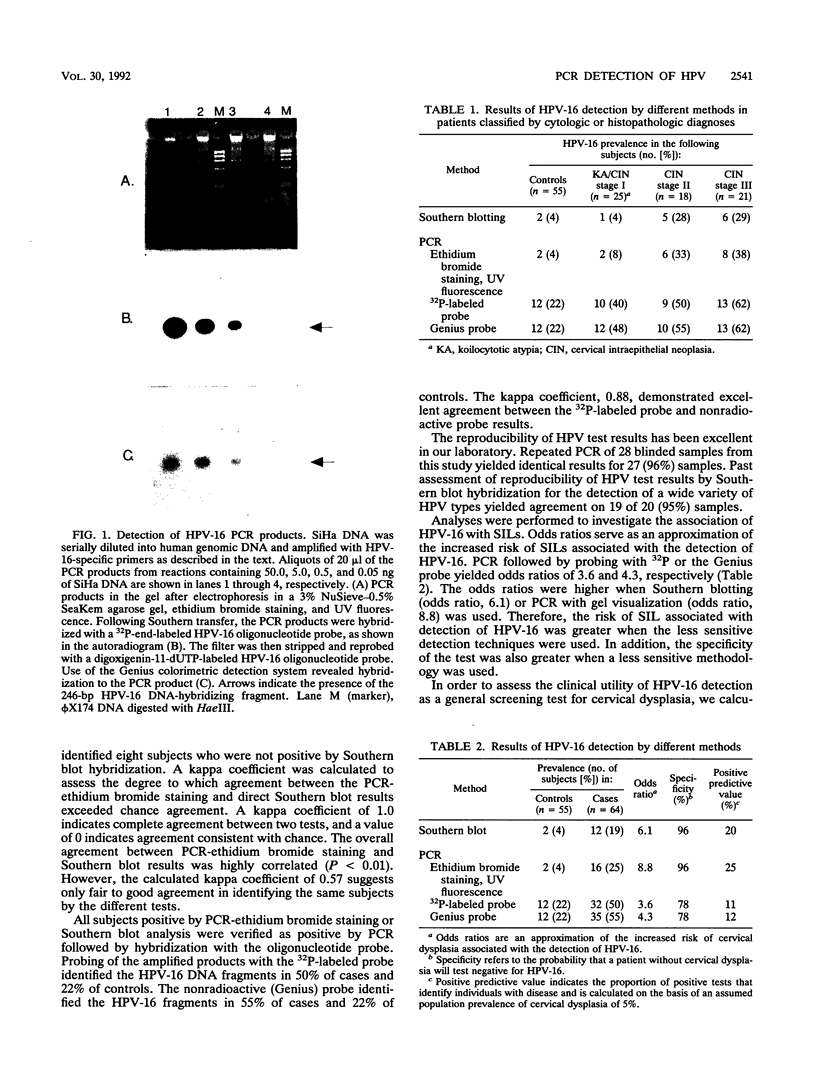
Abstract
A case-control study compared detection by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) specific for human papillomavirus (HPV) type 16 with restriction enzyme analysis and Southern blot hybridization detection of HPV type 16. Cervicovaginal lavage samples from 64 women with histopathologic evidence of a cervical squamous intraepithelial lesion and 55 samples from cytologically healthy women were studied. Several methods of PCR product analysis, including radioactive and nonradioactive probing, were compared. The sensitivity of HPV detection by PCR when the amplified DNA fragment was visualized on a gel was equivalent to those of detection by restriction enzyme and Southern blot analyses. Hybridization of the PCR product with radioactively or nonradioactively labeled oligonucleotide probes increased the sensitivity of HPV detection by 100-fold. However, an increase in the sensitivity of the assay preferentially identified low levels of the virus in cytologically healthy women. Therefore, the value of HPV detection in identifying women with cervical neoplastic disease was greater, and the odds ratio for the presence of a cervical squamous intraepithelial lesion was higher when the less sensitive modalities were used. These results suggest that quantitation of HPV by PCR may maximize the clinical significance of a positive test result. Further studies will be needed to determine the optimal level of virus detection which has the highest positive predictive value of clinical disease.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bauer H. M., Ting Y., Greer C. E., Chambers J. C., Tashiro C. J., Chimera J., Reingold A., Manos M. M. Genital human papillomavirus infection in female university students as determined by a PCR-based method. JAMA. 1991 Jan 23;265(4):472–477. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burmer G. C., Parker J. D., Bates J., East K., Kulander B. G. Comparative analysis of human papillomavirus detection by polymerase chain reaction and Virapap/Viratype kits. Am J Clin Pathol. 1990 Nov;94(5):554–560. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/94.5.554. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dürst M., Gissmann L., Ikenberg H., zur Hausen H. A papillomavirus DNA from a cervical carcinoma and its prevalence in cancer biopsy samples from different geographic regions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(12):3812–3815. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.12.3812. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franco E. L. The sexually transmitted disease model for cervical cancer: incoherent epidemiologic findings and the role of misclassification of human papillomavirus infection. Epidemiology. 1991 Mar;2(2):98–106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg G. L., Vermund S. H., Schiffman M. H., Ritter D. B., Spitzer C., Burk R. D. Comparison of Cytobrush and cervicovaginal lavage sampling methods for the detection of genital human papillomavirus. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1989 Dec;161(6 Pt 1):1669–1672. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(89)90947-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kellogg D. E., Sninsky J. J., Kwok S. Quantitation of HIV-1 proviral DNA relative to cellular DNA by the polymerase chain reaction. Anal Biochem. 1990 Sep;189(2):202–208. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(90)90108-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison E. A., Ho G. Y., Vermund S. H., Goldberg G. L., Kadish A. S., Kelley K. F., Burk R. D. Human papillomavirus infection and other risk factors for cervical neoplasia: a case-control study. Int J Cancer. 1991 Aug 19;49(1):6–13. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910490103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeves W. C., Brinton L. A., García M., Brenes M. M., Herrero R., Gaitán E., Tenorio F., de Britton R. C., Rawls W. E. Human papillomavirus infection and cervical cancer in Latin America. N Engl J Med. 1989 Jun 1;320(22):1437–1441. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198906013202201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roman A., Fife K. H. Human papillomaviruses: are we ready to type? Clin Microbiol Rev. 1989 Apr;2(2):166–190. doi: 10.1128/cmr.2.2.166. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiffman M. H., Bauer H. M., Lorincz A. T., Manos M. M., Byrne J. C., Glass A. G., Cadell D. M., Howley P. M. Comparison of Southern blot hybridization and polymerase chain reaction methods for the detection of human papillomavirus DNA. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Mar;29(3):573–577. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.3.573-577.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shibata D. K., Arnheim N., Martin W. J. Detection of human papilloma virus in paraffin-embedded tissue using the polymerase chain reaction. J Exp Med. 1988 Jan 1;167(1):225–230. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.1.225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young L. S., Bevan I. S., Johnson M. A., Blomfield P. I., Bromidge T., Maitland N. J., Woodman C. B. The polymerase chain reaction: a new epidemiological tool for investigating cervical human papillomavirus infection. BMJ. 1989 Jan 7;298(6665):14–18. doi: 10.1136/bmj.298.6665.14. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- el Awady M. K., Kaplan J. B., O'Brien S. J., Burk R. D. Molecular analysis of integrated human papillomavirus 16 sequences in the cervical cancer cell line SiHa. Virology. 1987 Aug;159(2):389–398. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90478-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]