Abstract
Background/Aims
Tannic acid is an orally active plant polyphenol with potential for use as an anti-cancer agent for cholangiocarcinoma. To determine the potential use of tannic acid as an adjunct therapy, we sought to evaluate the interaction between tannic acid and chemotherapeutic agents.
Methods
Cytotoxicity was assessed in malignant human cholangiocytes. Interactions between tannic acid and chemotherapeutic drugs were quantitated by calculating the combination index and dose reduction index. Cellular efflux pathways were assessed by calcein retention assays, and expression of membrane pumps was assessed by western blots and real-time PCR.
Results
Tannic acid and the three agents decreased growth of malignant cholangiocytes to a similar extent. Tannic acid had a synergistic effect to mitomycin C and 5-fluorouracil, but not gemcitabine. However, the structurally related polyphenol gallic acid did not have a synergistic interaction with any of the agents. Tannic acid decreased calcein efflux and the expression of PGP, MRP1 and MRP2 membrane efflux pumps.
Conclusions
Tannic acid has a synergistic effect with selected chemotherapeutic drugs by a mechanism involving modulation of drug efflux pathways. Thus, tannic acid will be a useful adjunct to improve the effectiveness of chemotherapeutic agents in the treatment of cholangiocarcinoma.
Keywords: chemotherapy, plant polyphenol, pharmacology, biliary cancers, treatment
INTRODUCTION
Cholangiocarcinomas are malignant tumors which arise from biliary epithelial cells (1-3). Although surgical removal offers the possibility of cure, these tumors often present at an advanced unresectable stage (4). The response to radiation therapy and currently available chemotherapeutic regimens is dismal, and consequently the prognosis is poor. In recent years, we and others have reported increases in the incidence and mortality from cholangiocarcinoma occurring worldwide (5-8). The reasons for these increases are unclear, but they emphasize the urgent need for improved treatments for these lethal tumors.
Plant derived compounds are gaining increasing interest as potential cancer therapeutics, particularly for treatment-refractory cancers such as cholangiocarcinoma. Biologically active plant-derived polyphenols can be derived from common dietary sources. Many natural compounds have anti-tumoral effects, and the underlying molecular and cellular mechanisms of action are being extensively studied. However, there is a paucity of information regarding the rational application of these agents for the clinical management of patients with human cancers. Tannic acid is a plant-derived polyphenol with direct effects against cholangiocarcinoma cells in vitro and in vivo (9). These effects include growth inhibition by blocking cell cycle progression in vitro and decreased growth of xenografts in nude athymic mice. These studies provide a rationale for the use of tannic acid in the treatment of this cancer. Therefore, further study of tannic acid in the management of patients with cholangiocarcinoma is warranted. Tannic acid is found in a variety of common foods including nuts, beans, and grapes. It is often used as a food additive and has been classified as “Generally Regarded As Safe” by the United States Food and Drug Administration (10).
Cholangiocarcinomas have a poor response to currently available chemotherapeutic agents, and moreover have a poor prognosis. It is unlikely that tannic acid would be clinically used as the sole therapy for cholangiocarcinoma until phase I/II studies have demonstrated the safety and superior efficacy compared to other conventional agents has been established. Given the aggressive nature of these tumors, a more rational approach would be to use tannic acid as an adjunct to conventional chemotherapeutic agents in the treatment of cholangiocarcinoma. The commercial availability of tannic acid extracts also raises the possibility that these may be taken by patients with cholangiocarcinoma seeking to improve their outcomes. However, the effects of combining tannic acid with other chemotherapeutic agents are completely unknown. Thus, our aim was to systematically quantitate the interactions between tannic acid and selected chemotherapeutic agents used for the treatment of cholangiocarcinoma. We asked the following questions: What is the sensitivity of human cholangiocarcinoma cells to tannic acid compared to other chemotherapeutic drugs? What is the nature of the interaction between tannic acid and chemotherapy? Will combining tannic acid with chemotherapeutic agents allow for a reduction in dose for the latter without affecting efficacy? Does tannic acid modulate chemotherapy-induced apoptosis?
Materials and Methods
Cell Lines and Culture
MzChA-1, TFK-1 and CC-LP-1 human cholangiocarcinoma cells originating from gall-bladder, extrahepatic and intrahepatic tumors respectively. Mz-ChA-1 and TFK-1 cells were obtained and cultured as previously reported (9, 11), whereas CC-LP-1 cells were obtained from Patricia Whiteside (University of Pittsburgh, Pittsburgh, PA) and cultured in Dulbecco's Modified Eagle Medium, supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (Sigma, St. Louis, MO), 1% pyruvate and 1% antibiotic/antimycotic solution (Gibco BRL, Gaithersburg, MD).
