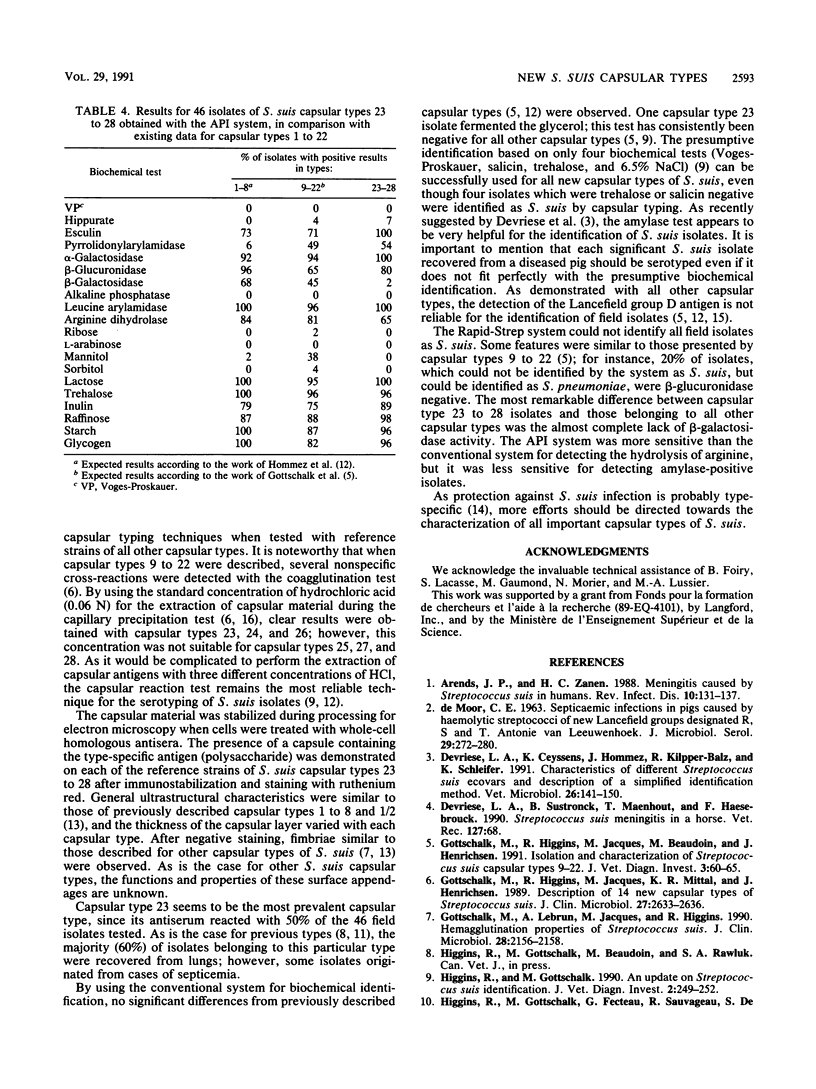
Abstract
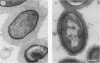
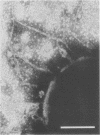
Six new capsular types of Streptococcus suis (types 23 to 28) are described. All reference strains were isolated from diseased pigs and were morphologically and biochemically similar to previously described capsular types 1 to 22. Clear and specific reactions were obtained for each of the new capsular types with three different typing techniques; no cross-reactions were detected among them or with other S. suis capsular types. Their capsular material presented similar ultrastructural characteristics, as shown by electron microscopy, and fimbriae similar to those described for other capsular types of S. suis were observed. When untypeable field isolates were tested with antisera raised against the six new capsular types, capsular type 23 appeared to be the most prevalent, representing more than 50% of all these isolates. Most isolates were recovered from cases of pneumonia, septicemia, and meningitis. Presumptive biochemical identification described for S. suis capsular types 1 to 22 may also be used for capsular types 23 to 28.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arends J. P., Zanen H. C. Meningitis caused by Streptococcus suis in humans. Rev Infect Dis. 1988 Jan-Feb;10(1):131–137. doi: 10.1093/clinids/10.1.131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEMOOR C. E. SEPTICAEMIC INFECTIONS IN PIGS, CAUSED BY HAEMOLYTIC STREPTOCOCCI OF NEW LANCEFIELD GROUPS DESIGNATED R, S, AND T. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1963;29:272–280. doi: 10.1007/BF02046069. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devriese L. A., Ceyssens K., Hommez J., Kilpper-Bälz R., Schleifer K. H. Characteristics of different Streptococcus suis ecovars and description of a simplified identification method. Vet Microbiol. 1991 Jan;26(1-2):141–150. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(91)90050-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devriese L. A., Sustronck B., Maenhout T., Haesebrouck F. Streptococcus suis meningitis in a horse. Vet Rec. 1990 Jul 21;127(3):68–68. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottschalk M., Higgins R., Jacques M., Beaudoin M., Henrichsen J. Isolation and characterization of Streptococcus suis capsular types 9-22. J Vet Diagn Invest. 1991 Jan;3(1):60–65. doi: 10.1177/104063879100300113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottschalk M., Higgins R., Jacques M., Mittal K. R., Henrichsen J. Description of 14 new capsular types of Streptococcus suis. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Dec;27(12):2633–2636. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.12.2633-2636.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottschalk M., Lebrun A., Jacques M., Higgins R. Hemagglutination properties of Streptococcus suis. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Sep;28(9):2156–2158. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.9.2156-2158.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins R., Gottschalk M. An update on Streptococcus suis identification. J Vet Diagn Invest. 1990 Jul;2(3):249–252. doi: 10.1177/104063879000200324. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins R., Gottschalk M., Fecteau G., Sauvageau R., De Guise S., Du Tremblay D. Quebec. Isolation of Streptococcus suis from cattle. Can Vet J. 1990 Jul;31(7):529–529. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins R., Gottschalk M., Mittal K. R., Beaudoin M. Streptococcus suis infection in swine. A sixteen month study. Can J Vet Res. 1990 Jan;54(1):170–173. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hommez J., Devriese L. A., Henrichsen J., Castryck F. Identification and characterization of Streptococcus suis. Vet Microbiol. 1986 Apr;11(4):349–355. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(86)90065-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacques M., Gottschalk M., Foiry B., Higgins R. Ultrastructural study of surface components of Streptococcus suis. J Bacteriol. 1990 Jun;172(6):2833–2838. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.6.2833-2838.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kebede M., Chengappa M. M., Stuart J. G. Isolation and characterization of temperature-sensitive mutants of Streptococcus suis: efficacy trial of the mutant vaccine in mice. Vet Microbiol. 1990 Apr;22(2-3):249–257. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(90)90112-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perch B., Pedersen K. B., Henrichsen J. Serology of capsulated streptococci pathogenic for pigs: six new serotypes of Streptococcus suis. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Jun;17(6):993–996. doi: 10.1128/jcm.17.6.993-996.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson I. D., Blackmore D. K. Occupational exposure to Streptococcus suis type 2. Epidemiol Infect. 1989 Aug;103(1):157–164. doi: 10.1017/s0950268800030454. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]