Abstract
S-shaped tetrakisporphyrin 2 forms supramolecular polymeric assemblies via a complementary affinity of its bisporphyrin units in solution. The self-association constant determined by applying the isodesmic model is >106 L mol−1, which suggests that a sizable polymer forms at millimolar concentrations at room temperature. The electron deficient aromatic guest (TNF) binds within the molecular clefts provided by the bisporphyrin units via a charge-transfer interaction. This guest complexation completely disrupts supramolecular polymeric assembly. The long, fibrous fragments of the polymeric assemblies were characterized by atomic-force microscopy imaging of a film cast on a mica surface. The polymeric assemblies have lengths of >1μm and show a coiled structure with a higher level of organization. The approach discussed in this report concerning the quick preparation of supramolecular polymeric assemblies driven by noncovalent forces sets the stage for the preparation of a previously undescribed class of macromolecular porphyrin architectures.
Keywords: porphyrin, supramolecular chemistry
Significant effort has been directed toward elucidating the energy transport phenomena occurring in natural light-harvesting complexes. A variety of porphyrin-based model compounds have been created to mimic natural light-harvesting complexes with the goal of applying them to artificial light-harvesting systems and molecular photonic devices (1–4). Among them, nanometric multiporphyrin arrays are the most challenging target, wherein, their covalent synthesis offers a high stability and a precisely controlled arrangement of multiporphyrin arrays (5, 6). Unfortunately, the growth of size and complexity of these systems makes their synthesis tedious and inefficient.
In contrast, supramolecular self-assembly is a versatile alternative and offers the quick construction of 1-, 2-, or 3-dimensional nanometric architectures that have discrete structures, properties, and functions in which the molecular components are held together by reversible interactions (7–11). Self-assembled nanometric multiporphyrin arrays having well-defined shapes and dimensions provide unique optical and electrochemical properties for photochemical energy conversion and storage. As a consequence, their practical applications can be foreseen in the field of molecular electronics: conductive molecular wires, switches, and photovoltaic cells. These creative developments should pave the way for research directions in creating key materials for emerging field of nanotechnology and science.
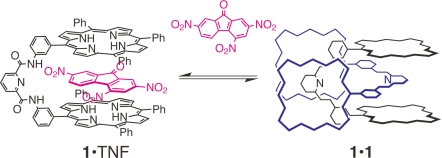
Coordination-driven self-assembly of porphyrin is one of the most useful approaches for developing large and elaborate molecular architectures (12, 13). Hunter and coworkers developed unique self-assembled porphyrin arrays (14–18). Giant porphyrin arrays and large porphyrin wheels via metal coordination for modeling light-harvesting antenna have been reported by Kobuke and coworkers (19–26). Aida and coworkers have investigated self-assembled nanometric porphyrin arrays (27–29). There are limited examples of porphyrin self-assembly by subtle forces, such as van der Waals and CH/π interactions in organic media, despite the fact that porphyrin possesses a flat and electron-rich surface that creates van der Waals, stacking, and charge transfer interactions that play a significant role in its self-assembly (30, 31). We have reported that simple bisporphyrin 1 assembles to form the unique dimer 1·1 in organic media, whereas the complexation of an electron-deficient flat aromatic guest into the cleft of the bisporphyrin leads to the simultaneous dissociation of the dimer (32, 33) (Fig. 1).
Fig. 1.
Schematic representation of the dimer formation of the bisporphyrin and its dissociation induced by the complexation of 2,4,7-trinitrofluorenone (TNF).
