Calicheamicin (CLM) γ1I (Fig. 1, 5) is a prominent member of the 10-membered enediyne family.1 Like all enediynes, CLM-induced oxidative DNA strand scission is enabled by cycloaromatization of the enediyne core to form a highly reactive diradical species.2 In CLM, this reactive intermediate is positioned in the DNA minor groove via the aryltetrasaccharide wherein the unique conformation of the CLM hydroxylamino glycosidic bond contributes to both DNA specificity and affinity.3 The incredible potency of CLM has been harnessed for clinical use (Mylotarg®),4 and CLM biosynthetic studies have unveiled a variety of unique features. For example, the recent elucidation of gene clusters encoding both 9-membered and 10-membered enediynes revealed a unified, divergent polyketide paradigm for enediyne core biosynthesis,5 likely originating from a common polyene precursor.6 Studies on CLM self-resistance also revealed the first ‘self-sacrifice’ resistance mechanism,7 while CLM glycosyltransferase-catalyzed ‘sugar exchange’ and ‘aglycon exchange’ reactions enabled the production of >70 differentially glycosylated CLM variants.8 Despite the prevalence of deoxy- and aminosugars in nature,9 only a few naturally-occuring N-oxidized aminosugars, such as the one found in CLM, have been identified.10 Putative N-oxidase genes for rubranitrose, kijanose, and the CLM/esperamicin hydroxylaminosugar biosynthesis have been put forth yet, the enzymes involved in aminosugar N-oxidation remain elusive.5b,5d,10,11 Herein we describe the first reported in vitro characterization of an aminosugar N-oxidase, CalE10, responsible for CLM hydroxylaminosugar formation.
Figure 1.
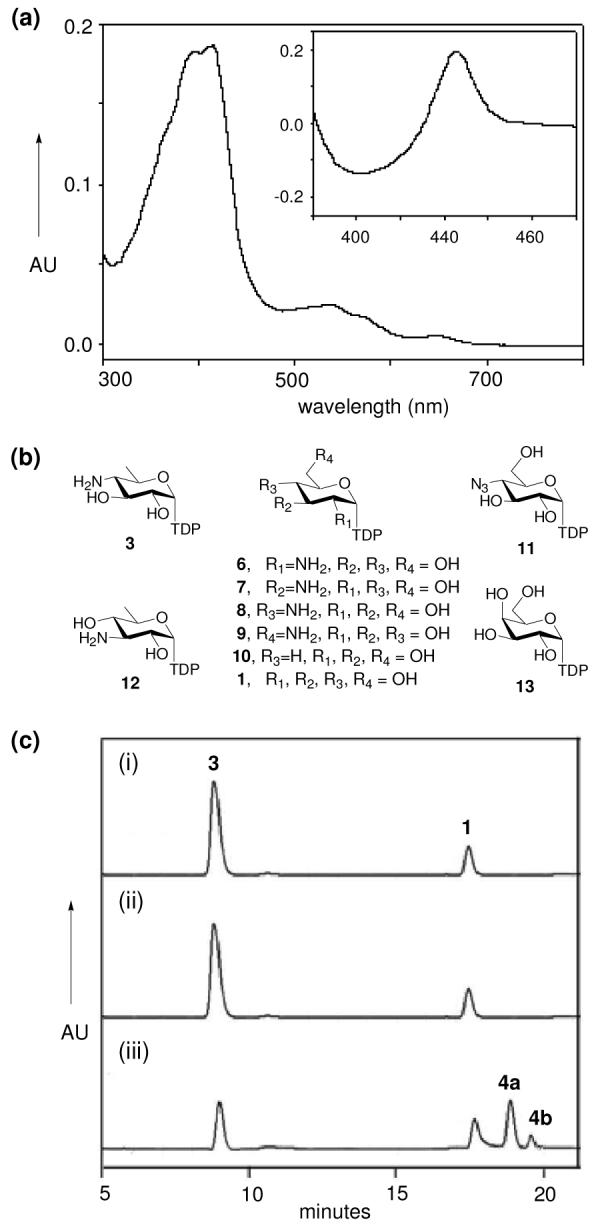
(a) Oxidized spectrum of CalE10 and difference spectra of reduced CO-bound species (inset). (b) Putative sugar nucleotide substrates used in this study. (c) HPLC analyses of assays with 3 as the substrate: (i) no P450 (control); (ii) CalO2; (iii) CalE10. A trace amount of 1 remains from chemoenzymatic synthesis of 3. See supporting information for experimental details.
