Abstract
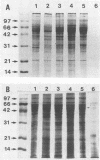
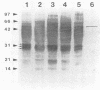
Reactions to Pythium insidiosum by sera from horses with active pythiosis were investigated by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) and immunoblotting. Five strains of P. insidiosum were grown in nutrient broth and then sonicated. After centrifugation, supernatant antigens were separated by SDS-PAGE. An exoantigen of Conidiobolus coronatus was also tested. Bands with molecular weights between 97,000 and 14,000 were identified by Coomassie blue and silver staining. After being transferred to nitrocellulose, the antigens were reacted against sera from six horses with pythiosis, sera from four horses cured a year earlier by vaccination, and sera from five healthy horses. The sera from horses with pythiosis recognized at least 20 antigens in all strains. Three antigens with molecular weights of 32,000, 30,000, and 28,000 appeared to be immunodominant and specific. Sera from horses cured by immunotherapy showed only five very weak bands, three of them the 32,000-molecular-weight (32K), 30K, and 28K antigens. No bands were observed with sera from healthy horses or sera from horses with a variety of other infections. Sera from horses with pythiosis cross-reacted with the 44K antigen of C. coronatus. The immunodominant antigens described here may be useful for diagnostic purposes and in immunotherapy for this oomycotic infection in horses.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alfaro A. A., Mendoza L. Four cases of equine bone lesions caused by Pythium insidiosum. Equine Vet J. 1990 Jul;22(4):295–297. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-3306.1990.tb04273.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Austwick P. K., Copland J. W. Swamp cancer. Nature. 1974 Jul 5;250(461):84–84. doi: 10.1038/250084a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bissonnette K. W., Sharp N. J., Dykstra M. H., Robertson I. R., Davis B., Padhye A. A., Kaufman L. Nasal and retrobulbar mass in a cat caused by Pythium insidiosum. J Med Vet Mycol. 1991;29(1):39–44. doi: 10.1080/02681219180000071. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown C. C., Roberts E. D. Intestinal pythiosis in a horse. Aust Vet J. 1988 Mar;65(3):88–89. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-0813.1988.tb07369.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Cock A. W., Mendoza L., Padhye A. A., Ajello L., Kaufman L. Pythium insidiosum sp. nov., the etiologic agent of pythiosis. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Feb;25(2):344–349. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.2.344-349.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goad M. E. Pulmonary pythiosis in a horse. Vet Pathol. 1984 Mar;21(2):261–262. doi: 10.1177/030098588402100224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imwidthaya P., Srimuang S. Immunodiffusion test for diagnosing human pythiosis. Mycopathologia. 1989 May;106(2):109–112. doi: 10.1007/BF00437089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman L., Mendoza L., Standard P. G. Immunodiffusion test for serodiagnosing subcutaneous zygomycosis. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Sep;28(9):1887–1890. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.9.1887-1890.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendoza L., Alfaro A. A. Equine pythiosis in Costa Rica: report of 39 cases. Mycopathologia. 1986 May;94(2):123–129. doi: 10.1007/BF00437377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendoza L., Kaufman L., Standard P. G. Immunodiffusion test for diagnosing and monitoring pythiosis in horses. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 May;23(5):813–816. doi: 10.1128/jcm.23.5.813-816.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendoza L., Kaufman L., Standard P. Antigenic relationship between the animal and human pathogen Pythium insidiosum and nonpathogenic Pythium species. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Nov;25(11):2159–2162. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.11.2159-2162.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendoza L., Marin G. Antigenic relationship between Pythium insidiosum de Cock et al. 1987 and its synonym Pythium destruens Shipton 1987. Mycoses. 1989 Feb;32(2):73–77. doi: 10.1111/j.1439-0507.1989.tb02205.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendoza L., Villalobos J., Calleja C. E., Solis A. Evaluation of two vaccines for the treatment of pythiosis insidiosi in horses. Mycopathologia. 1992 Aug;119(2):89–95. doi: 10.1007/BF00443939. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. I., Campbell R. S. Immunological studies on equine phycomycosis. Aust Vet J. 1982 Jun;58(6):227–231. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-0813.1982.tb00682.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. I., Olcott B. M., Archer M. Cutaneous pythiosis in beef calves. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1985 May 1;186(9):984–986. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. I. Treatment of equine phycomycosis by immunotherapy and surgery. Aust Vet J. 1981 Aug;57(8):377–382. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-0813.1981.tb00526.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pracharktam R., Changtrakool P., Sathapatayavongs B., Jayanetra P., Ajello L. Immunodiffusion test for diagnosis and monitoring of human pythiosis insidiosi. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Nov;29(11):2661–2662. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.11.2661-2662.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sathapatayavongs B., Leelachaikul P., Prachaktam R., Atichartakarn V., Sriphojanart S., Trairatvorakul P., Jirasiritham S., Nontasut S., Eurvilaichit C., Flegel T. Human pythiosis associated with thalassemia hemoglobinopathy syndrome. J Infect Dis. 1989 Feb;159(2):274–280. doi: 10.1093/infdis/159.2.274. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yangco B. G., Nettlow A., Okafor J. I., Park J., Te Strake D. Comparative antigenic studies of species of Basidiobolus and other medically important fungi. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Apr;23(4):679–682. doi: 10.1128/jcm.23.4.679-682.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]