Abstract
To evaluate the usefulness of phenotypic and genotypic analyses for the epidemiologic typing of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), we characterized 64 epidemic MRSA isolates and 10 sporadic methicillin-susceptible S. aureus isolates from a university hospital and 18 MRSA isolates from hospitals in different geographical areas. Chromosomal DNA macrorestriction analysis with SstII was resolved by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis and compared with antibiotype analysis, phage type analysis, and standard genomic DNA restriction analysis with BglII. Indices of the discriminatory ability of these methods were 0.982, 0.959, 0.947, and 0.959, respectively. Macrorestriction patterns of 94% of MRSA isolates from patients, personnel, and the environment associated with a nosocomial outbreak were closely related (similarity coefficient, 85 to 100%). In contrast, methicillin-susceptible S. aureus isolates showed a marked diversity of macrorestriction patterns (median similarity, 41%). MRSA isolates from other geographical areas showed diverse macrorestriction patterns, with the exception of four isolates displaying identical or closely related patterns; these isolates were associated with concurrent outbreaks in four other Belgian hospitals. A concordance of genomic DNA macrorestriction typing with phenotypic methods was observed for 60 to 65% of MRSA isolates, and a concordance with standard DNA restriction analysis was found for 79 to 98% of these isolates. In conclusion, genomic DNA macrorestriction analysis was a useful complement to phenotypic methods for delineating epidemic isolates of MRSA, for identifying their nosocomial reservoirs, and for tracing their intra- and interhospital spread. The genetic relatedness of MRSA isolates, as estimated by this technique, appeared to correlate with their space-time clustering.
Full text
PDF

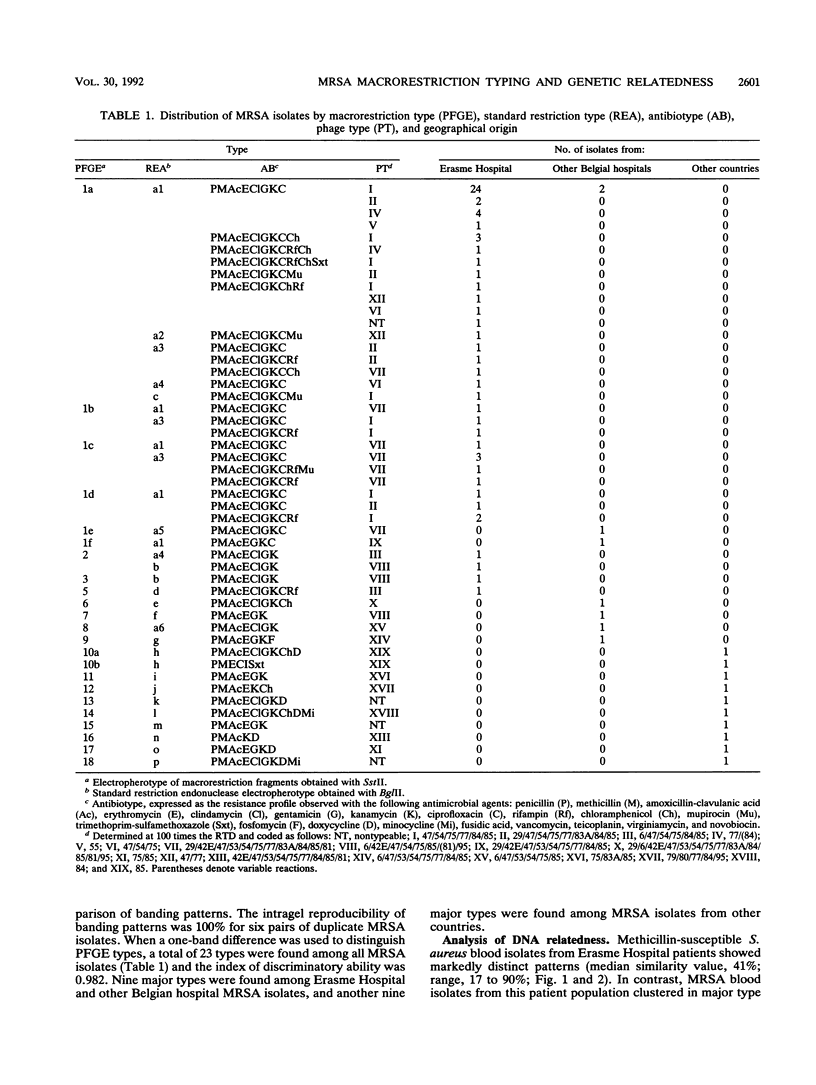
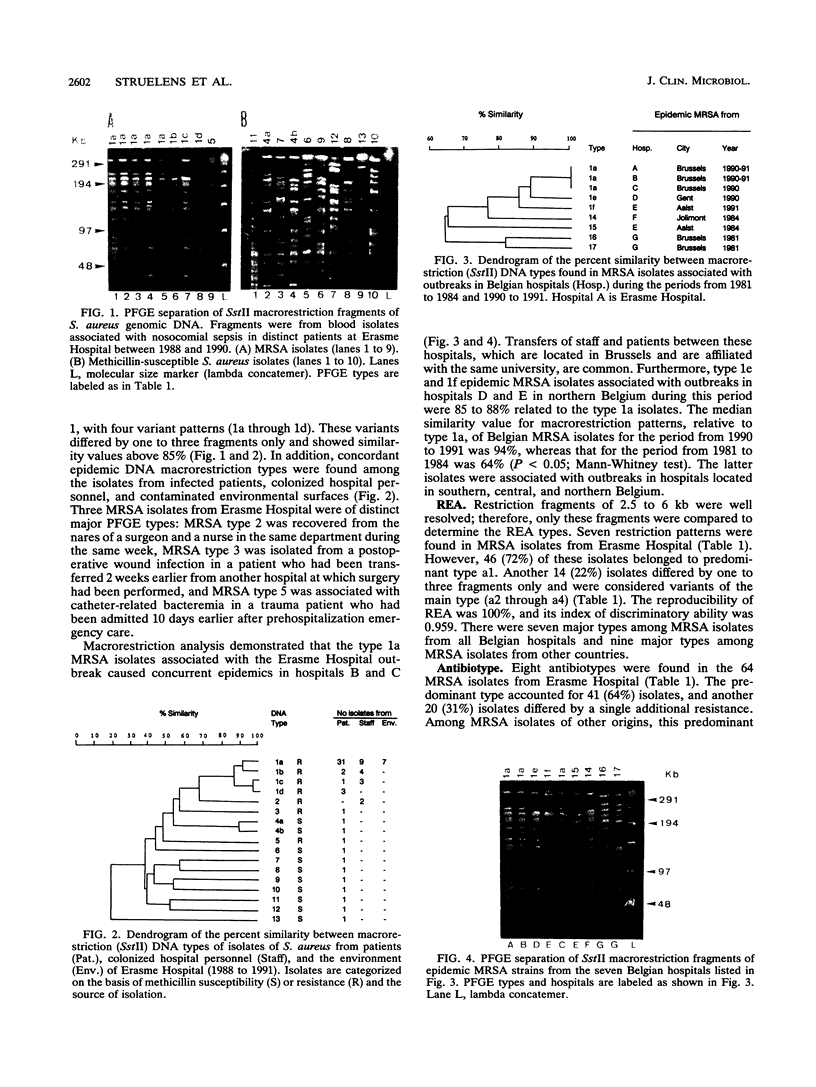



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arbeit R. D., Arthur M., Dunn R., Kim C., Selander R. K., Goldstein R. Resolution of recent evolutionary divergence among Escherichia coli from related lineages: the application of pulsed field electrophoresis to molecular epidemiology. J Infect Dis. 1990 Feb;161(2):230–235. doi: 10.1093/infdis/161.2.230. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bialkowska-Hobrzanska H., Jaskot D., Hammerberg O. Evaluation of restriction endonuclease fingerprinting of chromosomal DNA and plasmid profile analysis for characterization of multiresistant coagulase-negative staphylococci in bacteremic neonates. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Feb;28(2):269–275. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.2.269-275.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyce J. M. Increasing prevalence of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in the United States. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 1990 Dec;11(12):639–642. doi: 10.1086/646114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Branger C., Goullet P., Boutonnier A., Fournier J. M. Correlation between esterase electrophoretic types and capsular polysaccharide types 5 and 8 among methicillin-susceptible and methicillin-resistant strains of Staphylococcus aureus. