Abstract
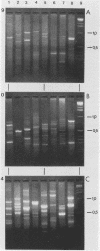
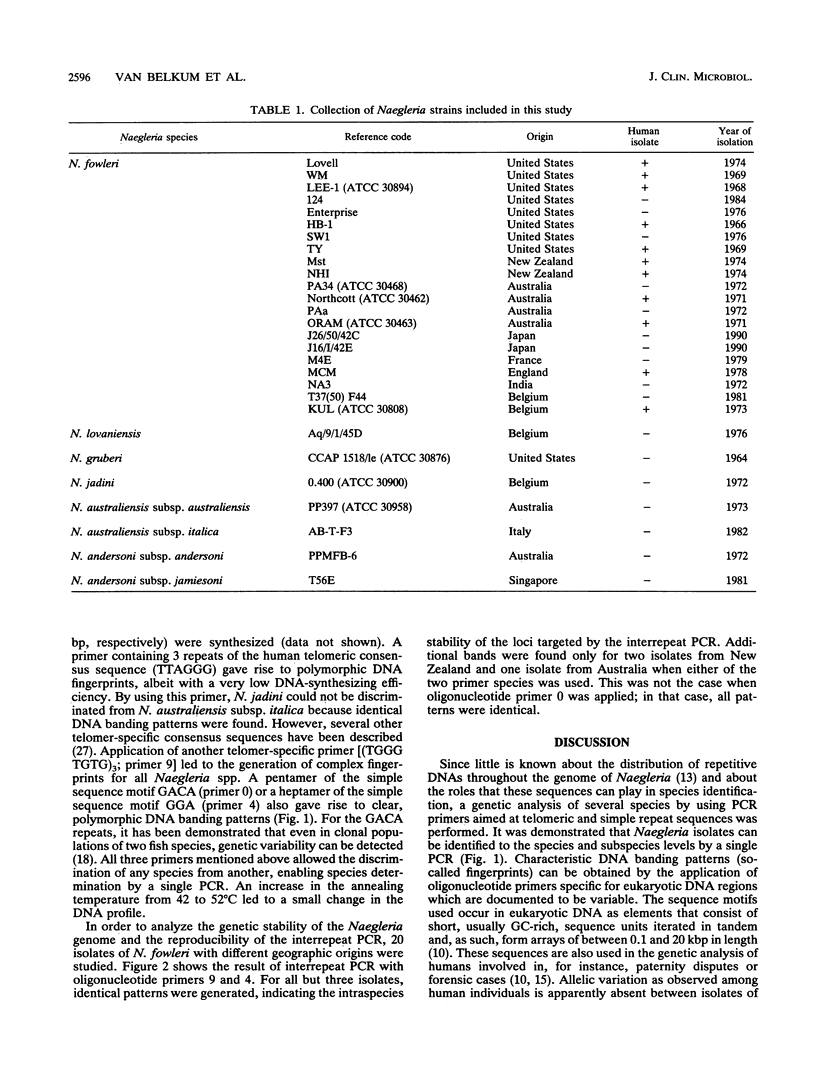
All six Naegleria species recognized to date were studied by interrepeat polymerase chain reaction (PCR). Priming at repeat sequences, which are known to be variable among eukaryotes, yielded electrophoretic DNA banding patterns that were specific for any single species. With a single PCR and simple gel electrophoresis, species determination could be performed in less than 1 day. Unambiguous discrimination between the pathogen N. fowleri and nonpathogenic Naegleria species appeared to be possible. Analysis of DNAs obtained from 20 separate isolates of N. fowleri revealed that geographic variation of the genetic fingerprints rarely occurs. All but 3 of 20 isolates of N. fowleri which were investigated showed identical banding patterns; for two isolates from New Zealand and one from Australia, a limited number of additional bands was detected, independent of the PCR primers used. These data corroborate previous findings on the genetic stability of pathogenic N. fowleri.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bogler S. A., Zarley C. D., Burianek L. L., Fuerst P. A., Byers T. J. Interstrain mitochondrial DNA polymorphism detected in Acanthamoeba by restriction endonuclease analysis. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1983 Jun;8(2):145–163. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(83)90006-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Jonckheere J. F. Characterization of Naegleria species by restriction endonuclease digestion of whole-cell DNA. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1987 May;24(1):55–66. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(87)90115-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Jonckheere J. F. Geographic origin and spread of pathogenic Naegleria fowleri deduced from restriction enzyme patterns of repeated DNA. Biosystems. 1988;21(3-4):269–275. doi: 10.1016/0303-2647(88)90022-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Jonckheere J. Differences in virulence of Naegleria fowleri. Pathol Biol (Paris) 1979 Oct;27(8):453–458. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erlich H. A., Gelfand D., Sninsky J. J. Recent advances in the polymerase chain reaction. Science. 1991 Jun 21;252(5013):1643–1651. doi: 10.1126/science.2047872. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunderson J. H., Sogin M. L. Length variation in eukaryotic rRNAs: small subunit rRNAs from the protists Acanthamoeba castellanii and Euglena gracilis. Gene. 1986;44(1):63–70. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90043-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeffreys A. J., Wilson V., Thein S. L. Hypervariable 'minisatellite' regions in human DNA. Nature. 1985 Mar 7;314(6006):67–73. doi: 10.1038/314067a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLaughlin G. L., Brandt F. H., Visvesvara G. S. Restriction fragment length polymorphisms of the DNA of selected Naegleria and Acanthamoeba amebae. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Sep;26(9):1655–1658. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.9.1655-1658.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLaughlin G. L., Vodkin M. H., Huizinga H. W. Amplification of repetitive DNA for the specific detection of Naegleria fowleri. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Feb;29(2):227–230. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.2.227-230.