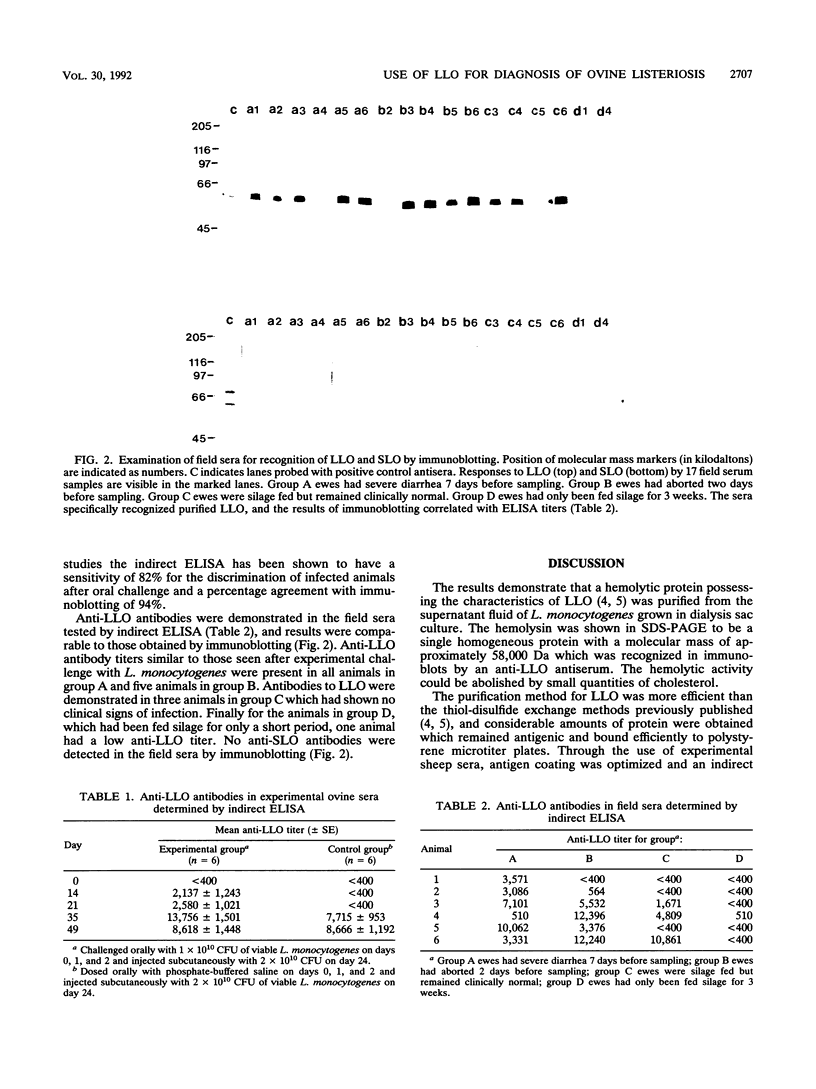
Abstract
A protein of 58,000-Da molecular mass was purified from the supernatant fluid of a dialysis sac culture of Listeria monocytogenes by cation-exchange chromatography. The purified protein, homogeneous by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and possessing the characteristics of listeriolysin O (LLO), was used to develop an indirect enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Anti-LLO antibodies were shown to be consistently produced in sheep after experimental challenge with L. monocytogenes serovar 4b. The assay also successfully detected and measured specific anti-LLO antibodies in the sera of silage-fed sheep among which listeric enteritis and abortions had occurred.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berche P., Reich K. A., Bonnichon M., Beretti J. L., Geoffroy C., Raveneau J., Cossart P., Gaillard J. L., Geslin P., Kreis H. Detection of anti-listeriolysin O for serodiagnosis of human listeriosis. Lancet. 1990 Mar 17;335(8690):624–627. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)90411-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geoffroy C., Gaillard J. L., Alouf J. E., Berche P. Purification, characterization, and toxicity of the sulfhydryl-activated hemolysin listeriolysin O from Listeria monocytogenes. Infect Immun. 1987 Jul;55(7):1641–1646. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.7.1641-1646.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreft J., Funke D., Haas A., Lottspeich F., Goebel W. Production, purification and characterization of hemolysins from Listeria ivanovii and Listeria monocytogenes Sv4b. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1989 Jan 15;48(2):197–202. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1989.tb03298.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low J. C., Donachie W. Clinical and serum antibody responses to lambs to infection by Listeria monocytogenes. Res Vet Sci. 1991 Sep;51(2):185–192. doi: 10.1016/0034-5288(91)90012-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low J. C., Renton C. P. Septicaemia, encephalitis and abortions in a housed flock of sheep caused by Listeria monocytogenes type 1/2. Vet Rec. 1985 Feb 9;116(6):147–150. doi: 10.1136/vr.116.6.147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mengaud J., Chenevert J., Geoffroy C., Gaillard J. L., Cossart P. Identification of the structural gene encoding the SH-activated hemolysin of Listeria monocytogenes: listeriolysin O is homologous to streptolysin O and pneumolysin. Infect Immun. 1987 Dec;55(12):3225–3227. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.12.3225-3227.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miettinen A., Husu J. Antibodies to listeriolysin O reflect the acquired resistance to Listeria monocytogenes in experimentally infected goats. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1991 Jan 15;61(2-3):181–186. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(91)90548-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrissey J. H. Silver stain for proteins in polyacrylamide gels: a modified procedure with enhanced uniform sensitivity. Anal Biochem. 1981 Nov 1;117(2):307–310. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90783-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nato F., Reich K., Lhopital S., Rouyre S., Geoffroy C., Mazie J. C., Cossart P. Production and characterization of neutralizing and nonneutralizing monoclonal antibodies against listeriolysin O. Infect Immun. 1991 Dec;59(12):4641–4646. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.12.4641-4646.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peel M., Donachie W., Shaw A. Temperature-dependent expression of flagella of Listeria monocytogenes studied by electron microscopy, SDS-PAGE and western blotting. J Gen Microbiol. 1988 Aug;134(8):2171–2178. doi: 10.1099/00221287-134-8-2171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutherland A. D. Effects of Pasteurella haemolytica cytotoxin on ovine peripheral blood leucocytes and lymphocytes obtained from gastric lymph. Vet Microbiol. 1985 Aug;10(5):431–438. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(85)90025-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]