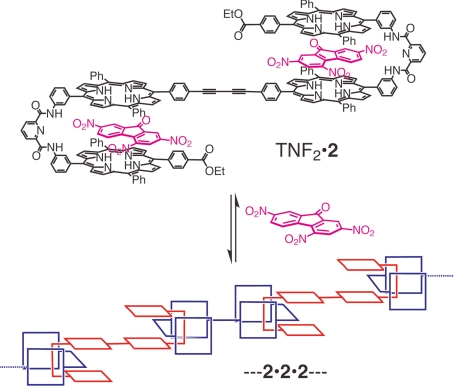
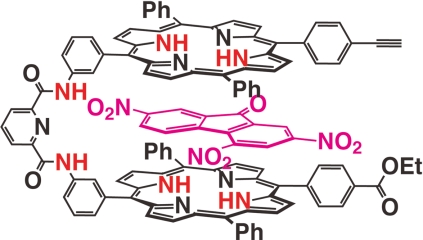
We envisioned that this complementary affinity of the bisporphyrin could be applied to the construction of nanometric multiporphyrin assemblies. One of the porphyrin units of 1 can be connected with 1,4-dibutyne units, giving rise to tetrakisporphyrin 2, with a ditopic nature that should lead to an iterative self-assembly to form supramolecular nanometric polymeric assemblies (Fig. 2). The association and dissociation of the supramolecular assemblies can be regulated by the guest complexation.
Fig. 2.
Schematic representation of the formation of the supramolecular polymeric assemblies of tetrakisporphyrin 2 via the complementary affinity of the bisporphyrin units, and the dissociation of the assemblies induced by TNF complexation.
Results and Discussion
Synthesis.
The synthesis of tetrakisporphyrin 2 is outlined in Scheme 1. Palladium-mediated coupling between 3 (34) and 4-ethoxycarbonylphenyl boronic acid, followed by subsequent iodination, produced porphyrin 4, onto which a nitrophenyl group was introduced via Suzuki's coupling reaction with 3-nitrophenyl boronic acid. The following reduction of the nitro group produced aminophenylporphyrin 5. The other porphyrin unit of bisporphyrin 8 was prepared from 3. A 3-nitrophenyl group was introduced onto 3 through Suziki's coupling reaction, followed by the reduction of the nitro group with tin(II)chloride to produce aminophenylporphyrin 6, which reacted with 6-methoxycarbonylpicolinic acid chloride (35) to yield 7. Hydrolysis of the methyl ester resulted in the corresponding carboxylic acid. A condensation reaction of the resulting acid with porphyrin 5 under standard conditions produced bisporphyrin 8, which was converted to iodobisporphyrin. The 4-trimethylethynylphenyl group was introduced onto the iododerivative of 8 via palladium-mediated coupling with 4-trimethylsilylethynylphenyl boronic acid (36). The subsequent deprotection of the trimethylsilyl group yielded bisporphyrin 9. Zinc ions were introduced into the 2 porphyrin units to avoid copper complexation in the next step. Eglinton coupling of the resultant zinc complexes produced the tetrakisporphyrin, which was treated with aqueous acid to furnish the desired tetrakisporphyrin 2 [supporting information (SI) Fig. S1].
Scheme 1.
Synthesis of tetrakisporphyrin 2. Conditions: 4-ethoxycarbonylphenylboronic acid, Pd(PPh3)4, Na2CO3, toluene-EtOH (3:2), 64% (a); I2, (CF3CO2)2IPh, pyridine, CHCl3, 95% (b); 3-nitrophenylboronic acid, Pd(PPh3)4, Na2CO3, toluene-EtOH (3:2), 86% (c); SnCl2, conc.HCl-EtOH-CHCl3 (1:1:12), 94% (d); 3-nitrophenylboronic acid, Pd(PPh3)4, Na2CO3, toluene-EtOH (3:2), 73% (e); SnCl2, conc.HCl-EtOH-CHCl3 (1:1:12), 88% (f); 6-methoxycarbonyl-pyridine-2-carboxylic acid chloride, pyridine, THF, 92% (g); KOH, MeOH, 84% (h); 5, EDAC, DMAP, pyridine, CH2Cl2, 82% (i); I2, (CF3CO2)2IPh, pyridine, CHCl3, 91% (j); 4-trimethylsilylethynylphenyl boronic acid, Pd(PPh3)4, Cs2CO3, toluene-EtOH (12:1) (k); TBAF, THF, (2 steps) 55% (l); Zn(OAc)2, CHCl3-EtOH (2:1), 96% (m); and Cu(OAc)2, pyridine, 84% (n).
