Abstract
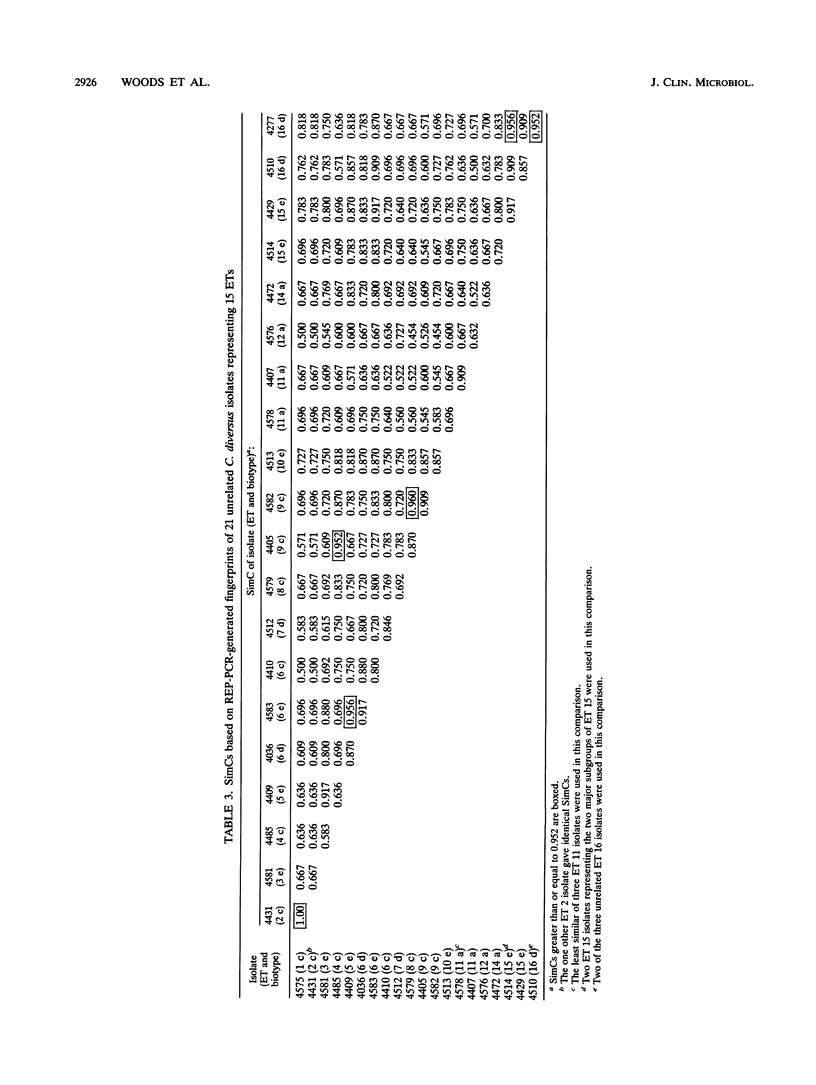
Oligonucleotide probes which match consensus sequences of the repetitive extragenic palindromic (REP) element hybridize to genomic DNA of diverse bacterial species. Primers based on the REP sequence generate complex band patterns with genomic DNA in the polymerase chain reaction (PCR), a technique named REP-PCR. We used REP-PCR with genomic DNA to fingerprint 47 isolates of Citrobacter diversus. Previously, 37 were assigned electrophoretic types (ETs) by multilocus enzyme electrophoresis and 35 were evaluated by using outer membrane protein profiles. Fingerprints were compared by visual inspection and by similarity coefficients (SimCs) based on the number of common bands versus total bands between two given isolates. DNA fingerprints were highly similar visually for patient pairs and outbreak-related sets. SimCs for these were > or = 0.952. Fingerprints of isolates with different ETs generally were distinctive. Among 21 unrelated isolates representing 15 ETs, only 6 of 210 comparisons had SimCs of > or = 0.952. REP-PCR rapidly generated DNA fingerprints which were highly similar for epidemiologically linked isolates of C. diversus and distinct for previously characterized strains within this species. The ability of this method to discriminate between C. diversus isolates with the same biotype was similar to that of multilocus enzyme electrophoresis and outer membrane protein profiles. REP-PCR may be useful in evaluation of apparent outbreaks of this or other bacterial species which possess these extragenic, repetitive elements.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blake P. A., Allegra D. T., Snyder J. D., Barrett T. J., McFarland L., Caraway C. T., Feeley J. C., Craig J. P., Lee J. V., Puhr N. D. Cholera--a possible endemic focus in the United States. N Engl J Med. 1980 Feb 7;302(6):305–309. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198002073020601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falkiner F. R. Epidemiological typing: a user's view. J Hosp Infect. 1988 May;11(4):303–309. doi: 10.1016/0195-6701(88)90082-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrar W. E., Jr Molecular analysis of plasmids in epidemiologic investigation. J Infect Dis. 1983 Jul;148(1):1–6. doi: 10.1093/infdis/148.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finn A., Talbot G. H., Anday E., Skros M., Provencher M., Hoegg C. Vertical transmission of Citrobacter diversus from mother to infant. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1988 Apr;7(4):293–294. doi: 10.1097/00006454-198804000-00012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilson E., Clément J. M., Brutlag D., Hofnung M. A family of dispersed repetitive extragenic palindromic DNA sequences in E. coli. EMBO J. 1984 Jun;3(6):1417–1421. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01986.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goering R. V., Ehrenkranz N. J., Sanders C. C., Sanders W. E., Jr Long term epidemiological analysis of Citrobacter diversus in a neonatal intensive care unit. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1992 Feb;11(2):99–104. doi: 10.1097/00006454-199202000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham D. R., Anderson R. L., Ariel F. E., Ehrenkranz N. J., Rowe B., Boer H. R., Dixon R. E. Epidemic nosocomial meningitis due to Citrobacter diversus in neonates. J Infect Dis. 1981 Sep;144(3):203–209. doi: 10.1093/infdis/144.3.203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham D. R., Band J. D. Citrobacter diversus brain abscess and meningitis in neonates. JAMA. 1981 May 15;245(19):1923–1925. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimont F., Grimont P. A. Ribosomal ribonucleic acid gene restriction patterns as potential taxonomic tools. Ann Inst Pasteur Microbiol. 