Analysis of Interactions
A commercial software package (Calcusyn, Biosoft, Cambridge, United Kingdom), was used for median-effect analysis as described by Chou and Talalay (12). The median effect equation: fa/fu = (D/Dm)m was applied where D is the dose, Dm is the potency, fa is the fraction affected, fu is the unaffected fraction, and m is the coefficient of sigmoidicity of the dose-effect curve. The dose effect curve was plotted using a logarithmic conversion of this equation to: log(fa/fu)=m log(D)-m log(Dm) for each agent and then in fixed ratio combinations. We calculated the combination index (CI) based on the formula: CI = (D)1/(Dx)1 + (D)2/(Dx)2 (CI = 1 an additive effect, CI > 1 an antagonistic effect, and CI < 1 a synergistic effect). A Dose Reduction Index (DRI) then provides the possible reduction in dose of a drug in a synergistic combination to achieve a given effect level compared with the dose of the drug alone. This was determined based on the CI equation (DRI)1 = (Dx)1/(D)1.
Proliferation Index
Cells were seeded onto 96-wellplates, and thn incubated in culture media in the presence or absence of test agent or diluent for 72 hours. The proliferation index was then assessed as we have previously described using a commercial cell proliferation assay (CellTiter96 AQ; Promega Corp., Madison, WI) (13).
Apoptosis assay
Cells with morphological changes indicative of cell death by apoptosis were identified and quantitated by fluorescence microscopy using an Olympus BX40 upright fluorescence microscope (Olympus America, Inc., Melville, NY) after staining with DAPI as previously described (14). Apoptotic nuclei were identified by condensed chromatin as well as nuclear fragmentation. At least 250 nuclei in 4 high-power fields were counted. Each experiment was performed in triplicate for each drug concentration and repeated at least three times.
Calcein Efflux
Cellular drug efflux was analyzed by determining the loss of intracellular calcein (Molecular Probes, Eugene OR), which is a marker of functional drug efflux. After being pre-incubated with polyphenol for 48 hours, 10,000 cells were plated in fresh media in 96 well plates. The cells were then labeled with calcein AM (1 μM) and maintained at 37°C for 30 minutes. The rate of loss of calcein fluorescence was assessed over a six hour period using a CytoFluor 4000 fluorometer (PerSeptive Biosystems, Framingham, MA) with excitation wavelengths of 485 nm and emission wavelengths of 535 nm.
5-Fluorouracil DNA incorporation assay
MzChA-1 cells (1 × 105) were plated in 60 mm dishes and pre-treated with 10 μM tannic acid or diluent for 48 hours in 2 ml of media containing 10% serum. Subsequently, 5μM [6-3H]-5-fluorouracil (Moravek Biochemicals, Brea, CA) or diluent was added to a final volume of 2.5 ml. After 24 hours, cells were harvested and DNA was isolated using a DNA extraction kit (Qiagen, Valencia, CA). 3H-5FU content in DNA was analyzed using a TRI-CARB 2100TR Liquid Scintillation Analyzer (Packard Instrument Co, Downers Grove, IL) and 3H-5-FU incorporation into DNA was expressed as disintegrations per minute (DPM) per μg DNA.
Western blot analysis
Western blots were performed as previously described (15). Cell lysates were obtained and separated on a 4-12% Bis-Tris gel (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA) and immunoblotted overnight onto a 0.45μm nitrocellulose membrane. The membranes were incubated sequentially with mouse monoclonal antibodies to PGP, MRP-1 or MRP-2 at a dilution of 1:1000, and with a secondary goat-anti-mouse or rabbit antibody at a dilution of 1:5000. Proteins were visualized and quantitated using the Odyssey imaging system (LiCor, Lincoln, NE).
Isolation of RNA and Real-Time PCR Quantification
Quantitative real-time PCR was performed using a MX 3000P™ PCR Instrument (Stratagene, San Diego, CA) as previously described(11). The mRNA level of β-actin was used as internal control. Each 20-μl reaction mixture consisted of 2 μl of cDNA (50 ng/μl), 10 μl of 2X Universal SYBR Green PCR Master Mix (Sigma), and 2 μl of 20 μm forward and reverse primers. Primer sequences were designed using Primer Express Software (PerkinElmer Life Sciences): PGP forward: 5-GCAAGAGGAGCAGCTTAT-GAAG-3′ and PGP reverse; 5-ACTCCCTACCTTCAAGTTGAGG-3′; MRP-1 forward: 5-GCAACCCCGACTTCACCAAGTG -3′ and MRP-1 reverse 5-GTAGAAGAGGTCTGCCCAGCAG-3′;MRP-2 forward: 5-CTGCCTCTTCAGAATCTTAG-3′ and MRP-2 reverse 5-CCCAAGTTGCAGGCTGGCC-3′; β-actin forward; 5′-CCAAGGCCAACCGCGAGAAGATGAC-3′ and β-actin reverse; 5′-AGGGTACATGGTGGTGCCGCCAGAC-3′. PCR parameters were as follows: 10 min at 95 °C, and then 40 cycles of 30 s at 94 °C, 1 min at 55°C, and 1 min at 70°C. The specificity of the produced amplification product was confirmed by melting curve analysis of the reaction products using SYBR Green as well as by visualization on ethidium bromide-stained 1.8% agarose gels to confirm a single band of the expected size. Each sample was tested in triplicate with quantitative PCR, and samples obtained from at least three independent experiments were used for calculation. Threshold values were determined for each sample/primer pair, and mRNA expression was normalized against β-actin expression.
