Abstract
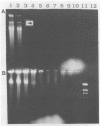
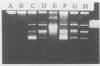
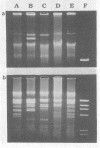
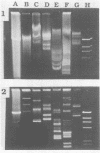
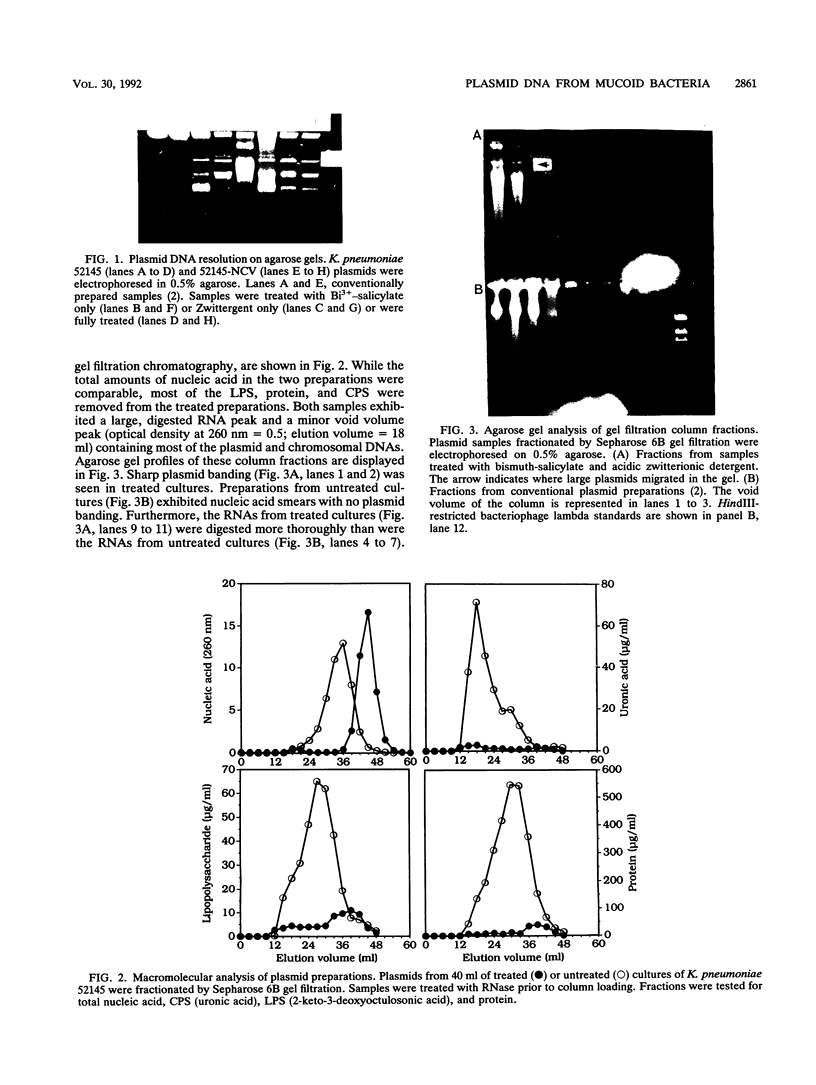
Exopolysaccharides interfere with the isolation and characterization of plasmid DNA from gram-negative bacteria. To repress capsular polysaccharide production, bacteria were cultured in medium containing bismuth nitrate and sodium salicylate. Rapid removal of other contaminating bacterial surface components was achieved by mild acidic zwitterionic detergent extraction. After treatment, bacterial cells were more readily lysed in alkaline detergents. The resulting plasmid preparations contained virtually no capsular polysaccharide and relatively small quantities of lipopolysaccharide and protein, yet they produced yields of nucleic acids similar to those of conventional plasmid preparations. Conventional preparations from encapsulated organisms were largely insoluble and appeared as smears following agarose gel electrophoresis, with indefinite plasmid banding. Plasmids prepared by the new method were highly soluble in conventional buffers and exhibited high-resolution plasmid banding patterns in agarose gels. Plasmids as large as 180 kbp could be isolated and visualized, without apparent nicking, and were readily digested by restriction endonuclease enzymes. The method proved effective with encapsulated or mucoid strains of Klebsiella pneumoniae, Escherichia coli, Acinetobacter anitratus, Salmonella typhimurium, and Enterobacter species. The complete method for plasmid isolation was not suitable for Pseudomonas aeruginosa because of the inhibitory effects of bismuth. Thus, removal of contaminating bacterial surface structures enabled the rapid isolation and characterization of plasmids from mucoid clinical isolates, without the use of organic solvents, CsCl gradients, or expensive, disposable columns.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumenkrantz N., Asboe-Hansen G. New method for quantitative determination of uronic acids. Anal Biochem. 1973 Aug;54(2):484–489. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(73)90377-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darfeuille-Michaud A., Jallat C., Aubel D., Sirot D., Rich C., Sirot J., Joly B. R-plasmid-encoded adhesive factor in Klebsiella pneumoniae strains responsible for human nosocomial infections. Infect Immun. 1992 Jan;60(1):44–55. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.1.44-55.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Domenico P., Landolphi D. R., Cunha B. A. Reduction of capsular polysaccharide and potentiation of aminoglycoside inhibition in gram-negative bacteria by bismuth subsalicylate. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1991 Dec;28(6):801–810. doi: 10.1093/jac/28.6.801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenstein B. I. New molecular techniques for microbial epidemiology and the diagnosis of infectious diseases. J Infect Dis. 1990 Apr;161(4):595–602. doi: 10.1093/infdis/161.4.595. