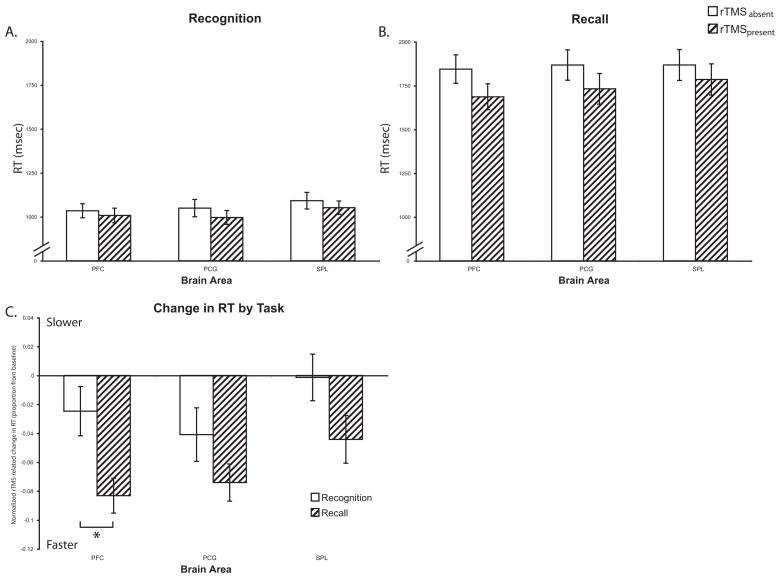
Figure 2.
Reaction Time: A) Delayed-recognition task B) Delayed-recall task. C) Change in accuracy with rTMS in both trial types normalized to the rTMSabsent condition. In recognition trials, PCG rTMS trended towards a greater decrease in RT compared to SPL rTMS [t(23) = 1.87; p=0.07]. Comparison of the effect of rTMS across trial types revealed that dlPFC rTMS led to a greater decrease in RT in recall versus recognition trials [t(23) = 3.44; p<0.005]. There was a similar trend with SPL rTMS [t(23) = 1.72; p=0.10]. * − p<0.05