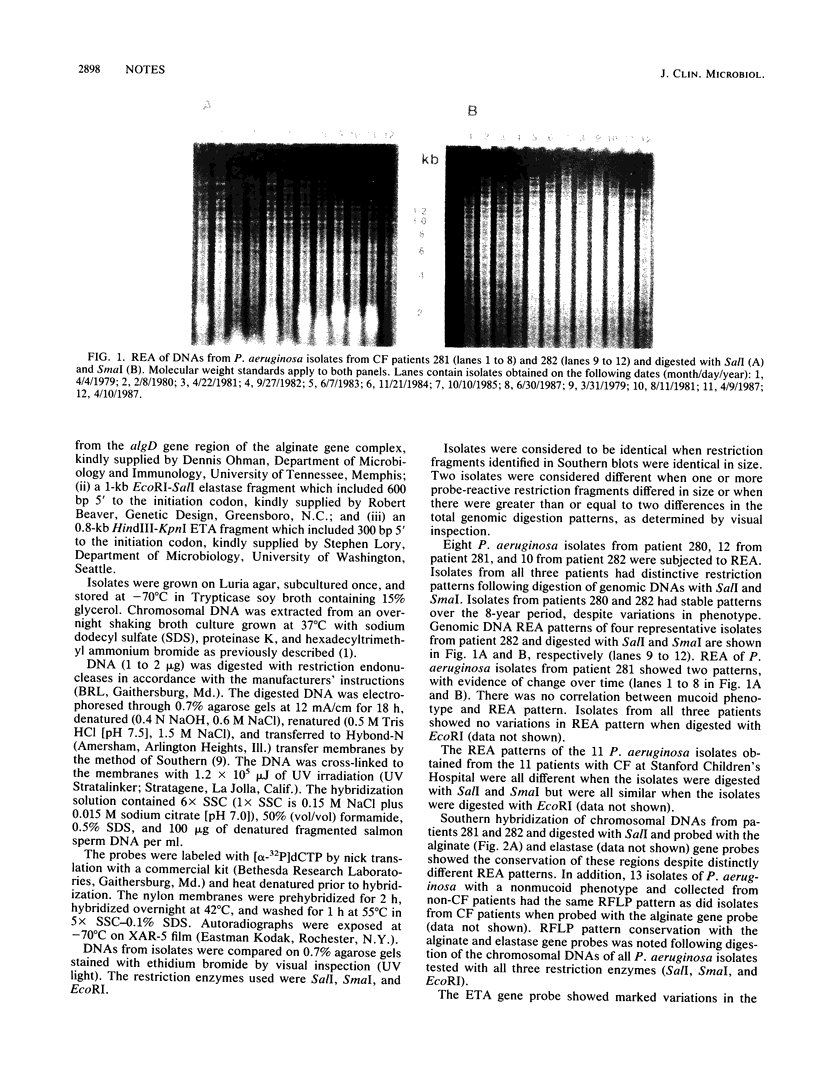
Abstract
Conventional typing schemes for Pseudomonas aeruginosa may not discriminate strains. P. aeruginosa isolates from patients with cystic fibrosis were examined by restriction enzyme analysis and Southern hybridization. There was marked diversity of restriction enzyme analysis patterns among P. aeruginosa DNAs from cystic fibrosis isolates; however, sequential isolates obtained from individual patients showed very little variation over an 8-year period. DNA fragments from the alginate biosynthesis gene complex, the exotoxin A gene, and the elastase gene of P. aeruginosa were used in Southern hybridization analysis. The patterns of hybridization to the elastase and algD gene probes were highly conserved in all isolates, therefore, these DNA fragments are not useful in discriminating strains, in contrast to the exotoxin A gene probe.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Grothues D., Koopmann U., von der Hardt H., Tümmler B. Genome fingerprinting of Pseudomonas aeruginosa indicates colonization of cystic fibrosis siblings with closely related strains. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Oct;26(10):1973–1977. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.10.1973-1977.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock R. E., Mutharia L. M., Chan L., Darveau R. P., Speert D. P., Pier G. B. Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates from patients with cystic fibrosis: a class of serum-sensitive, nontypable strains deficient in lipopolysaccharide O side chains. Infect Immun. 1983 Oct;42(1):170–177. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.1.170-177.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kharazmi A. Interactions of Pseudomonas aeruginosa proteases with the cells of the immune system. Antibiot Chemother (1971) 1989;42:42–49. doi: 10.1159/000417602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LiPuma J. J., Dasen S. E., Nielson D. W., Stern R. C., Stull T. L. Person-to-person transmission of Pseudomonas cepacia between patients with cystic fibrosis. Lancet. 1990 Nov 3;336(8723):1094–1096. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)92571-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samadpour M., Moseley S. L., Lory S. Biotinylated DNA probes for exotoxin A and pilin genes in the differentiation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Nov;26(11):2319–2323. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.11.2319-2323.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speert D. P., Campbell M. E., Farmer S. W., Volpel K., Joffe A. M., Paranchych W. Use of a pilin gene probe to study molecular epidemiology of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Nov;27(11):2589–2593. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.11.2589-2593.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tümmler B., Koopmann U., Grothues D., Weissbrodt H., Steinkamp G., von der Hardt H. Nosocomial acquisition of Pseudomonas aeruginosa by cystic fibrosis patients. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Jun;29(6):1265–1267. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.6.1265-1267.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolz C., Kiosz G., Ogle J. W., Vasil M. L., Schaad U., Botzenhart K., Döring G. Pseudomonas aeruginosa cross-colonization and persistence in patients with cystic fibrosis. Use of a DNA probe. Epidemiol Infect. 1989 Apr;102(2):205–214. doi: 10.1017/s0950268800029873. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Worlitzsch D., Wolz C., Botzenhart K., Hansis M., Burgdörfer H., Ogle J. W., Döring G. Molecular epidemiology of Pseudomonas aeruginosa--urinary tract infections in paraplegic patients. Zentralbl Hyg Umweltmed. 1989 Nov;189(2):175–184. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