Self-Association of Tetrakisporphyrin.
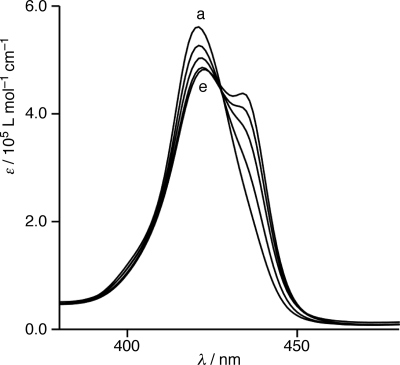
The self-association of 2 in toluene was studied by electronic absorption spectroscopy. The electronic absorption spectra of 2 depend on the temperatures and concentrations of its solution (Fig. 3). The toluene solution of 2 (5 × 10−6 mol L−1) at 353 K exhibited a single Soret band at 421 nm, characteristic of a nonaggregated porphyrin. A new band gradually emerged at 435 nm as the solution was gradually cooled to 273 K.
Fig. 3.
Variable-temperature electronic absorption spectra of 2 (5 × 10−6 mol L−1) in toluene: at 353 (a), 333 (b), 313 (c), 293 (d), and 273 K (e).
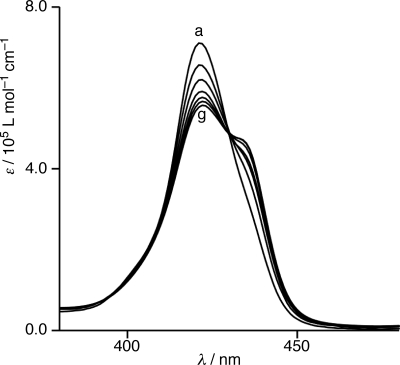
A similar band shift was observed when a solution of 2 was concentrated. A single Soret band at 421 nm shifted around 435 nm when the concentration changed from 6.00 × 10−8 mol L−1 to 7.50 × 10−6 mol L−1 at 298 K (Fig. 4). Plotting the molar extinction coefficients at 420 nm versus the concentrations of 2 yielded hyperbolic curves (Fig. S2). Nonlinear curve-fitting analysis of the plots by applying the isodesmic model produced the large association constant (Kagg = 1,500,000 ± 100,000 L mol−1). Accordingly, tetrakisporphyrin 2 aggregates and forms a sizable polymeric assembly in solution.
Fig. 4.
Electronic absorption spectra of 2 in toluene at 298 K at concentrations of: 6.0 (a), 20 (b), 25 (c), 50 (d), 100 (e), 500 (f), and 750 (g) × 10−8 mol L−1.
It is known that the self-assembly of a porphyrin forms H- and J-type supramolecular structures in its higher level of organization: The former has a face-to-face stacking structure that shows a characteristic blue-shift of a Soret absorption band, whereas the other adopts an edge-to-edge orientation, which is responsible for the red-shift of the Soret band (37–39). A tetraphenylporphyrin is not allowed to adopt a face-to-face stacking structure because of the steric repulsion of the phenyl groups; thus, the face-to-face stacking motif of the porphyrin units of 2 can be ruled out in its assembled structure. Based on our previous report on the self-association of 1 (Fig. 1), the complementary affinity of the bisporphyrin units of 2 can drive supramolecular association (Fig. 2). The red-shift of the Soret band of 2 probably suggests the formation of a linear array of the porphyrin units of 2 in its self-assembled state (Fig. 2).