A comparison among the gene clusters encoding 10-membered enediynes5b-5d and indolocarbazoles12 presented a genomic basis from which to propose the biosynthetic pathway for hydroxyaminosugar precursor TDP-4-hydroxyamino-6-deoxy-α-D-glucose (Scheme 1, 4). Specifically, this comparative genomic analysis (Scheme S1) enabled the elimination from consideration genes for the biosynthesis of the 10-membered enediyne core (common to 5, 14, and 16) and the CLM aminopentose (common to 5, 14, and 18, but not 19). Genes anticipated to be involved in the biosynthesis of orsellinic acid13 and the terminal rhamnose precursor9 were also excluded based upon well-established precedent for these pathways. The remaining genes were anticipated to be integral to CLM thiosugar or hydroxylaminosugar biosynthesis. In conjunction with the well-established routes to aminosugar biosynthesis,9 and reminiscent of the P450 N-oxidase in β-lactam biosynthesis (NocL),14 this information led to the proposed pathway highlighted in Scheme 1 wherein two P450s (CalO2 and CalE10) were identified as aminosugar oxidase candidates.
Scheme 1.
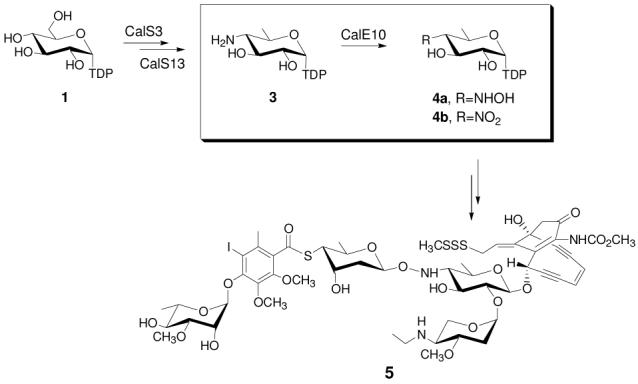
Proposed biosynthesis of 4-hydroxyamino-6-deoxy-α-Dglucose common to CLM (5) and esperamicin.
