Abstract
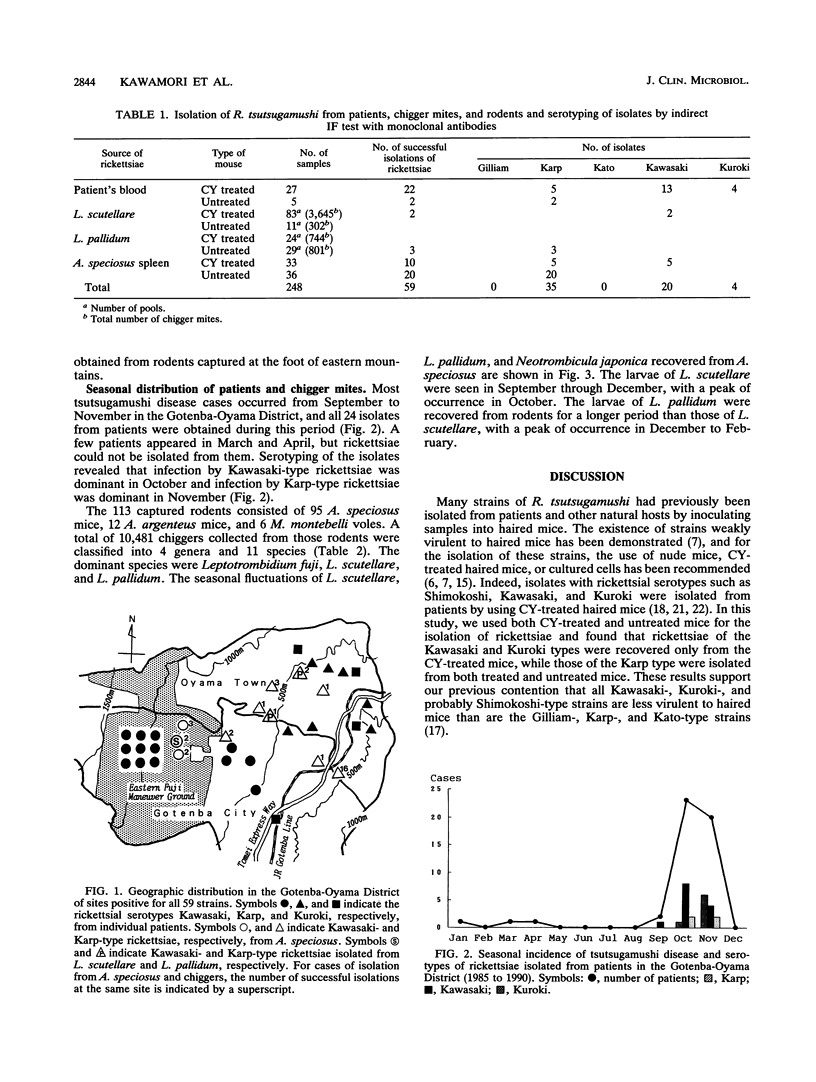
A total of 59 strains of Rickettsia tsutsugamushi were isolated from patients (24 isolates), Apodemus speciosus mice (30 isolates), and unfed larvae of Leptotrombidium scutellare (2 isolates) and Leptotrombidium pallidum (3 isolates) in the Gotenba-Oyama District, Shizuoka Prefecture, Japan. All these isolates were classified into the three serotypes Karp, Kawasaki, and Kuroki based on reactivity with strain-specific monoclonal antibodies. Kawasaki- and Karp-type rickettsiae were isolated from L. scutellare and L. pallidum, respectively, and the geographic distribution of patients and rodents infected with these two types of rickettsiae coincided with the areas densely populated by the respective chiggers. From these results, we conclude that Kawasaki-type rickettsiae are transmitted by L. scutellare and Karp-type ones are transmitted by L. pallidum. Kawasaki-type rickettsial infections were prevalent in early autumn, and Karp-type infections showed a peak of occurrence in the late autumn, reflecting the seasonal fluctuations of L. scutellare and L. pallidum. Isolates of Kuroki-type rickettsiae were obtained only from four patients in October and November, and the relationship between this type of rickettsia and its vector species could not be fully defined.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Kawamura A., Jr, Murata M., Osono M., Nogami S., Shirasaka A., Tanaka H., Sudo K., Suzuki K., Miyairi T., Kijima H. Studies on inapparent infection of tsutsugamuschi disease in Izu Shichito Islands: seroepidemiology and demonstration of an avirulent Rickettsia strain for mice. Jpn J Exp Med. 1980 Apr;50(2):91–105. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kulagin S. M., Tarasevic I. V., Kudryasová N. I., Plotnikova L. F. The investigation of scrub typhus in the USSR. J Hyg Epidemiol Microbiol Immunol. 1968;12(3):257–264. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murata M., Yoshida Y., Osono M., Ohashi N., Oyanagi M., Urakami H., Tamura A., Nogami S., Tanaka H., Kawamura A., Jr Production and characterization of monoclonal strain-specific antibodies against prototype strains of Rickettsia tsutsugamushi. Microbiol Immunol. 1986;30(7):599–610. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1986.tb02987.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohashi N., Tamura A., Sakurai H., Yamamoto S. Characterization of a new antigenic type, Kuroki, of Rickettsia tsutsugamushi isolated from a patient in Japan. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Sep;28(9):2111–2113. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.9.2111-2113.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tachibana N., Kusune E., Yokata T., Shishime E., Tsuda K., Kobayashi Y. [Growth of Rickettsia tsutsugamushi, isolated in Miyazaki district, in BSC-1 cell]. Kansenshogaku Zasshi. 1982 Aug;56(8):664–670. doi: 10.11150/kansenshogakuzasshi1970.56.664. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamura A., Takahashi K., Tsuruhara T., Urakami H., Miyamura S., Sekikawa H., Kenmotsu M., Shibata M., Abe S., Nezu H. Isolation of Rickettsia tsutsugamushi antigenically different from Kato, Karp, and Gilliam strains from patients. Microbiol Immunol. 1984;28(8):873–882. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1984.tb00743.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto S., Kawabata N., Ooura K., Murata M., Minamishima Y. [Antigenic types of Rickettsia tsutsugamushi isolated from patients with tsutsugamushi fever and their distribution in Miyazaki Prefecture]. Kansenshogaku Zasshi. 1989 Feb;63(2):109–117. doi: 10.11150/kansenshogakuzasshi1970.63.109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto S., Kawabata N., Tamura A., Urakami H., Ohashi N., Murata M., Yoshida Y., Kawamura A., Jr Immunological properties of Rickettsia tsutsugamushi, Kawasaki strain, isolated from a patient in Kyushu. Microbiol Immunol. 1986;30(7):611–620. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1986.tb02988.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