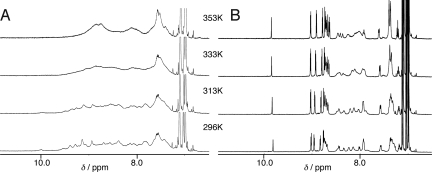
1H NMR studies of 2 and bisporphyrin 8 in toluene-d8 provide further insight into their self-associations (Fig. 5). The 1H NMR signals of the porphyrin protons of bisporphyrin 8 were slightly broadened at 296 K. The peaks gradually shifted and sharpened when the solution was warmed. The spectrum of 8 was also observed to depend on the concentration. These results indicate that bisporphyrin 8 equilibrates its self-assembled dimer with the dimerization constant (Kdim = 3,500 ± 1,000 L mol−1) (Fig. S3). In contrast, the 1H NMR signals of 2 (3.50 × 10−3 mol L−1) in the aromatic region were exceedingly broad, and could not be assigned. When the solution was warmed, the spectrum of 2 somewhat changed its shape but was still broadened. The substantial difference of the spectral behaviors between 2 and 8 proves the idea that the sizable polymeric assemblies of 2 form in toluene and that polymeric structures still exist even at high temperatures.
Fig. 5.
Variable temperature 1H NMR spectroscopic studies. (A) Tetrakisporphyrin 2 at the concentration of 3.50 × 10−3 mol L−1 in toluene-d8. Highly complex sets of peaks in the aromatic region arise from the polymeric species of 2. (B) Bisporphyrin 8 at the concentration of 3.00 × 10−3 mol L−1 in toluene-d8. The broad resonances in the aromatic region result from the monomer–dimer equilibrium of 8.
Tetrakisporphyrin 2 has 2 bisporphyrin clefts that can take up an electron-deficient aromatic guest (Fig. 2). TNF (2,4,7-trinitrofluorenone) is accommodated within the bisporphyrin cleft of 1 with the large binding constant (Ka = 350,000 ± 10,000 L mol−1 in CDCl3) (33). Thus, guest binding into the bisporphyrin clefts of 2 competes with its self-assembly and can lead to the dissociation of the polymeric assemblies (Fig. 2).
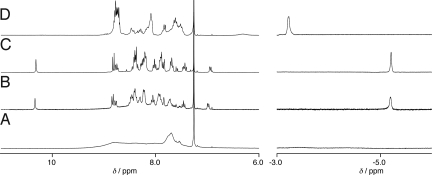
The 1H NMR spectrum of 2 at 296 K was rather broad, and the aromatic signals were not assignable as compared with that of 9 in chloroform-d1 (Fig. 6 A and D). The porphyrin N–H protons did not appear as a sharp signal. Accordingly, the large size of the polymeric assemblies of 2 exists even in chloroform. In contrast, the N–H signals of 9 showed as a singlet at −3.2 ppm, and the signals of the aromatic protons were slightly broadened (Fig. 6D), indicating the formation of a self-assembled dimer 9·9 having the same complementary structure as dimer 1·1 (Fig. 1). When TNF was added to the solution, the signals in the aromatic region sharpened, and the new signals appeared at −5.2 and 10.3 ppm, assignable to the N–H protons of the porphyrin and amide groups (Fig. 6C). The large up-field shift of the porphyrin N–H signal (Δδ = −2.0 ppm) places the TNF molecule within the bisporphyrin cleft to produce the host–guest complex TNF·9, in which the porphyrin N–H protons stay in the shielding region of the guest aromatic rings (Fig. 7).
Fig. 6.
1H NMR spectra of 2 (2.5 × 10−3 mol L−1) (A), 2 with TNF (3.7 × 10−3 mol L−1) (B), 9 (3.5 × 10−3 mol L−1) with TNF (5.2 × 10−3 mol L−1) (C), and 9 (3.5 × 10−3 mol L−1) (D) at 296 K in chloroform-d1.
Fig. 7.