To test the ability of CalO2 and CalE10 to catalyze aminosugar N-oxidation, the corresponding enzymes were overproduced in Streptomyces lividans as N-His6-fusions. While N-His6-CalO2 displayed a typical P450 Soret peak (418 nm),15 N-His6-CalE10 exhibited two distinct maxima (418 nm and 386 nm) of equal intensity indicative of a heme iron mixed spin state. The reduced CO bound spectra for both enzymes displayed a typical P450 Soret peak (450 nm) (Fig. 1A). Subsequent in vitro assays employed a series of putative TDP-sugar substrates (Fig. 1B, 1, 3, 6-13; 10 mM),8,16 0.5 mg mL−1 P450 (CalO2 or CalE10) and a standard spinach ferredoxin/reductase system.17 N-His6-CalE10-catalyzed transformation of 3 afforded two new products (Fig. 1C) with mass and IR consistent with hydroxyaminosugar 4a (Scheme 1, major) and nitrosugar 4b (minor), while aminosugar 8 with the same enzyme led to the corresponding hydroxylamino derivative in trace amounts. Steady state kinetic analysis of the CalE10-catalyzed oxidation of 3 revealed kinetic parameters (kcat = 0.04 ± 0.01 sec−1; Km = 7.6 ± 1.2 μM) similar to other natural product P450s.17 Consistent with the stringent aminosugar regiospecificity observed, subsequent ligand-binding studies revealed a reverse type I difference spectrum17e,18 with determined Kd values of 9.1 ± 1.1 μM, 17.3 ± 1.8 μM, 165 ± 27 μM, and >150 μM for 3, 8, 1, and 10, respectively, while TDP or 4-amino-4-deoxy-α-D-Glc-1-phosphate led to no heme perturbation. No apparent sugar nucleotide binding or oxidation was observed with CalO2, consistent with the ability of CalO2 to bind substituted aromatic acids (as possible orsellinic acid surrogates).15
In summary, this study establishes, for the first time, CalE10 as the requisite CLM NDP-aminosugar N-oxidase and confirms that oxidation occurs at the sugar nucleotide stage prior to glycosyltransfer. Furthermore, substrate specificity studies revealed CalE10-catalyzed oxidation to be regiospecific with limited over-oxidation in vitro. As the first characterization of an aminosugar N-oxidase, this study also presents a foundation for the future study of other N-oxidases involved in hydroxylamino-, nitroso-, and/or nitrosugar formation.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgement
We thank the School of Pharmacy Analytical Instrumentation Center for analytical support and Professor Hung-wen (Ben) Liu for graciously providing overexpression constructs for rfbB and desI. This work was supported by the NIH (CA84374 and U19 CA113297). H.D.J. is UW Chemical Biology Interface Trainee (T32 GM008505).
Footnotes
Supporting Information Available: Assay procedures and spectroscopic data. This material is available free of charge via the Internet at http://pubs.acs.org.
References
- 1.For reviews see Thorson JS, Sievers EL, Ahlert J, Shephard E, Whitwam RE, Onwueme KC, Ruppen M. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2000;6:1841–1879. doi: 10.2174/1381612003398564. Galm U, Hager MH, Van Lanen SG, Ju J, Thorson JS, Shen B. Chem. Rev. 2005;105:739–758. doi: 10.1021/cr030117g. Van Lanen SG, Shen B. Curr. Topics Med. Chem. 2008;8:448–459. doi: 10.2174/156802608783955656.
- 2.(a) Zein N, Sinha AM, McGahren WJ, Ellestad GA. Science. 1988;240:1198–1201. doi: 10.1126/science.3240341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (b) Zein N, McGahren WJ, Morton GO, Ashcroft J, Ellestad GA. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1989;111:6888–6890. [Google Scholar]; (c) Zein N, Poncin M, Nilakantan R, Ellestad GA. Science. 1989;244:697–699. doi: 10.1126/science.2717946. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (d) DeVoss JJ, Townsend CA, Ding W-D, Morton GO, Ellestad GA, Zein N, Tabor AB, Schreiber SL. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1990;112:9669–9670. [Google Scholar]
- 3.(a) Walker S, Murnick J, Kahne D. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1993;115:7954–7961. [Google Scholar]; (b) Paloma LG, Smith JA, Chazin WJ, Nicolaou KC. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1994;116:3697–3708. [Google Scholar]; (c) Ikemoto N, Kumar RA, Ling TT, Ellestad GA, Danishefsky SJ, Patel DJ. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 1995;92:10506–10510. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.23.10506. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (d) Kumar RA, Ikemoto N, Patel DJ. J. Mol. Biol. 1997;265:187–201. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1996.0718. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.For reviews see Wu AM, Senter PD. Nat. Biotechnol. 2005;23:1137–1146. doi: 10.1038/nbt1141. Pui CH, Jeha S. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2007;6:149–165. doi: 10.1038/nrd2240. Jurcic JG. Cytotherapy. 2008;10:7–12. doi: 10.1080/14653240701519012.