1986 Sep-Oct;137B(2):165–175. doi: 10.1016/s0769-2609(86)80105-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hulton C. S., Higgins C. F., Sharp P. M. ERIC sequences: a novel family of repetitive elements in the genomes of Escherichia coli, Salmonella typhimurium and other enterobacteria. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Apr;5(4):825–834. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb00755.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irino K., Grimont F., Casin I., Grimont P. A. rRNA gene restriction patterns of Haemophilus influenzae biogroup aegyptius strains associated with Brazilian purpuric fever. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Aug;26(8):1535–1538. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.8.1535-1538.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- John J. F., Jr, Twitty J. A. Plasmids as epidemiologic markers in nosocomial gram-negative bacilli: experience at a university and review of the literature. Rev Infect Dis. 1986 Sep-Oct;8(5):693–704. doi: 10.1093/clinids/8.5.693. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kline M. W. Citrobacter meningitis and brain abscess in infancy: epidemiology, pathogenesis, and treatment. J Pediatr. 1988 Sep;113(3):430–434. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(88)80623-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kline M. W., Mason E. O., Jr, Kaplan S. L. Characterization of Citrobacter diversus strains causing neonatal meningitis. J Infect Dis. 1988 Jan;157(1):101–105. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.1.101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kline M. W., Mason E. O., Jr, Kaplan S. L. Epidemiologic marker system for Citrobacter diversus using outer membrane protein profiles. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Aug;27(8):1793–1796. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.8.1793-1796.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li J., Musser J. M., Beltran P., Kline M. W., Selander R. K. Genotypic heterogeneity of strains of Citrobacter diversus expressing a 32-kilodalton outer membrane protein associated with neonatal meningitis. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Aug;28(8):1760–1765. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.8.1760-1765.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin F. C., Devoe W. F., Morrison C., Libonati J., Powers P., Gross R. J., Rowe B., Israel E., Morris J. G., Jr Outbreak of neonatal Citrobacter diversus meningitis in a suburban hospital. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1987 Jan;6(1):50–55. doi: 10.1097/00006454-198701000-00013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lupski J. R., Weinstock G. M. Short, interspersed repetitive DNA sequences in prokaryotic genomes. J Bacteriol. 1992 Jul;174(14):4525–4529. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.14.4525-4529.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris J. G., Jr, Lin F. Y., Morrison C. B., Gross R. J., Khabbaz R., Maher K. O., Rowe B., Israel E., Libonati J. P. Molecular epidemiology of neonatal meningitis due to Citrobacter diversus: a study of isolates from hospitals in Maryland. J Infect Dis. 1986 Sep;154(3):409–414. doi: 10.1093/infdis/154.3.409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen R. J., Beck A., Dayal P. A., Dawson C. Detection of genomic variation in Providencia stuartii clinical isolates by analysis of DNA restriction fragment length polymorphisms containing rRNA cistrons. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Oct;26(10):2161–2166. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.10.2161-2166.