Abstract
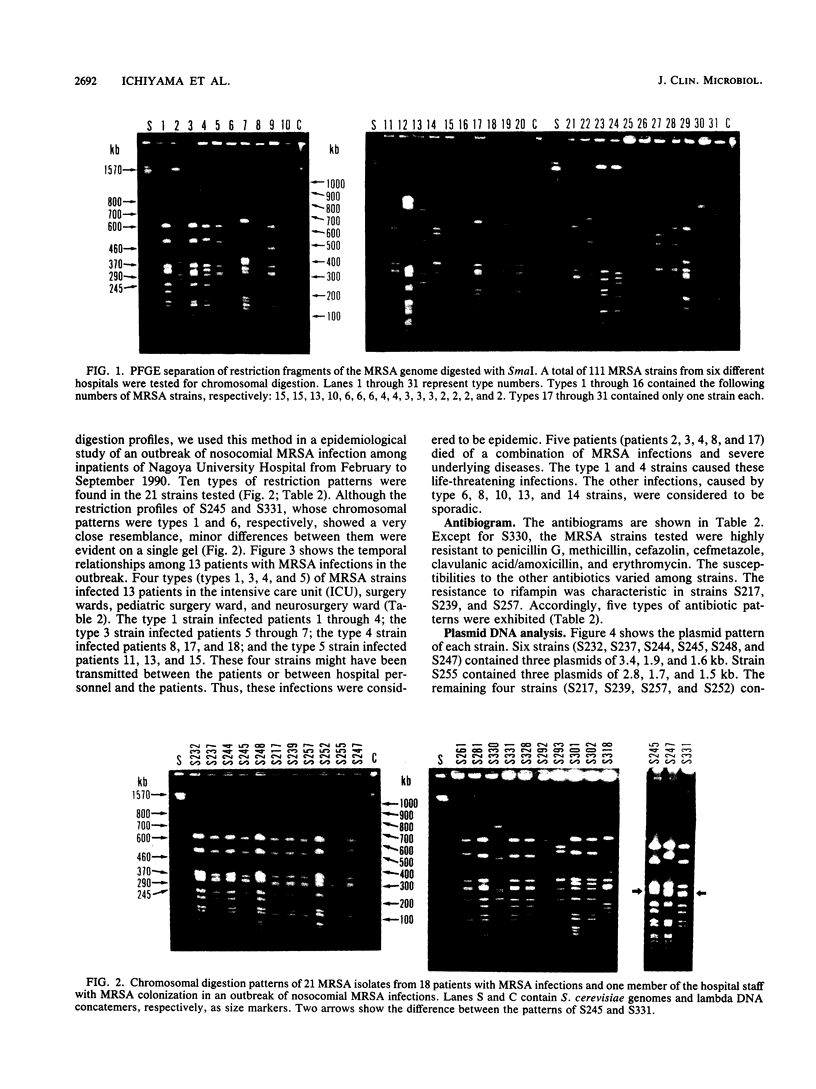
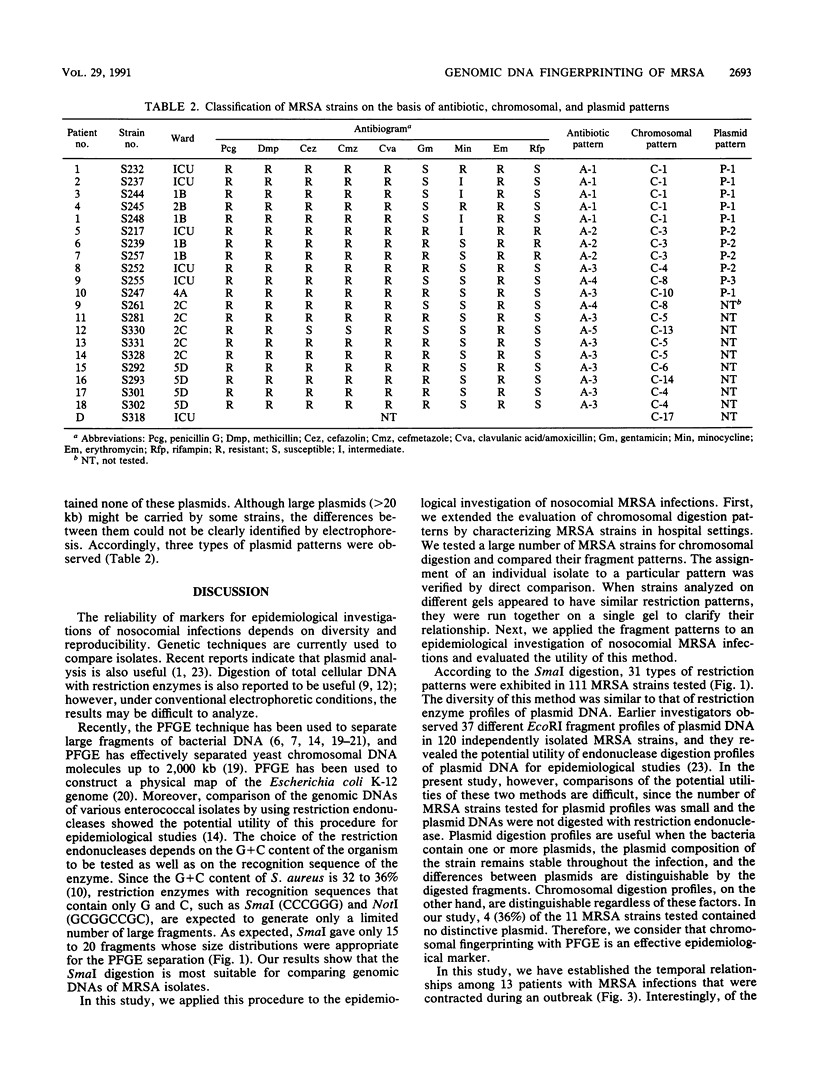
In this study, we have compared genomic DNA fingerprintings among isolates of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) by using pulsed-field gel electrophoresis (PFGE). Chromosomal fragments digested with SmaI were most suitable for the PFGE separation. SmaI cut genomic DNA into 15 to 20 fragments whose sizes ranged from about 30 to 1,500 kb. Thirty-one distinctive fragment patterns were identified in 111 infecting and colonizing MRSA isolates from six different hospitals in Japan. On the basis of the genomic typing by PFGE, we performed an epidemiological investigation of an outbreak of nosocomial MRSA infections among inpatients in Nagoya University Hospital. Ten types of chromosomal digestion were identified in the 20 strains isolated from 18 infected patients and 1 from colonized hospital personnel. According to the restriction patterns, we found that four types of these strains had caused epidemic infections among 13 patients in the outbreak. Two types (types 1 and 4) of the strains were involved in the death of five patients. The other infections were sporadic. The clarity and polymorphism of the chromosomal digestion patterns enabled us to discriminate between isolates which could not be differentiated by antibiogram or plasmid analysis. Classification of the genomic DNA fingerprinting patterns by PFGE is therefore proposed as a useful method for investigating the source, transmission, and spread of nosocomial MRSA infections.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Archer G. L., Mayhall C. G. Comparison of epidemiological markers used in the investigation of an outbreak of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infections. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Aug;18(2):395–399. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.2.395-399.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartzokas C. A., Paton J. H., Gibson M. F., Graham F., McLoughlin G. A., Croton R. S. Control and eradication of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus on a surgical unit. N Engl J Med. 1984 Nov 29;311(22):1422–1425. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198411293112207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouvet A., Fournier J. M., Audurier A., Branger C., Orsoni A., Girard C. Epidemiological markers for epidemic strain and carrier isolates in an outbreak of nosocomial oxacillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Jun;28(6):1338–1341. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.6.1338-1341.