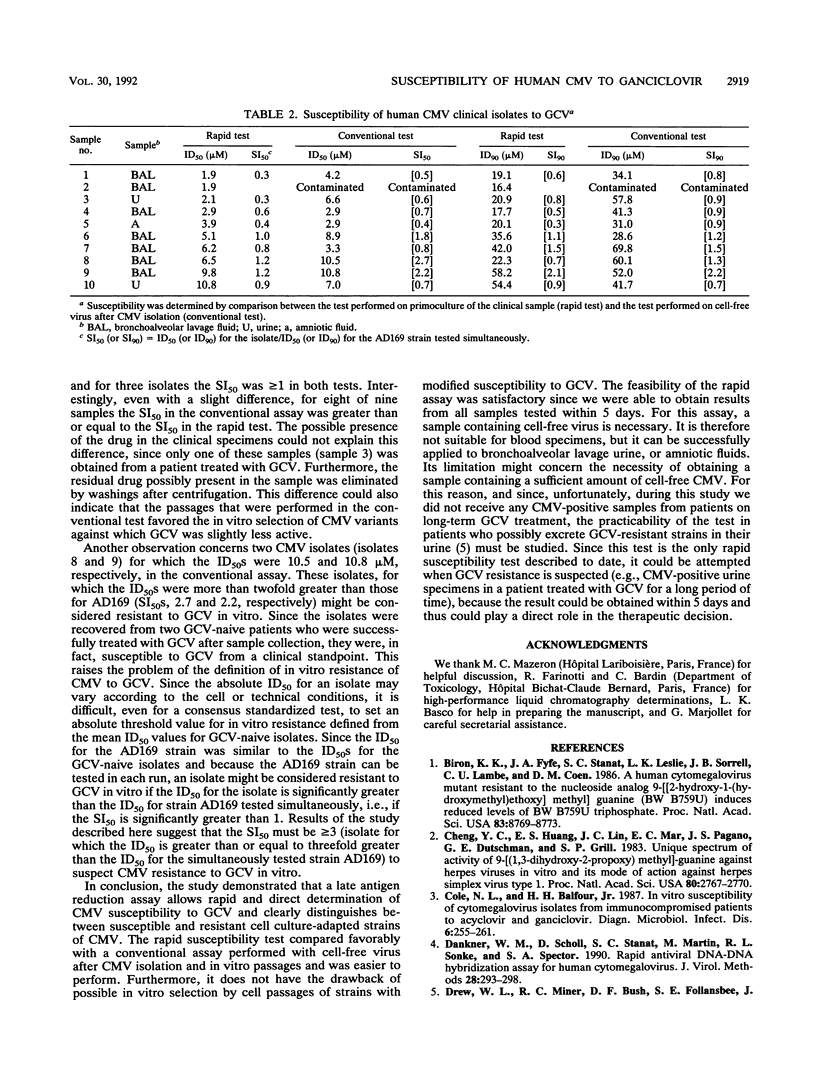
Abstract
We were able to rapidly determine the susceptibility of human cytomegalovirus to ganciclovir using a late antigen synthesis reduction assay directly on primocultures of clinical specimens. This test was compared with a conventional susceptibility assay which was performed with cell-free virus obtained after cytomegalovirus isolation and in vitro passages. Both tests produced similar results. The rapid test, unlike conventional assays, is able to provide a result within 5 days after receipt of the specimen and could thus play a direct role in the therapeutic decision.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Biron K. K., Fyfe J. A., Stanat S. C., Leslie L. K., Sorrell J. B., Lambe C. U., Coen D. M. A human cytomegalovirus mutant resistant to the nucleoside analog 9-([2-hydroxy-1-(hydroxymethyl)ethoxy]methyl)guanine (BW B759U) induces reduced levels of BW B759U triphosphate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(22):8769–8773. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.22.8769. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng Y. C., Huang E. S., Lin J. C., Mar E. C., Pagano J. S., Dutschman G. E., Grill S. P. Unique spectrum of activity of 9-[(1,3-dihydroxy-2-propoxy)methyl]-guanine against herpesviruses in vitro and its mode of action against herpes simplex virus type 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(9):2767–2770. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.9.2767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole N. L., Balfour H. H., Jr In vitro susceptibility of cytomegalovirus isolates from immunocompromised patients to acyclovir and ganciclovir. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 1987 Mar;6(3):255–261. doi: 10.1016/0732-8893(87)90020-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dankner W. M., Scholl D., Stanat S. C., Martin M., Sonke R. L., Spector S. A. Rapid antiviral DNA-DNA hybridization assay for human cytomegalovirus. J Virol Methods. 1990 Jun;28(3):293–298. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(90)90122-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drew W. L., Miner R. C., Busch D. F., Follansbee S. E., Gullett J., Mehalko S. G., Gordon S. M., Owen W. F., Jr, Matthews T. R., Buhles W. C. Prevalence of resistance in patients receiving ganciclovir for serious cytomegalovirus infection. J Infect Dis. 1991 Apr;163(4):716–719. doi: 10.1093/infdis/163.4.716. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erice A., Chou S., Biron K. K., Stanat S. C., Balfour H. H., Jr, Jordan M. C. Progressive disease due to ganciclovir-resistant cytomegalovirus in immunocompromised patients. N Engl J Med. 1989 Feb 2;320(5):289–293. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198902023200505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field A. K., Davies M. E., DeWitt C., Perry H. C., Liou R., Germershausen J., Karkas J. D., Ashton W. T., Johnston D. B., Tolman R. L. 9-([2-hydroxy-1-(hydroxymethyl)ethoxy]methyl)guanine: a selective inhibitor of herpes group virus replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(13):4139–4143. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.13.4139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freitas V. R., Smee D. F., Chernow M., Boehme R., Matthews T. R. Activity of 9-(1,3-dihydroxy-2-propoxymethyl)guanine compared with that of acyclovir against human, monkey, and rodent cytomegaloviruses. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Aug;28(2):240–245. doi: 10.1128/aac.28.2.240. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson M. A., Drew W. L., Feinberg J., O'Donnell J. J., Whitmore P. V., Miner R. D., Parenti D. Foscarnet therapy for ganciclovir-resistant cytomegalovirus retinitis in patients with AIDS. J Infect Dis. 1991 Jun;163(6):1348–1351. doi: 10.1093/infdis/163.6.1348. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plotkin S. A., Drew W. L., Felsenstein D., Hirsch M. S. Sensitivity of clinical isolates of human cytomegalovirus to 9-(1,3-dihydroxy-2-propoxymethyl)guanine. J Infect Dis. 1985 Oct;152(4):833–834. doi: 10.1093/infdis/152.4.833. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pépin J. M., Simon M., Simon F., Dazza M. C., Brun-Vézinet F. Comparison of two methods for rapid detection of cytomegalovirus viraemia in cell culture. Res Virol. 1991 Nov-Dec;142(6):443–448. doi: 10.1016/0923-2516(91)90066-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rasmussen L., Chen P. T., Mullenax J. G., Merigan T. C. Inhibition of human cytomegalovirus replication by 9-(1,3-dihydroxy-2-propoxymethyl)guanine alone and in combination with human interferons. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Oct;26(4):441–445. doi: 10.1128/aac.26.4.441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sommadossi J. P., Bevan R. High-performance liquid chromatographic method for the determination of 9-(1,3-dihydroxy-2-propoxymethyl)guanine in human plasma. J Chromatogr. 1987 Mar 6;414(2):429–433. doi: 10.1016/0378-4347(87)80069-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tatarowicz W. A., Lurain N. S., Thompson K. D. In situ ELISA for the evaluation of antiviral compounds effective against human cytomegalovirus. J Virol Methods. 1991 Nov-Dec;35(2):207–215. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(91)90136-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