- 5.Liu W, Christenson SD, Standage S, Shen B. Science. 2002;297:1170–1173. doi: 10.1126/science.1072110. Ahlert J, Shepard E, Lomovskaya N, Zazopoulos E, Staffa A, Bachmann BO, Huang K, Fonstein L, Czisny A, Whitwam RE, Farnet CM, Thorson JS. Science. 2002;297:1173–1176. doi: 10.1126/science.1072105. Gao Q, Thorson JS. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2008;282:105–114. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.2008.01112.x. Ahlert J, Shepard EM, Thorson JS. Van Lanen SG, Oh T-J, Liu W, Wendt-Pienkowski E, Shen B. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007;129:13082–13094. doi: 10.1021/ja073275o. Liu W, Nonaka K, Nie L, Zhang J, Christenson SD, Bae J, Van Lanen SG, Zazopoulos E, Farnet CM, Yang CF, Shen B. Chem. Biol. 2005;12:293–302. doi: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2004.12.013. Zazopoulos E, Huang K, Staffa A, Liu W, Bachmann BO, Nonaka K, Ahlert J, Thorson JS, Shen B. Nat. Biotechnol. 2003;21:187–190. doi: 10.1038/nbt784. Liu W, Ahlert J, Gao Q, Wendt-Pienkowski E, Shen B, Thorson JS. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA. 2003;100:11959–11963. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2034291100.
- 6.Zhang J, Van Lanen SG, Ju J, Liu W, Dorrestein PC, Li W, Kelleher NL, Shen B. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2008;105:1460–1465. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0711625105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.(a) Biggins JB, Onwueme KC, Thorson JS. Science. 2003;301:1537–1541. doi: 10.1126/science.1086695. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (b) Singh S, Hager MH, Zhang C, Griffith BR, Lee MS, Hallenga K, Markley JL, Thorson JS. ACS Chem. Biol. 2006;1:451–460. doi: 10.1021/cb6002898. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.(a) Zhang C, Griffith BR, Fu Q, Albermann C, Fu X, Lee I-K, Li L, Thorson JS. Science. 2006;313:1291–1294. doi: 10.1126/science.1130028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (b) Zhang C, Bitto E, Goff RD, Singh S, Bingman CA, Griffith BR, Albermann C, Phillips GN, Jr, Thorson JS. Chem. Biol. 2008;15:842–853. doi: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2008.06.011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.For reviews see Nedal A, Zotchev SB. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2004;64:7–15. doi: 10.1007/s00253-003-1535-9. Rupprath C, Schumacher T, Elling L. Curr. Med. Chem. 2005;12:1637–1675. doi: 10.2174/0929867054367167. Thibodeaux CJ, Melançon CE, Liu H-w. Nature. 2007;446:1008–1016. doi: 10.1038/nature05814. Salas JA, Méndez C. Trends Microbiol. 2007;15:219–232. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2007.03.004. Kren V, Řezanka T. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2008;32:858–889. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6976.2008.00124.x.
- 10.For a review see - Timmons SC, Thorson JS. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2008;12:297–305. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpa.2008.03.017.