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Jan;28(1):150–151. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.1.150-151.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cookson B. D., Phillips I. Epidemic methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1988 Apr;21 (Suppl 100):57–65. doi: 10.1093/jac/21.suppl_c.57. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cookson B., Talsania H., Naidoo J., Phillips I. Strategies for typing and properties of epidemic methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Dec;5(6):702–709. doi: 10.1007/BF02013309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costas M., Cookson B. D., Talsania H. G., Owen R. J. Numerical analysis of electrophoretic protein patterns of methicillin-resistant strains of Staphylococcus aureus. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Nov;27(11):2574–2581. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.11.2574-2581.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goering R. V., Duensing T. D. Rapid field inversion gel electrophoresis in combination with an rRNA gene probe in the epidemiological evaluation of staphylococci. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Mar;28(3):426–429. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.3.426-429.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grothues D., Koopmann U., von der Hardt H., Tümmler B. Genome fingerprinting of Pseudomonas aeruginosa indicates colonization of cystic fibrosis siblings with closely related strains. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Oct;26(10):1973–1977. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.10.1973-1977.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hadorn K., Lenz W., Kayser F. H., Shalit I., Krasemann C. Use of a ribosomal RNA gene probe for the epidemiological study of methicillin and ciprofloxacin resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1990 Sep;9(9):649–653. doi: 10.1007/BF01964265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall L. M., Jordens J. Z., Wang F. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus from China characterized by digestion of total DNA with restriction enzymes. Epidemiol Infect. 1989 Aug;103(1):183–192. doi: 10.1017/s095026880003048x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter P. R. Reproducibility and indices of discriminatory power of microbial typing methods. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Sep;28(9):1903–1905. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.9.1903-1905.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ichiyama S., Ohta M., Shimokata K., Kato N., Takeuchi J. Genomic DNA fingerprinting by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis as an epidemiological marker for study of nosocomial infections caused by methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Dec;29(12):2690–2695. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.12.2690-2695.