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coovadia Y. M., Bhana R. H., Johnson A. P., Haffejee I., Marples R. R. A laboratory-confirmed outbreak of rifampicin-methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus (RMRSA) in a newborn nursery. J Hosp Infect. 1989 Nov;14(4):303–312. doi: 10.1016/0195-6701(89)90070-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ely B., Gerardot C. J. Use of pulsed-field-gradient gel electrophoresis to construct a physical map of the Caulobacter crescentus genome. Gene. 1988 Sep 7;68(2):323–333. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90035-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frutos R., Pages M., Bellis M., Roizes G., Bergoin M. Pulsed-field gel electrophoresis determination of the genome size of obligate intracellular bacteria belonging to the genera Chlamydia, Rickettsiella, and Porochlamydia. J Bacteriol. 1989 Aug;171(8):4511–4513. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.8.4511-4513.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guiguet M., Rekacewicz C., Leclercq B., Brun Y., Escudier B., Andremont A. Effectiveness of simple measures to control an outbreak of nosocomial methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infections in an intensive care unit. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 1990 Jan;11(1):23–26. doi: 10.1086/646074. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall L. M., Jordens J. Z., Wang F. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus from China characterized by digestion of total DNA with restriction enzymes. Epidemiol Infect. 1989 Aug;103(1):183–192. doi: 10.1017/s095026880003048x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Locksley R. M., Cohen M. L., Quinn T. C., Tompkins L. S., Coyle M. B., Kirihara J. M., Counts G. W. Multiply antibiotic-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: introduction, transmission, and evolution of nosocomial infection. Ann Intern Med. 1982 Sep;97(3):317–324. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-97-3-317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin N. J., Kaplan E. L., Gerber M. A., Menegus M. A., Randolph M., Bell K., Cleary P. P. Comparison of epidemic and endemic group G streptococci by restriction enzyme analysis. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Sep;28(9):1881–1886. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.9.1881-1886.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muder R. R., Brennen C., Wagener M. M., Vickers R. M., Rihs J. D., Hancock G. A., Yee Y. C., Miller J. M., Yu V. L. Methicillin-resistant staphylococcal colonization and infection in a long-term care facility. Ann Intern Med. 1991 Jan 15;114(2):107–112. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-114-2-1-107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray B. E., Singh K. V., Heath J. D., Sharma B. R., Weinstock G. M. Comparison of genomic DNAs of different enterococcal isolates using restriction endonucleases with infrequent recognition sites. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Sep;28(9):2059–2063. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.9.2059-2063.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ribner B. S., Landry M. N., Kidd K., Peninger M., Riddick J. Outbreak of multiply resistant Staphylococcus aureus in a pediatric intensive care unit after consolidation with a surgical intensive care unit. Am J Infect Control. 1989 Oct;17(5):244–249. doi: 10.1016/0196-6553(89)90170-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaberg D. R., Zervos M. Plasmid analysis in the study of the epidemiology of nosocomial gram-positive cocci. Rev Infect Dis. 1986 Sep-Oct;8(5):705–712. doi: 10.1093/clinids/8.5.705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz D. C., Cantor C. R. Separation of yeast chromosome-sized DNAs by pulsed field gradient gel electrophoresis. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):67–75. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90301-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. L., Cantor C. R. Purification, specific fragmentation, and separation of large DNA molecules. Methods Enzymol. 1987;155:449–467. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)55030-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. L., Econome J. G., Schutt A., Klco S., Cantor C. R. A physical map of the Escherichia coli K12 genome. Science. 1987 Jun 12;236(4807):1448–1453. doi: 10.1126/science.3296194. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas J. C., Bridge J., Waterman S., Vogt J., Kilman L., Hancock G. Transmission and control of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in a skilled nursing facility. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 1989 Mar;10(3):106–110. doi: 10.1086/645976. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuccarelli A. J., Roy I., Harding G. P., Couperus J. J. Diversity and stability of restriction enzyme profiles of plasmid DNA from methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Jan;28(1):97–102. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.1.97-102.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]