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hale T. L. Genetic basis of virulence in Shigella species. Microbiol Rev. 1991 Jun;55(2):206–224. doi: 10.1128/mr.55.2.206-224.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkey P. M. Molecular methods for the investigation of bacterial cross-infection. J Hosp Infect. 1987 May;9(3):211–218. doi: 10.1016/0195-6701(87)90116-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmberg S. D., Wachsmuth I. K., Hickman-Brenner F. W., Cohen M. L. Comparison of plasmid profile analysis, phage typing, and antimicrobial susceptibility testing in characterizing Salmonella typhimurium isolates from outbreaks. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Feb;19(2):100–104. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.2.100-104.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes D. S., Quigley M. A rapid boiling method for the preparation of bacterial plasmids. Anal Biochem. 1981 Jun;114(1):193–197. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90473-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- John J. F., Jr Molecular analysis of nosocomial epidemics. Infect Dis Clin North Am. 1989 Dec;3(4):683–700. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kado C. I., Liu S. T. Rapid procedure for detection and isolation of large and small plasmids. J Bacteriol. 1981 Mar;145(3):1365–1373. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.3.1365-1373.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karkhanis Y. D., Zeltner J. Y., Jackson J. J., Carlo D. J. A new and improved microassay to determine 2-keto-3-deoxyoctonate in lipopolysaccharide of Gram-negative bacteria. Anal Biochem. 1978 Apr;85(2):595–601. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90260-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leive L. Studies on the permeability change produced in coliform bacteria by ethylenediaminetetraacetate. J Biol Chem. 1968 May 10;243(9):2373–2380. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer L. W. Use of plasmid profiles in epidemiologic surveillance of disease outbreaks and in tracing the transmission of antibiotic resistance. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1988 Apr;1(2):228–243. doi: 10.1128/cmr.1.2.228. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nassif X., Fournier J. M., Arondel J., Sansonetti P. J. Mucoid phenotype of Klebsiella pneumoniae is a plasmid-encoded virulence factor. Infect Immun. 1989 Feb;57(2):546–552. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.2.546-552.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards H., Hughes V., Datta N. Diversity of plasmids responsible for multiple resistance in Klebsiella serotype K2. J Hyg (Lond) 1981 Apr;86(2):189–194. doi: 10.1017/s002217240006890x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi S., Nagano Y. Rapid procedure for isolation of plasmid DNA and application to epidemiological analysis. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Oct;20(4):608–613. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.4.608-613.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]