Plausible structure of the host–guest complex between 9 and TNF. The porphyrin N–H protons are in the shielding region created by the guest aromatic rings, whereas the amide N–H protons are deshielded by the guest.
TNF was also observed to strongly bind within the clefts of tetrakisporphyrin 2. The addition of TNF sharpened the signals, and the resultant spectrum was similar to that of TNF·9 (Fig. 6 B and C). It is obvious that the supramolecular polymeric assembly of 2 is completely disrupted by the guest complexation to form TNF2·2 (Fig. 2).
Atomic-Force Microscopy (AFM) of Supramolecular Polymeric Assemblies.
Recent progress of AFM allows us to obtain the molecular images of supramolecular assemblies prepared on flat surface. The AFM images may not directly reflect the solution structure of supramolecular assemblies; however, some extent of the solution structures can be fixed. Thus, the AFM measurement of supramolecular assemblies should provide an insight into their molecular structure in solution even though the observed structures and morphology may be exaggerated because of multiple interactions during the drying process of the solution.
The size and morphology of the polymeric assemblies of tetrakisporphyrin 2 were directly confirmed by AFM. AFM images were measured by tapping mode. The measurement of the prepared film reveals the existence of the long, winding, and fibrous fragments of 2 (Fig. 8 A and B) with lengths >1 μm, demonstrating that 2 iteratively creates complementary connections with others at both ends to form the supramolecular polymeric assemblies.
Fig. 8.
AFM topographic images of a drop-cast of a solution of 2 in chloroform on mica. (A) Topographical image (10 × 10 μm2). (B) High-contrast image of A. (C) Line profile along with the black line in A. (D) High-contrast image (500 × 500 nm2). (E) Phase image of D.
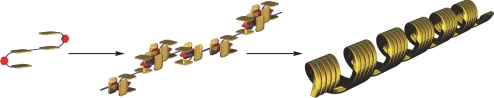
According to the cross-section of the AFM height image (Fig. 8A), the fibrous assemblies exhibit a width of 266 ± 10 nm and a height of 5.3 ± 0.3 nm (Fig. 8C). The expanded images (Fig. 8 D and E) display a coiled structure with a pitch of 64 ± 6 nm. Judging from the calculated structure of the linear oligomer of 2 (Fig. S4), the oligomeric structure has a height and width of 1.7–2.5 nm. These values are obviously smaller that those obtained from the AFM images, implying that the supramolecular polymeric assembles into a bundle, adopting coiled superstructures. Based on the value of the pitch, the coiled tape is composed of a bundle of ≈30 chains of the polymeric assemblies (Fig. 9).
Fig. 9.
Schematic representation of the formation of the supramolecular polymer and the helical morphology in its higher level of supramolecular organization.
Conclusions
In summary, we synthesized tetrakisporphyrin 2, which is capable of assembling via complementary affinity with the bisporphyrin components with an extremely large association constant to form supramolecular polymeric assemblies. The guest complexation into the bisporphyrin clefts disrupts supramolecular polymeric assembly, which gives rise to the 1:2 host–guest complex. Moreover, analysis of individual supramolecular polymeric assemblies dispersed on mica by AFM measurements indicates that the supramolecular polymeric assemblies have a fibrous and coiled morphology. It is possible that the supramolecular polymeric assemblies adopt a bundled helical structure to create a coiled superstructure with a higher level of organization. This research provides a unique strategy for controlling, at the nanometer scale, the size and morphology of supramolecular polymeric assemblies that exhibit elaborate structures. Future work should focus on the development of stimuli-responsive supramolecular polymeric systems with the aid of guest binding.