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parry M. F., Hutchinson J. H., Brown N. A., Wu C. H., Estreller L. Gram-negative sepsis in neonates: a nursery outbreak due to hand carriage of Citrobacter diversus. Pediatrics. 1980 Jun;65(6):1105–1109. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penner J. L., Hennessy J. N., Mills S. D., Bradbury W. C. Application of serotyping and chromosomal restriction endonuclease digest analysis in investigating a laboratory-acquired case of Campylobacter jejuni enteritis. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Dec;18(6):1427–1428. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.6.1427-1428.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richard C., Brisou B., Lioult J. Etude taxonomique de "Levinea" nouveau genre de la famille des entérobactéries. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1972 Jun;122(6):1137–1146. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharples G. J., Lloyd R. G. A novel repeated DNA sequence located in the intergenic regions of bacterial chromosomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Nov 25;18(22):6503–6508. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.22.6503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern M. J., Ames G. F., Smith N. H., Robinson E. C., Higgins C. F. Repetitive extragenic palindromic sequences: a major component of the bacterial genome. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):1015–1026. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90436-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Versalovic J., Koeuth T., Lupski J. R. Distribution of repetitive DNA sequences in eubacteria and application to fingerprinting of bacterial genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Dec 25;19(24):6823–6831. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.24.6823. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wachsmuth K. Molecular epidemiology of bacterial infections: examples of methodology and of investigations of outbreaks. Rev Infect Dis. 1986 Sep-Oct;8(5):682–692. doi: 10.1093/clinids/8.5.682. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams W. W., Mariano J., Spurrier M., Donnell H. D., Jr, Breckenridge R. L., Jr, Anderson R. L., Wachsmuth I. K., Thornsberry C., Graham D. R., Thibeault D. W. Nosocomial meningitis due to Citrobacter diversus in neonates: new aspects of the epidemiology. J Infect Dis. 1984 Aug;150(2):229–235. doi: 10.1093/infdis/150.2.229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods T. C., Helsel L. O., Swaminathan B., Bibb W. F., Pinner R. W., Gellin B. G., Collin S. F., Waterman S. H., Reeves M. W., Brenner D. J. Characterization of Neisseria meningitidis serogroup C by multilocus enzyme electrophoresis and ribosomal DNA restriction profiles (ribotyping). J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Jan;30(1):132–137. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.1.132-137.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Bruijn F. J. Use of repetitive (repetitive extragenic palindromic and enterobacterial repetitive intergeneric consensus) sequences and the polymerase chain reaction to fingerprint the genomes of Rhizobium meliloti isolates and other soil bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1992 Jul;58(7):2180–2187. doi: 10.1128/aem.58.7.2180-2187.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Soolingen D., Hermans P. W., de Haas P. E., Soll D. R., van Embden J. D. Occurrence and stability of insertion sequences in Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex strains: evaluation of an insertion sequence-dependent DNA polymorphism as a tool in the epidemiology of tuberculosis. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Nov;29(11):2578–2586. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.11.2578-2586.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]