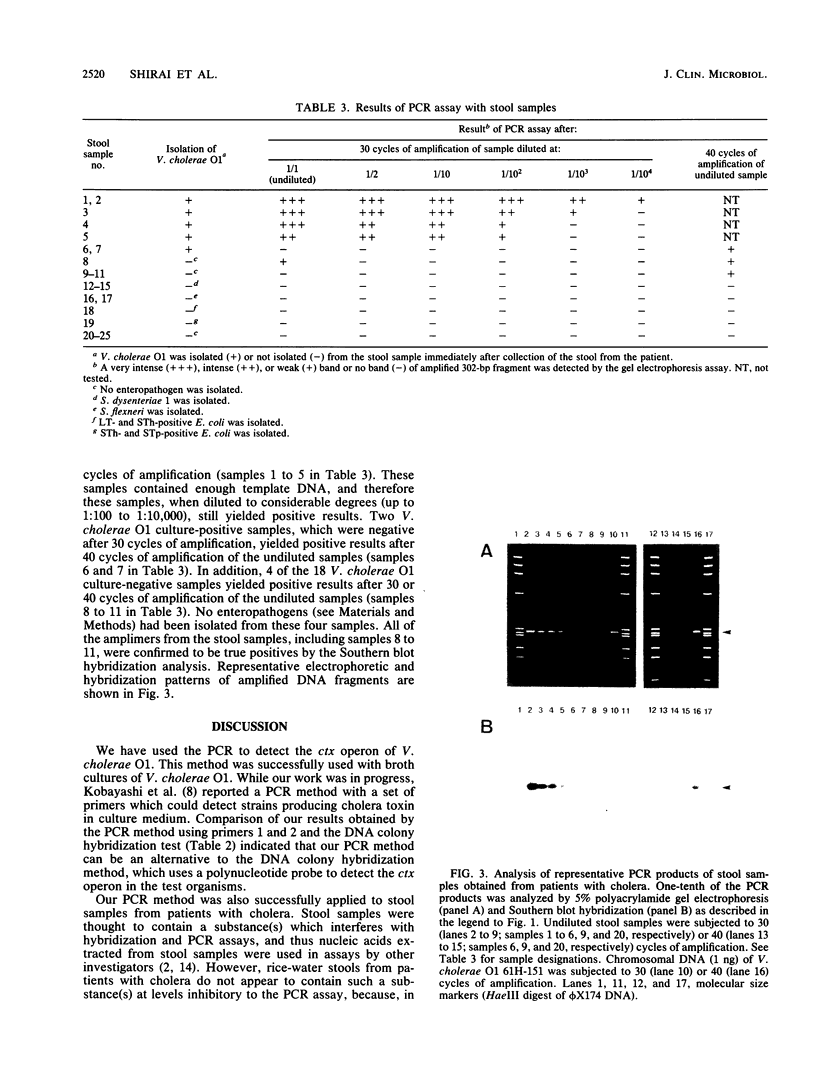
Abstract
We report a set of oligonucleotide primers and amplification conditions for the polymerase chain reaction to detect the ctx operon of Vibrio cholerae. The results of this assay on strains of V. cholerae and related organisms were identical with those obtained by the DNA colony hybridization test with the polynucleotide probe. The detection limit of this system was 1 pg of chromosomal DNA or broth culture containing three viable cells. The polymerase chain reaction method could directly detect the ctx operon sequences in rice-water stool samples from patients with cholera.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Coll P., Phillips K., Tenover F. C. Evaluation of a rapid method of extracting DNA from stool samples for use in hybridization assays. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Oct;27(10):2245–2248. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.10.2245-2248.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craig J. P., Yamamoto K., Takeda Y., Miwatani T. Production of cholera-like enterotoxin by a Vibrio cholerae non-O1 strain isolated from the environment. Infect Immun. 1981 Oct;34(1):90–97. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.1.90-97.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honda T., Arita M., Takeda Y., Miwatani T. Further evaluation of the Biken test (modified Elek test) for detection of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli producing heat-labile enterotoxin and application of the test to sampling of heat-stable enterotoxin. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Jul;16(1):60–62. doi: 10.1128/jcm.16.1.60-62.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaper J. B., Moseley S. L., Falkow S. Molecular characterization of environmental and nontoxigenic strains of Vibrio cholerae. Infect Immun. 1981 May;32(2):661–667. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.2.661-667.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi K., Seto K., Akasaka S., Makino M. [Detection of toxigenic Vibrio cholerae O1 using polymerase chain reaction for amplifying the cholera enterotoxin gene]. Kansenshogaku Zasshi. 1990 Oct;64(10):1323–1329. doi: 10.11150/kansenshogakuzasshi1970.64.1323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mekalanos J. J., Swartz D. J., Pearson G. D., Harford N., Groyne F., de Wilde M. Cholera toxin genes: nucleotide sequence, deletion analysis and vaccine development. Nature. 1983 Dec 8;306(5943):551–557. doi: 10.1038/306551a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moseley S. L., Echeverria P., Seriwatana J., Tirapat C., Chaicumpa W., Sakuldaipeara T., Falkow S. Identification of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli by colony hybridization using three enterotoxin gene probes. J Infect Dis. 1982 Jun;145(6):863–869. doi: 10.1093/infdis/145.6.863. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishibuchi M., Ishibashi M., Takeda Y., Kaper J. B. Detection of the thermostable direct hemolysin gene and related DNA sequences in Vibrio parahaemolyticus and other vibrio species by the DNA colony hybridization test. Infect Immun. 1985 Sep;49(3):481–486. doi: 10.1128/iai.49.3.481-486.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishibuchi M., Murakami A., Arita M., Jikuya H., Takano J., Honda T., Miwatani T. Detection with synthetic oligonucleotide probes of nucleotide sequence variations in the genes encoding enterotoxins of Escherichia coli. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Oct;27(10):2272–2276. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.10.2272-2276.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olive D. M. Detection of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli after polymerase chain reaction amplification with a thermostable DNA polymerase. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Feb;27(2):261–265. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.2.261-265.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto K., Takeda Y., Miwatani T., Craig J. P. Purification and some properties of a non-o1 Vibrio cholerae enterotoxin that is identical to cholera enterotoxin. Infect Immun. 1983 Mar;39(3):1128–1135. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.3.1128-1135.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto T., Tamura T., Yokota T. Primary structure of heat-labile enterotoxin produced by Escherichia coli pathogenic for humans. J Biol Chem. 1984 Apr 25;259(8):5037–5044. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]