Abstract
The value and convenience of testing for specific anti-Toxoplasma gondii antibodies have led to the development of various antibody detection methods, such as the enzyme immunoassay. Two enzyme immunoassays, the Vitek Immuno-Diagnostic Assay System (VIDAS; Vitek Systems, Hazelwood, Mo.) and the Toxostat Test Kit (TST; Whittaker Bioproducts, Walkersville, Md.), were compared for their ability to detect T. gondii immunoglobulin G antibodies in fresh human sera. Specimens were tested according to the instructions of each manufacturer. Of 304 serum specimens tested, the results for 282 (93%) agreed in both assays (77 were positive and 205 were negative). The results for the remaining 22 (7%) specimens were discrepant; 20 of the 22 specimens tested low positive or equivocal by Toxostat and negative by VIDAS. Upon retesting, 8 of these 22 specimens were in concordance, increasing the level of agreement to 95.3%. Intra-assay reproducibility was tested with four to nine replicates of each of seven samples (four positive, one negative, and two equivocal) by both tests and six replicates of one standard by VIDAS. Coefficients of variation (CVs) for VIDAS were 6, 8, 10, 15, 18, 19, and 23% for the samples and 14% for the standard. For Toxostat the CVs were 2, 8, 10, 10, 13, and 16%. In general, CVs for VIDAS were slightly larger than the CVs for Toxostat. Day-to-day variability over 3 days was tested by VIDAS for only six samples (three positive, two negative, and one equivocal) and four standards; CVs ranged from 2 to 15% for the samples and from 6 to 13% for the standards. In conclusions, VIDAS is a rapid, convenient, non-labor-intensive, and easily performed test for the detection of immunoglobulin G antibodies to T. gondii in serum specimens.
Full text
PDF
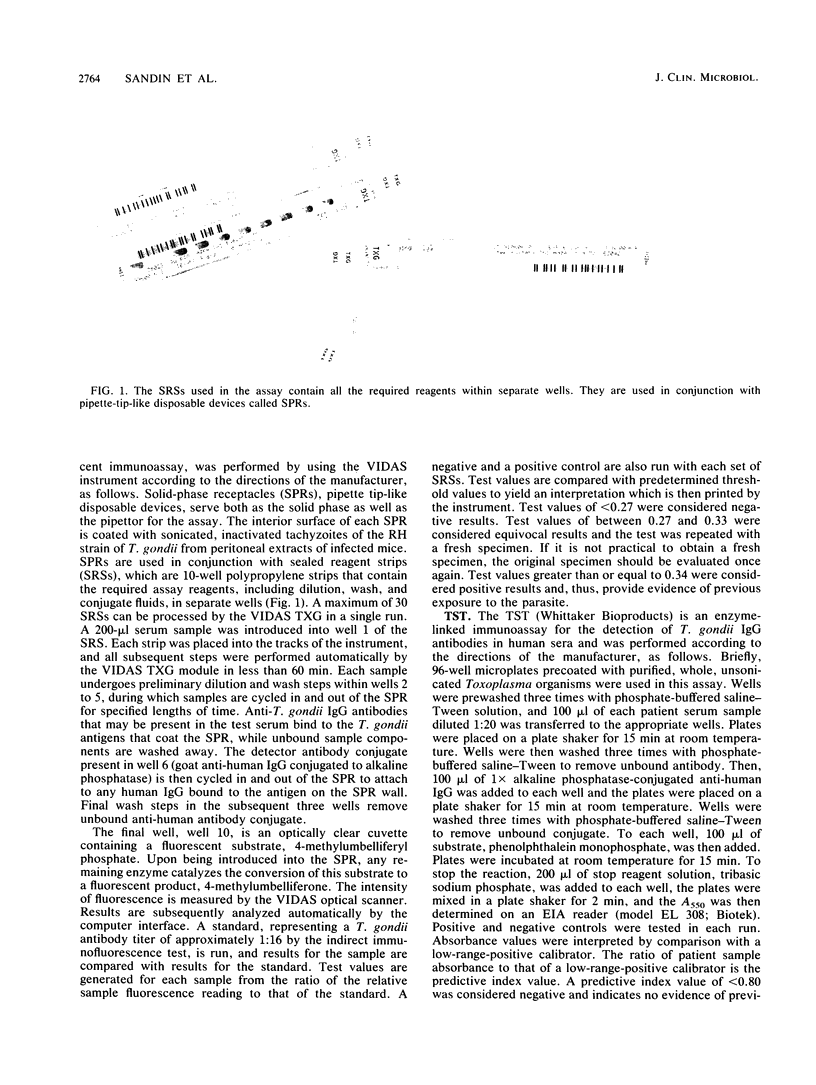
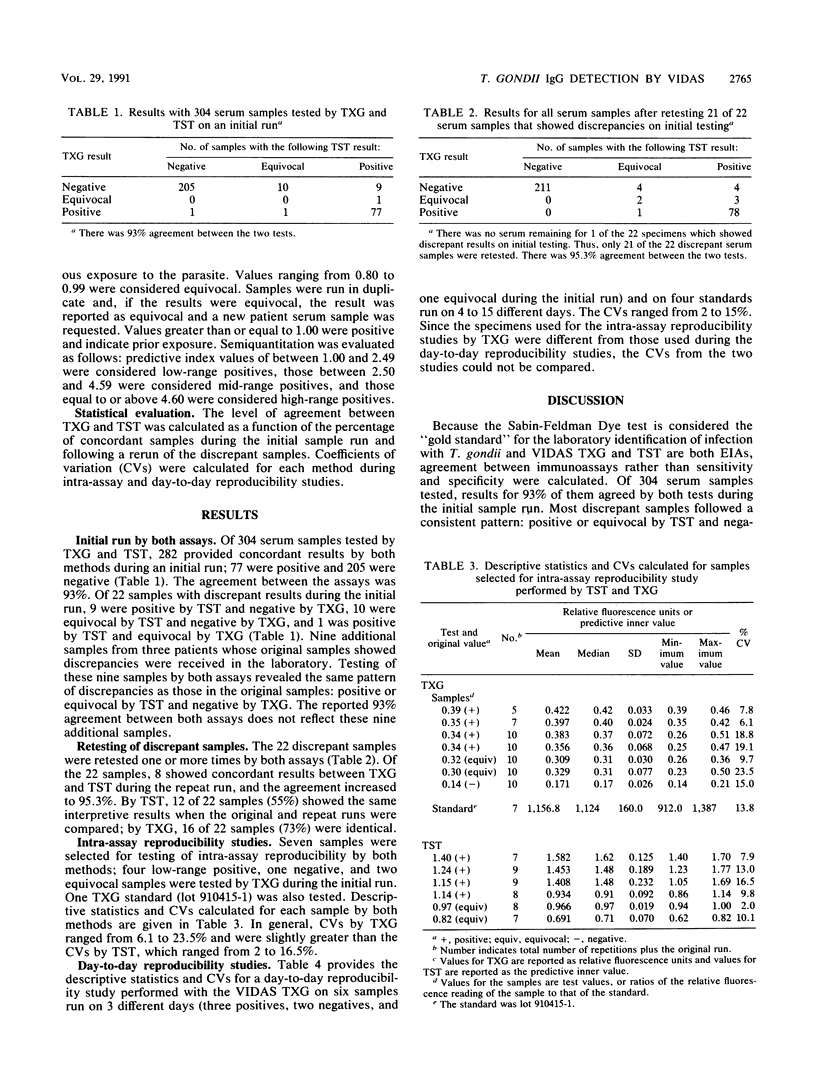
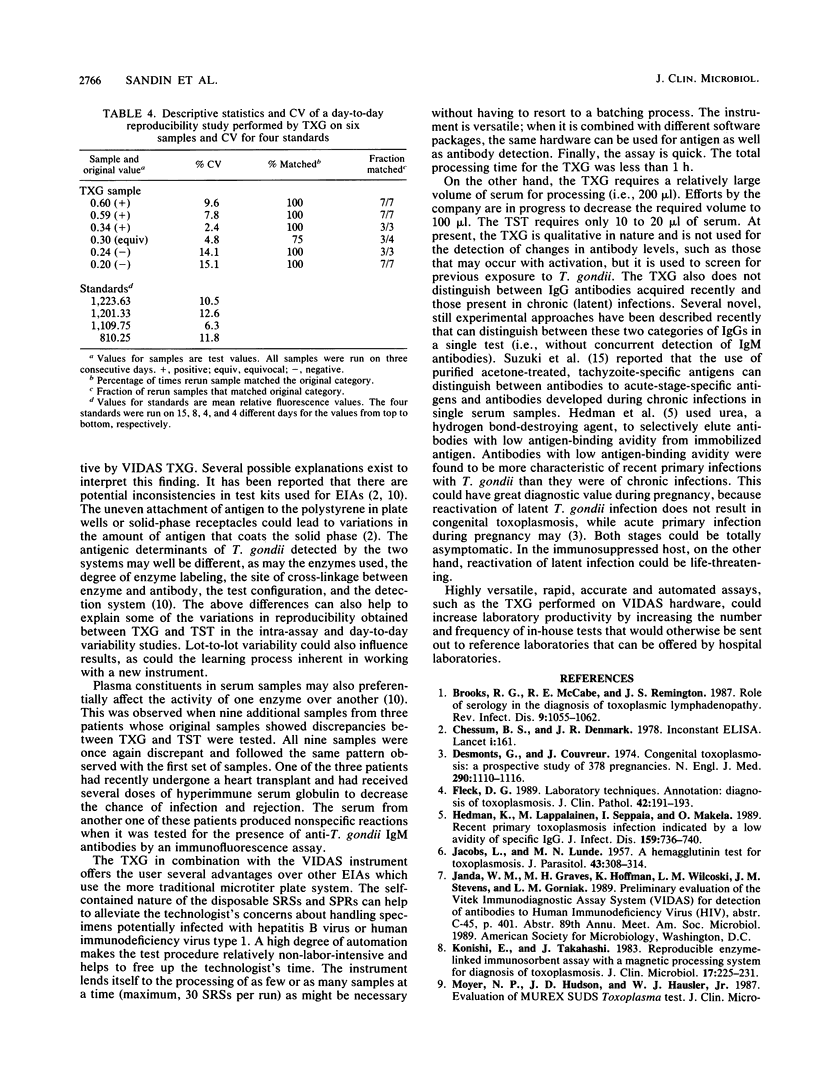