- 11.(a) Song JK, Oh TJ, Lee JJ, Kim CG. Mol. Cells. 1997;7:674–681. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (b) Lamichhane J, Liou K, Lee HC, Kim C-G, Sohng JK. Biotechnol. Lett. 2006;28:545–553. doi: 10.1007/s10529-006-0013-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (c) Zhang H, White-Phillip JA, Melançon CE, Kwon H.-j., Yu W.-l., Liu H.-w. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007;129:14670–14683. doi: 10.1021/ja0744854. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (d) Fang J, Zhang Y, Huang L, Jia X, Zhang Q, Zhang X, Tang G, Liu W. J. Bacteriol. 2008;190:6014–6025. doi: 10.1128/JB.00533-08. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.(a) Sánchez C, Butovich IA, Brana AF, Rohr J, Méndez C, Salas JA. Chem. Biol. 2002;9:519–531. doi: 10.1016/s1074-5521(02)00126-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (b) Hyun C-G, Bililign T, Liao J, Thorson JS. ChemBioChem. 2003;4:114–117. doi: 10.1002/cbic.200390004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (c) Gao Q, Zhang C, Blanchard S, Thorson JS. Chem. Biol. 2006;13:733–743. doi: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2006.05.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (d) Sánchez C, Méndez C, Salas JA. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2006;23:1007–1045. doi: 10.1039/b601930g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.(a) Gaisser S, Trefzer A, Stockert S, Kirschning A, Bechthold A. J. Bacteriol. 1997;179:6271–6278. doi: 10.1128/jb.179.20.6271-6278.1997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (b) Jia XY, Tian ZH, Shao L, Qu XD, Zhao QF, Tang J, Tang GL, Liu W. Chem. Biol. 2006;13:575–585. doi: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2006.03.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (c) Shao L, Qu XD, Jia XY, Zhao QF, Tian ZH, Wang M, Tang GL, Liu W. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2006;345:133–139. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2006.04.069. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Kelly WL, Townsend CA. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002;124:8186–8187. doi: 10.1021/ja025926g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.McCoy JG, Johnson HD, Singh S, Bingman CA, Lei I-K, Thorson JS, Phillips GN., Jr. Proteins. 2008 doi: 10.1002/prot.22131. in press. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.(a) Jiang J, Biggins JB, Thorson JS. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2000;122:6803–6804. [Google Scholar]; (b) Jiang J, Biggins JB, Thorson JS. Angew. Chem. Intl. Ed. 2001;40:1502–1505. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (c) Albermann C, Jiang J, Thorson JS. ChemBioChem. 2003;4:443–446. doi: 10.1002/cbic.200200566. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (d) Fu X, Albermann C, Jiang J, Liao J, Zhang C, Thorson JS. Nat. Biotechnol. 2003;21:1467–1469. doi: 10.1038/nbt909. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.(a) Lambalot RH, Cane DE, Aparicio JJ, Katz L. Biochemistry. 1995;34:1858–1866. doi: 10.1021/bi00006a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (b) Xue Y, Wilson D, Zhao L, Liu H.-w., Sherman DH. Chem. Biol. 1998;5:661–667. doi: 10.1016/s1074-5521(98)90293-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (c) Walczak RJ, Hines JV, Strohl WR, Priestley ND. Org. Lett. 2001;3:2277–2279. doi: 10.1021/ol015998x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (d) Davydov DR, Botchkareva AE, Kumar S, He YQ, Halpert JR. Biochemistry. 2004;43:6475–6485. doi: 10.1021/bi036260l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (e) Ogura H, Nishida CR, Hoch UR, Perera R, Dawson JH, Ortiz de Montellano PR. Biochemistry. 2004;43:14712–14721. doi: 10.1021/bi048980d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (f) Lawson RJ, Leys D, Sutcliffe MJ, Kemp CA, Cheesman MR, Smith SJ, Clarkson J, Smith WE, Haq I, Perkins JB, Munro AW. Biochemistry. 2004;43:12410–12426. doi: 10.1021/bi049132l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (g) Mendes MV, Anton N, Martin JF, Aparicio JA. Biochem. J. 2005;386:57–62. doi: 10.1042/BJ20040490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.(a) Kahn RA, Bak S, Svendsen I, Halkier BA, Moller BL. Plant Physiol. 1997;115:1661–1670. doi: 10.1104/pp.115.4.1661. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (b) Kahn RA, Fahrendorf T, Halkier BA, Moller BL. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1999;363:9–18. doi: 10.1006/abbi.1998.1068. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (c) Bak S, Feyereisen R. Plant Physiol. 2001;127:108–118. doi: 10.1104/pp.127.1.108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.