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordens J. Z., Hall L. M. Characterisation of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolates by restriction endonuclease digestion of chromosomal DNA. J Med Microbiol. 1988 Oct;27(2):117–123. doi: 10.1099/00222615-27-2-117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li W. H. Simple method for constructing phylogenetic trees from distance matrices. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):1085–1089. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.1085. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monzon-Moreno C., Aubert S., Morvan A., Solh N. E. Usefulness of three probes in typing isolates of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). J Med Microbiol. 1991 Aug;35(2):80–88. doi: 10.1099/00222615-35-2-80. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulligan M. E., Arbeit R. D. Epidemiologic and clinical utility of typing systems for differentiating among strains of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 1991 Jan;12(1):20–28. doi: 10.1086/646234. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulvey M., Arbuthnott J. P., Coleman D. C. Molecular typing of methicillin and gentamicin resistant Staphylococcus aureus in Dublin. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Dec;5(6):719–725. doi: 10.1007/BF02013312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preheim L., Pitcher D., Owen R., Cookson B. Typing of methicillin resistant and susceptible Staphylococcus aureus strains by ribosomal RNA gene restriction patterns using a biotinylated probe. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1991 May;10(5):428–436. doi: 10.1007/BF01968023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prévost G., Pottecher B., Dahlet M., Bientz M., Mantz J. M., Piémont Y. Pulsed field gel electrophoresis as a new epidemiological tool for monitoring methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in an intensive care unit. J Hosp Infect. 1991 Apr;17(4):255–269. doi: 10.1016/0195-6701(91)90270-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struelens M. J., Maes N., Rost F., Deplano A., Jacobs F., Liesnard C., Bornstein N., Grimont F., Lauwers S., McIntyre M. P. Genotypic and phenotypic methods for the investigation of a nosocomial Legionella pneumophila outbreak and efficacy of control measures. J Infect Dis. 1992 Jul;166(1):22–30. doi: 10.1093/infdis/166.1.22. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van der Auwera P., Godard C., Denis C., De Maeyer S., Vanhoof R. In vitro activities of new antimicrobial agents against multiresistant Staphylococcus aureus isolated from septicemic patients during a Belgian national survey from 1983 to 1985. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Nov;34(11):2260–2262. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.11.2260. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wenzel R. P., Nettleman M. D., Jones R. N., Pfaller M. A. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: implications for the 1990s and effective control measures. Am J Med. 1991 Sep 16;91(3B):221S–227S. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(91)90372-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]