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brooks R. G., McCabe R. E., Remington J. S. Role of serology in the diagnosis of toxoplasmic lymphadenopathy. Rev Infect Dis. 1987 Sep-Oct;9(5):1055–1062. doi: 10.1093/clinids/9.5.1055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chessum B. S., Denmark J. R. Inconstant ELISA. Lancet. 1978 Jan 21;1(8056):161–161. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(78)90468-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desmonts G., Couvreur J. Congenital toxoplasmosis. A prospective study of 378 pregnancies. N Engl J Med. 1974 May 16;290(20):1110–1116. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197405162902003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleck D. G. Annotation: Diagnosis of toxoplasmosis. J Clin Pathol. 1989 Feb;42(2):191–193. doi: 10.1136/jcp.42.2.191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedman K., Lappalainen M., Seppäiä I., Mäkelä O. Recent primary toxoplasma infection indicated by a low avidity of specific IgG. J Infect Dis. 1989 Apr;159(4):736–740. doi: 10.1093/infdis/159.4.736. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JACOBS L., LUNDE M. N. A hemagglutination test for toxoplasmosis. J Parasitol. 1957 Jun;43(3):308–314. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konishi E., Takahashi J. Reproducible enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay with a magnetic processing system for diagnosis of toxoplasmosis. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Feb;17(2):225–231. doi: 10.1128/jcm.17.2.225-231.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Sullivan M. J., Bridges J. W., Marks V. Enzyme immunoassay: a review. Ann Clin Biochem. 1979 Sep;16(5):221–240. doi: 10.1177/000456327901600162. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabin A. B., Feldman H. A. Dyes as Microchemical Indicators of a New Immunity Phenomenon Affecting a Protozoon Parasite (Toxoplasma). Science. 1948 Dec 10;108(2815):660–663. doi: 10.1126/science.108.2815.660. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sluiters J. F., Balk A. H., Essed C. E., Mochtar B., Weimar W., Simoons M. L., Ijzerman E. P. Indirect enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for immunoglobulin G and four immunoassays for immunoglobulin M to Toxoplasma gondii in a series of heart transplant recipients. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Mar;27(3):529–535. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.3.529-535.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith S. B., Repetti C. F. Evaluation of a rapid screening immunoassay for antibodies to Toxoplasma gondii. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Nov;25(11):2207–2208. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.11.2207-2208.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sulzer A. J., Hall E. C. Indirect fluorescent antibody tests for parasitic diseases. IV. Statistical study of variation in the indirect fluorescent antibody (IFA) test for toxoplasmosis. Am J Epidemiol. 1967 Sep;86(2):401–407. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a120750. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki Y., Thulliez P., Remington J. S. Use of acute-stage-specific antigens of Toxoplasma gondii for serodiagnosis of acute toxoplasmosis. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Aug;28(8):1734–1738. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.8.1734-1738.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Enk R. A., James K. K., Thompson K. D. Evaluation of three commercial enzyme immunoassays for toxoplasma and cytomegalovirus antibodies. Am J Clin Pathol. 1991 Mar;95(3):428–434. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/95.3.428. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voller A., Bidwell D. E., Bartlett A., Fleck D. G., Perkins M., Oladehin B. A microplate enzyme-immunoassay for toxoplasma antibody. J Clin Pathol. 1976 Feb;29(2):150–153. doi: 10.1136/jcp.29.2.150. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson M., Ware D. A., Walls K. W. Evaluation of commercial serodiagnostic kits for toxoplasmosis. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Dec;25(12):2262–2265. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.12.2262-2265.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