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milligan S. M., Band R. N. Restriction endonuclease analysis of mitochondrial DNA as an aid in the taxonomy of Naegleria and Vahlkampfia. J Protozool. 1988 May;35(2):198–204. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1988.tb04323.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura Y., Leppert M., O'Connell P., Wolff R., Holm T., Culver M., Martin C., Fujimoto E., Hoff M., Kumlin E. Variable number of tandem repeat (VNTR) markers for human gene mapping. Science. 1987 Mar 27;235(4796):1616–1622. doi: 10.1126/science.3029872. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riley D. E., Samadpour M., Krieger J. N. Detection of variable DNA repeats in diverse eukaryotic microorganisms by a single set of polymerase chain reaction primers. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Dec;29(12):2746–2751. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.12.2746-2751.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seidel J. S., Harmatz P., Visvesvara G. S., Cohen A., Edwards J., Turner J. Successful treatment of primary amebic meningoencephalitis. N Engl J Med. 1982 Feb 11;306(6):346–348. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198202113060607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner B. J., Elder J. F., Jr, Laughlin T. F., Davis W. P. Genetic variation in clonal vertebrates detected by simple-sequence DNA fingerprinting. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(15):5653–5657. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.15.5653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uitterlinden A. G., Slagboom P. E., Johnson T. E., Vijg J. The Caenorhabditis elegans genome contains monomorphic minisatellites and simple sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Dec 11;17(23):9527–9530. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.23.9527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Upcroft P., Mitchell R., Boreham P. F. DNA fingerprinting of the intestinal parasite Giardia duodenalis with the M13 phage genome. Int J Parasitol. 1990 May;20(3):319–323. doi: 10.1016/0020-7519(90)90146-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vodkin M. H., Howe D. K., Visvesvara G. S., McLaughlin G. L. Identification of Acanthamoeba at the generic and specific levels using the polymerase chain reaction. J Protozool. 1992 May-Jun;39(3):378–385. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1992.tb01467.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogt P. Potential genetic functions of tandem repeated DNA sequence blocks in the human genome are based on a highly conserved "chromatin folding code". Hum Genet. 1990 Mar;84(4):301–336. doi: 10.1007/BF00196228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welsh J., Petersen C., McClelland M. Polymorphisms generated by arbitrarily primed PCR in the mouse: application to strain identification and genetic mapping. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jan 25;19(2):303–306. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.2.303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zakian V. A. Structure and function of telomeres. Annu Rev Genet. 1989;23:579–604. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.23.120189.003051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Belkum A., Trommelen G., Uitterlinden A. Minisatellite-like repeat sequences in the genome of rodent malaria parasites. Acta Leiden. 1991;60(1):83–91. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]