Materials and Methods
Chemicals were purchased from commercial suppliers and used as received unless otherwise specified. All solvents were purified and dried before use. Column chromatography was performed on Silica Gel 60 (230–400 mesh; Merck). Deuterated solvents (Merck) for NMR spectroscopic analysis were used as received. Proton and carbon NMR spectra were recorded on Varian Mercury-300 or JEOL LAMBDA-500 spectrometers. All chemical shifts are quoted in parts per million relative to the residual solvent peak as a reference standard. IR spectra were obtained on a JASCO FT/IR-420S. UV-vis absorption spectra were measured on a JASCO V-560 spectrometer. Mass spectra were reported with JEOL JMX-SX 102A and/or SHIMAZU AXIMA-CFR plus spectrometers. Melting points were measured with a Yanagimoto micro melting point apparatus and uncorrected. Detailed synthetic procedures and spectroscopic data of all of the compounds are presented in the SI Text.
Aggregation Study Using Electronic Absorption Spectroscopy.
A set of spectra of 2 were recorded at various concentrations in toluene. The apparent extinction coefficients at 420 nm were plotted as a function of the concentrations of 2. The isodesmic model (40–43) was applied for nonlinear regression analysis according to Eq. 1.
ε Denotes the apparent extinction coefficient; εf and εa are the extinction coefficients for the free and the aggregated species, respectively; K is the association constant; and c is the total concentration of 2 in solution.
General Procedure for AFM.
AFM was carried out under ambient conditions with a SPI-3800N and SPA-400 system (SII Nanotechnology Inc.). Silicon cantilevers (SI-DF20) with spring constants of 15 N/m, tip radii of 15 nm, and first longitudinal resonance frequencies from 110 to 150 kHz were used in dynamic force mode. Samples were prepared by simple drop-casting 0.1 mM chloroform solutions of tetrakisporphyrin 2 onto freshly cleaved mica surfaces. The solution was removed under a stream of dry nitrogen, and the substrate was subsequently dried over 12 h in an evacuated desiccator.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments.
We thank Prof. Y. Fujiwara (Hiroshima University) for his kind help with the SPM system. This work was supported by Japan Society for the Promotion of Science Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research 18350065 and Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science, and Technology of Japan Grant-in-Aid for Science Research 19022024 in Priority Area “SuperHierarchical Structures.” This work was supported by the Murata, Ogasawara, Iketani, and Inamori Foundations.
Footnotes
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
This article is a PNAS Direct Submission.
This article contains supporting information online at www.pnas.org/cgi/content/full/0809602106/DCSupplemental.
References
- 1.Holten D, Bocian DF, Lindsey JS. Probing electronic communication in covalently linked multiporphyrin arrays. A guide to the rational design of molecular photonic devices. Acc Chem Res. 2002;35:57–69. doi: 10.1021/ar970264z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Gust D, Moore TA, Moore AL. Mimicking photosynthetic solar energy transduction. Acc Chem Res. 2001;34:40–48. doi: 10.1021/ar9801301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Choi MS, Aida T, Yamazaki T, Yamazaki I. A large dendritic multiporphyrin array as a mimic of the bacterial light-harvesting antenna complex: Molecular design of an efficient energy funnel for visible photons. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2001;40:3194–3198. doi: 10.1002/1521-3773(20010903)40:17<3194::AID-ANIE3194>3.0.CO;2-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Kobuke Y. Artificial light-harvesting systems by use of metal coordination. Eur J Inorg Chem. 2006:2333–2351. [Google Scholar]
- 5.Aratani N, Tsuda A, Osuka A. Discrete giant porphyrin arrays: Challenges to molecular size, length and the extent of electronic π-conjugation. Synlett. 2001:1663–1674. [Google Scholar]
