-3):129–137. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90039-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitley R. J., Cobbs C. G., Alford C. A., Jr, Soong S. J., Hirsch M. S., Connor J. D., Corey L., Hanley D. F., Levin M., Powell D. A. Diseases that mimic herpes simplex encephalitis. Diagnosis, presentation, and outcome. NIAD Collaborative Antiviral Study Group. JAMA. 1989 Jul 14;262(2):234–239. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitley R. J. Viral encephalitis. N Engl J Med. 1990 Jul 26;323(4):242–250. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199007263230406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitley R., Lakeman A. D., Nahmias A., Roizman B. Dna restriction-enzyme analysis of herpes simplex virus isolates obtained from patients with encephalitis. N Engl J Med. 1982 Oct 21;307(17):1060–1062. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198210213071706. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]