Abstract
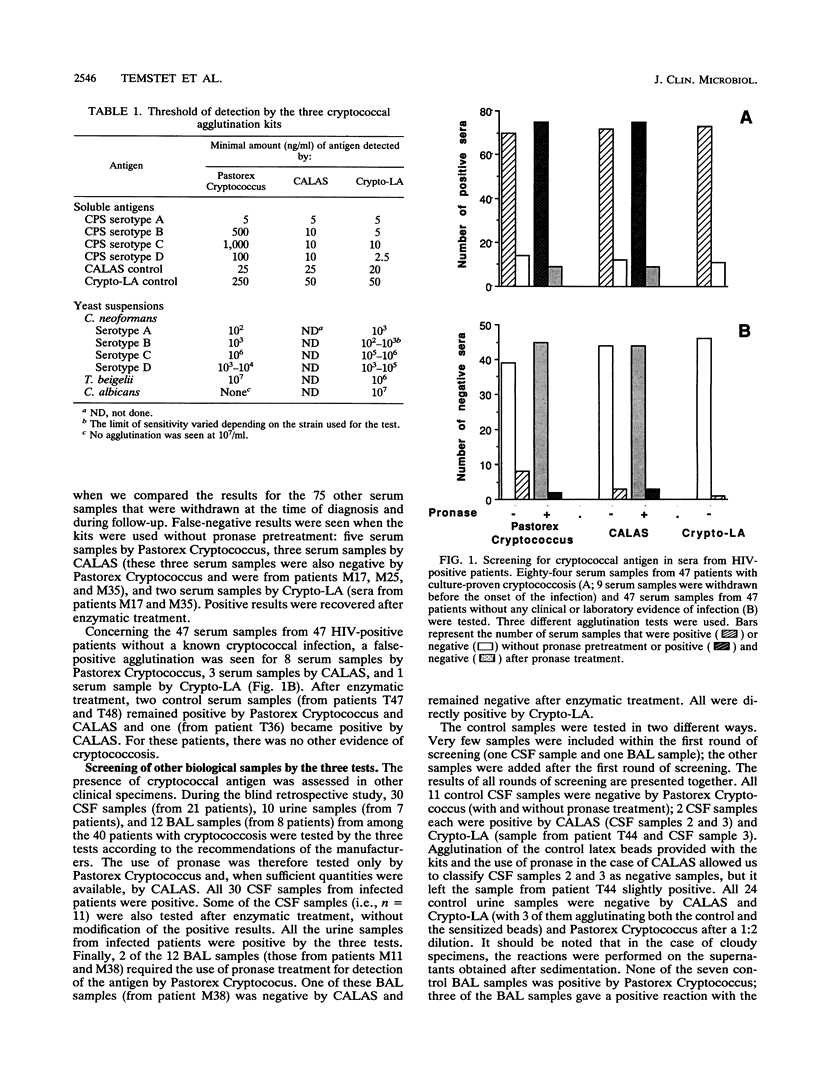
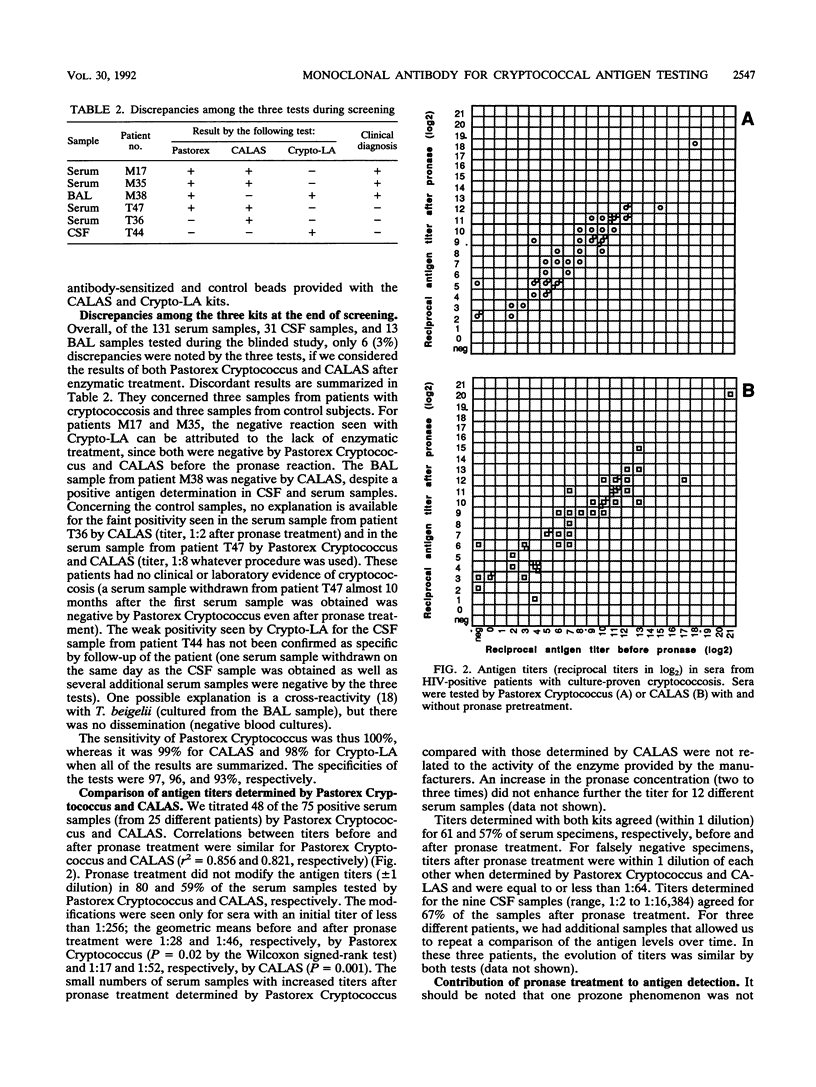
Cryptococcal antigen detection has become a routine biological test performed for patients with AIDS. The poor prognosis of cryptococcosis explains the need for reliable tests. We evaluated the performances of a newly commercialized agglutination test that uses a monoclonal antibody specific for cryptococcal capsular polysaccharide (Pastorex Cryptococcus; Sanofi-Diagnostics Pasteur, Marnes-la-Coquette, France) and compared them with those of tests that use polyclonal immune sera (Cryptococcal Antigen Latex Agglutination System, Meridian Diagnostics, Inc., Cincinnati, Ohio; and Crypto-LA, International Biological Labs Inc., Cranbury, N.J.). The sensitivities and specificities of the tests were compared by using purified polysaccharides and yeast suspensions. Clinical specimens (131 serum samples, 41 cerebrospinal fluid samples, 34 urine samples, and 19 bronchoalveolar lavage samples) from 87 human immunodeficiency virus-positive subjects with (40 patients) and without (47 patients) culture-proven cryptococcosis were retrospectively tested during a blinded study. The effect of pronase treatment of samples was assessed for Pastorex Cryptococcus and the Cryptococcal Antigen Latex Agglutination System, and the antigen titers were compared. Our results show that (i) during the screening, concordance among the three tests was 97%; (ii) the use of pronase enhanced both the sensitivities and specificities of the Pastorex Cryptococcus test; (iii) titers agreed for 67% of the cerebrospinal fluid samples and 60% of the serum samples; and (iv) cryptococcosis was detected equally well with Pastorex Cryptococcus and with the other tests, whatever the infecting serotype (A, B, or D). The meaning of in vitro sensitivity and the relationship between titers and sensitivity are discussed. The results show that Pastorex Cryptococcus is a rapid and reliable test for the detection of cryptococcal antigen in body fluids and suggest that kits cannot be used interchangeably to monitor antigen titers in patients.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bottone E. J., Kirschner P. A., Salkin I. F. Isolation of highly encapsulated Cryptococcus neoformans serotype B from a patient in New York City. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Jan;23(1):186–188. doi: 10.1128/jcm.23.1.186-188.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bottone E. J., Salkin I. F., Hurd N. J., Wormser G. P. Serogroup distribution of Cryptococcus neoformans in patients with AIDS. J Infect Dis. 1987 Jul;156(1):242–242. doi: 10.1093/infdis/156.1.242. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cameron M. L., Bartlett J. A., Gallis H. A., Waskin H. A. Manifestations of pulmonary cryptococcosis in patients with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Rev Infect Dis. 1991 Jan-Feb;13(1):64–67. doi: 10.1093/clinids/13.1.64. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chuck S. L., Sande M. A. Infections with Cryptococcus neoformans in the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1989 Sep 21;321(12):794–799. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198909213211205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clancy M. N., Fleischmann J., Howard D. H., Kwon-Chung K. J., Shimizu R. Y. Isolation of Cryptococcus neoformans gattii from a patient with AIDS in southern California. J Infect Dis. 1990 Apr;161(4):809–809. doi: 10.1093/infdis/161.4.809. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dismukes W. E. Cryptococcal meningitis in patients with AIDS. J Infect Dis. 1988 Apr;157(4):624–628. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.4.624. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dromer F., Salamero J., Contrepois A., Carbon C., Yeni P. Production, characterization, and antibody specificity of a mouse monoclonal antibody reactive with Cryptococcus neoformans capsular polysaccharide. Infect Immun. 1987 Mar;55(3):742–748. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.3.742-748.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gade W., Hinnefeld S. W., Babcock L. S., Gilligan P., Kelly W., Wait K., Greer D., Pinilla M., Kaplan R. L. Comparison of the PREMIER cryptococcal antigen enzyme immunoassay and the latex agglutination assay for detection of cryptococcal antigens. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Aug;29(8):1616–1619. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.8.1616-1619.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray L. D., Roberts G. D. Experience with the use of pronase to eliminate interference factors in the latex agglutination test for cryptococcal antigen. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Nov;26(11):2450–2451. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.11.2450-2451.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haldane D. J., Bauman D. S., Chow A. W., Doyle P., Garber G., Ngui-Yen J., Smith J. A. False negative latex agglutination test in cryptococcal meningitis. Ann Neurol. 1986 Apr;19(4):412–413. doi: 10.1002/ana.410190424. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton J. R., Noble A., Denning D. W., Stevens D. A. Performance of cryptococcus antigen latex agglutination kits on serum and cerebrospinal fluid specimens of AIDS patients before and after pronase treatment. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Feb;29(2):333–339. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.2.333-339.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikeda R., Shinoda T., Fukazawa Y., Kaufman L. Antigenic characterization of Cryptococcus neoformans serotypes and its application to serotyping of clinical isolates. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Jul;16(1):22–29. doi: 10.1128/jcm.16.1.22-29.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapend'a K., Komichelo K., Swinne D., Vandepitte J. Meningitis due to Cryptococcus neoformans biovar gattii in a Zairean AIDS patient. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Jun;6(3):320–321. doi: 10.1007/BF02017627. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kauffman C. A., Bergman A. G., Severance P. J., McClatchey K. D. Detection of cryptococcal antigen. Comparison of two latex agglutination tests. Am J Clin Pathol. 1981 Jan;75(1):106–109. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/75.1.106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwon-Chung K. J., Bennett J. E. Epidemiologic differences between the two varieties of Cryptococcus neoformans. Am J Epidemiol. 1984 Jul;120(1):123–130. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a113861. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levitz S. M. The ecology of Cryptococcus neoformans and the epidemiology of cryptococcosis. Rev Infect Dis. 1991 Nov-Dec;13(6):1163–1169. doi: 10.1093/clinids/13.6.1163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rinaldi M. G., Drutz D. J., Howell A., Sande M. A., Wofsy C. B., Hadley W. K. Serotypes of Cryptococcus neoformans in patients with AIDS. J Infect Dis. 1986 Mar;153(3):642–642. doi: 10.1093/infdis/153.3.642. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roux P., Touboul J. L., de Chauvin M. F., Delacour T., Revuz J., Basset D., Mayaud C., Lancastre F. Disseminated cryptococcosis diagnosed in AIDS patient by screening for soluble serum antigens. Lancet. 1986 May 17;1(8490):1154–1154. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)91866-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozenbaum R., Gonçalves A. J., Wanke B., Vieira W. Cryptococcus neoformans var. gattii in a Brazilian AIDS patients. Mycopathologia. 1990 Oct;112(1):33–34. doi: 10.1007/BF01795177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu R. Y., Howard D. H., Clancy M. N. The variety of Cryptococcus neoformans in patients with AIDS. J Infect Dis. 1986 Dec;154(6):1042–1042. doi: 10.1093/infdis/154.6.1042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St-Germain G., Noël G., Chung K. J. Disseminated cryptococcosis due to Cryptococcus neoformans variety gattii in a Canadian patient with AIDS. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1988 Aug;7(4):587–588. doi: 10.1007/BF01962626. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu T. C., Koo S. Y. Comparison of three commercial cryptococcal latex kits for detection of cryptococcal antigen. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Nov;18(5):1127–1130. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.5.1127-1130.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