- 6.Tsuda A, Osuka A. Fully conjugated porphyrin tapes with electronic absorption bands that reach into infrared. Science. 2001;293:79–82. doi: 10.1126/science.1059552. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Gulikkrzywicki T, Fouquey C, Lehn JM. Electron microscopic study of supramolecular liquid crystalline polymers formed by molecular-recognition-directed self-assembly from complementary chiral components. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1993;90:163–167. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.1.163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Castellano RK, Clark R, Craig SL, Nuckolls C, Rebek J. Emergent mechanical properties of self-assembled polymeric capsules. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2000;97:12418–12421. doi: 10.1073/pnas.97.23.12418. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Castellano RK, Rudkevich DM, Rebek J. Polycaps: Reversibly formed polymeric capsules. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1997;94:7132–7137. doi: 10.1073/pnas.94.14.7132. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Yebeutchou RM, et al. Host–guest driven self-assembly of linear and star supramolecular polymers. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2008;47:4504–4508. doi: 10.1002/anie.200801002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Yount WC, Juwarker H, Craig SL. Orthogonal control of dissociation dynamics relative to thermodynamics in a main-chain reversible polymer. J Am Chem Soc. 2003;125:15302–15303. doi: 10.1021/ja036709y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Satake A, Kobuke Y. Dynamic supramolecular porphyrin systems. Tetrahedron. 2005;61:13–41. [Google Scholar]
- 13.Iengo E, Zangrando E, Alessio E. Synthetic strategies and structural aspects of metal-mediated multiporphyrin assemblies. Acc Chem Res. 2006;39:841–851. doi: 10.1021/ar040240+. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Hunter CA, et al. Noncovalent assembly of [2]rotaxane architectures. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2001;40:2678–2682. doi: 10.1002/1521-3773(20010716)40:14<2678::AID-ANIE2678>3.0.CO;2-U. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Haycock RA, Yartsev A, Michelsen U, Sundstrom V, Hunter CA. Self-assembly of pentameric porphyrin light-harvesting antennae complexes. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2000;39:3616–3619. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Michelsen U, Hunter CA. Self-assembled porphyrin polymers. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2000;39:764–767. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Camara-Campos A, Hunter CA, Tomas S. Cooperativity in the self-assembly of porphyrin ladders. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2006;103:3034–3038. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0508071103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Haycock RA, Hunter CA, James DA, Michelsen U, Sutton LR. Self-assembly of oligomeric porphyrin rings. Org Lett. 2000;2:2435–2438. doi: 10.1021/ol000129d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Ogawa K, Kobuke Y. Formation of a giant supramolecular porphyrin array by self-coordination. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2000;39:4070–4073. doi: 10.1002/1521-3773(20001117)39:22<4070::aid-anie4070>3.0.co;2-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Hajjaj F, et al. Assemblies of supramolecular porphyrin dimers in pentagonal and hexagonal arrays exhibiting light-harvesting antenna function. J Am Chem Soc. 2006;128:4612–4623. doi: 10.1021/ja0583214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Takahashi R, Kobuke Y. Hexameric macroring of gable-porphyrins as a light-harvesting antenna mimic. J Am Chem Soc. 2003;125:2372–2373. doi: 10.1021/ja028325y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Shoji O, Okada S, Satake A, Kobuke Y. Coordination assembled rings of ferrocene-bridged trisporphyrin with flexible hinge-like motion: Selective dimer ring formation, its transformation to larger rings, and vice versa. J Am Chem Soc. 2005;127:2201–2210. doi: 10.1021/ja0445746. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Satake A, Tanaka H, Hajjaj F, Kawai T, Kobuke Y. Single molecular observation of penta- and hexagonic assembly of bisporphyrin on a gold surface. Chem Commun. 2006:2542–2544. doi: 10.1039/b603360a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Kuramochi Y, et al. Light-harvesting supramolecular porphyrin macrocycle accommodating a fullerene-tripodal ligand. Chem Eur J. 2008;14:2827–2841. doi: 10.1002/chem.200701720. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Morisue M, Yamatsu S, Haruta N, Kobuke Y. Surface-grafted multiporphyrin arrays as light-harvesting antennae to amplify photocurrent generation. Chem Eur J. 2005;11:5563–5574. doi: 10.1002/chem.200500040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Ikeda C, Fujiwara E, Satake A, Kobuke Y. Long rod-like array of bis(imidazolyl)porphyrinatocobalt(III) by successive complementary coordination. Chem Commun. 2003:616–617. doi: 10.1039/b211434h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Choi MS, Yamazaki T, Yamazaki I, Aida T. Bioinspired molecular design of light-harvesting multiporphyrin arrays. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2004;43:150–158. doi: 10.1002/anie.200301665. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Yamaguchi T, Kimura T, Matsuda H, Aida T. Macroscopic spinning chirality memorized in spin-coated films of spatially designed dendritic zinc porphyrin J-aggregates. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2004;43:6350–6355. doi: 10.1002/anie.200461431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Toyofuku K, et al. Amplified chiral transformation through helical assembly. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2007;46:6476–6480. doi: 10.1002/anie.200701668. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Schneider HJ, Liu T, Sirish M, Malinovski V. Dispersive interactions in supramolecular porphyrin complexes. Tetrahedron. 2002;58:779–786. [Google Scholar]
- 31.Balaban TS, Eichhofer A, Lehn JM. Self-assembly by hydrogen bonding and π–π interactions in the crystal of a porphyrin—Attempts to mimic bacteriochlorophyll c. Eur J Org Chem. 2000:4047–4057. [Google Scholar]
- 32.Haino T, Fujii T, Fukazawa Y. Self-complementary bis-porphyrins. Tetrahedron Lett. 2005;46:257–260. [Google Scholar]
- 33.Haino T, Fujii T, Fukazawa Y. Guest binding and new self-assembly of bisporphyrins. J Org Chem. 2006;71:2572–2580. doi: 10.1021/jo052224b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Shanmugathasan S, et al. Regioselective halogenation and palladium-catalysed couplings on 5,15-diphenylporphyrin. J Porphyrins Phthalocyanines. 2000;4:228–232. [Google Scholar]
- 35.Young R, Chang CK. Synthesis and characterization of blocked and ligand-appended hemes derived from atropisomeric meso-diphenylporphyrins. J Am Chem Soc. 1985;107:898–909. [Google Scholar]
- 36.Thoresen LH, Jiao G-S, Haaland WC, Metzker ML, Burgess K. Rigid, conjugated, fluoresceinated thymidine triphosphates: Syntheses and polymerase mediated incorporation into DNA analogs. Chem Eur J. 2003;9:4603–4610. doi: 10.1002/chem.200304944. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Okada S, Segawa H. Substituent-control exciton in J-aggregates of protonated water-insoluble porphyrins. J Am Chem Soc. 2003;125:2792–2796. doi: 10.1021/ja017768j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Kano K, Fukuda K, Wakami H, Nishiyabu R, Pasternack RF. Factors influencing self-aggregation tendencies of cationic porphyrins in aqueous solution. J Am Chem Soc. 2000;122:7494–7502. [Google Scholar]
- 39.Kobuke Y, Miyaji H. Supramolecular stacks of bis(imidazolyl)porphyrin through metal coordination. Bull Chem Soc Jpn. 1996:3563–3569. [Google Scholar]
- 40.Sijbesma RP, et al. Reversible polymers formed from self-complementary monomers using quadruple hydrogen bonding. Science. 1997;278:1601–1604. doi: 10.1126/science.278.5343.1601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Martin RB. Comparisons of indefinite self-association models. Chem Rev. 1996;96:3043–3064. doi: 10.1021/cr960037v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Baxter NJ, Williamson MP, Lilley TH, Haslam E. Stacking interactions between caffeine and methyl gallate. J Chem Soc Faraday Trans. 1996;92:231–234. [Google Scholar]
- 43.Würthner F, Thalacker C, Diele S, Tschierske C. Fluorescent J-type aggregates and thermotropic columnar mesophases of perylene bisimide dyes. Chem Eur J. 2001;7:2245–2253. doi: 10.1002/1521-3765(20010518)7:10<2245::aid-chem2245>3.0.co;2-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.