Materials
Fetal bovine serum and Bradford reagent were obtained from Sigma (St Louis, MO). All other cell culture reagents and media were from Gibco BRL (Grand Island, New York). Antibodies to PGP, MRP-1 and MRP-2 were obtained from Chemicon International (Temecula, CA). Gemcitabine was provided by Eli Lilly (Indianapolis, IN). 5-fluorouracil and mitomycin C were purchased from Calbiochem (San Diego, CA)
Statistical Analysis
Data are expressed as the mean ± standard error (SE) from at least three separate experiments performed in triplicate, unless otherwise noted. The differences between groups were analyzed using a double sided Student's t test when only two groups were present. Statistical significance was considered as p < 0.05. Statistical analyses were performed with the GB-STAT statistical software program (Dynamic Microsystems Inc., Silver Spring, MD).
RESULTS
Sensitivity of Mz-ChA-1 malignant cholangiocytes to chemotherapy
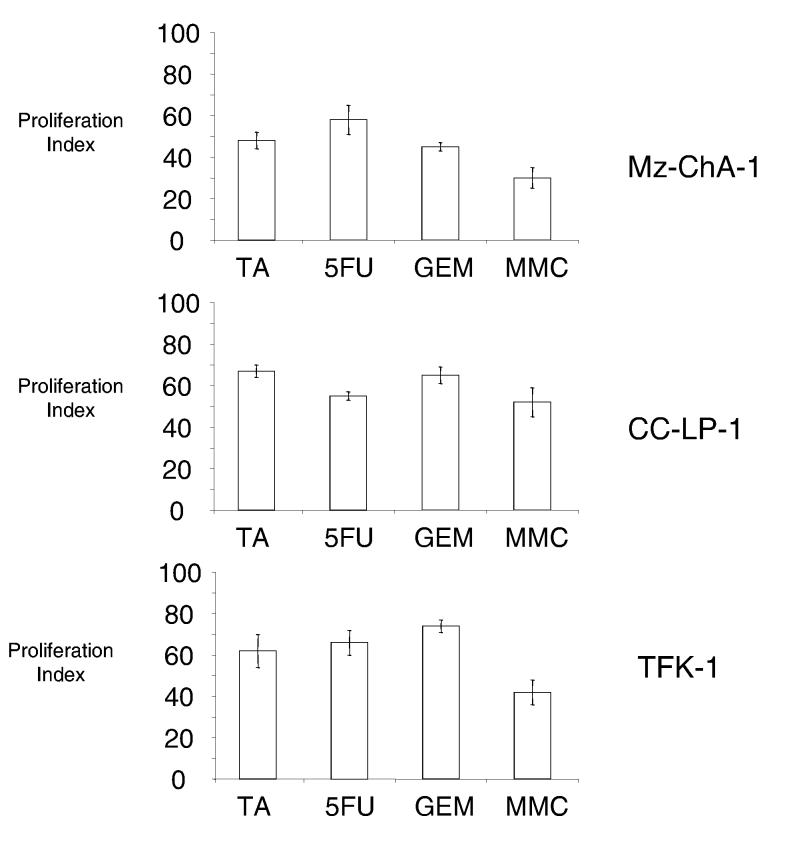
We began by characterizing the chemosensitivity of Mz-ChA-1 cells to conventional chemotherapeutic agents. For our studies, we chose 5-fluorouracil, gemcitabine, and mitomycin C given their reported efficacy in patient-based clinical studies in persons with biliary tract cancers. Furthermore, these drugs differ in their major mechanism of action. Growth inhibition by 5-fluorouracil, gemcitabine and tannic acid is concentration-dependent (9). Similar results were also observed with mitomycin C, and moreover, similar growth inhibition was observed with all agents at equimolar concentrations in several different cholangiocarcinoma cell lines (Fig 1).
Figure 1.
Growth inhibitory effects of tannic acid and chemotherapeutic agents. Mz-ChA-1, CC-LP-1 and TFK-1 human cholangiocarcinoma cells were incubated with 50 μM tannic acid (TA), 5-fluorouracil (5FU), gemcitabine (GEM), mitomycin C (MMC) or their respective control diluents. Proliferation was assessed after 72 hours, and the proliferation index calculated. Growth inhibition by tannic acid was similar to that of the chemotherapeutic agents. The data represents mean and 95% confidence intervals from 3-5 separate studies.
Tannic acid increases sensitivity of Mz-ChA-1 malignant cholangiocytes to chemotherapy
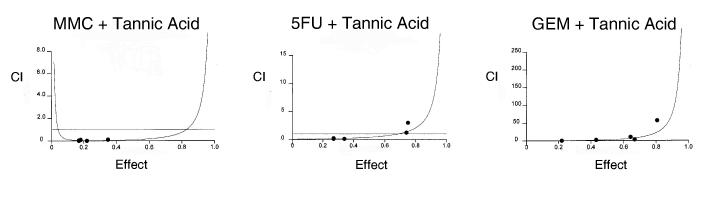
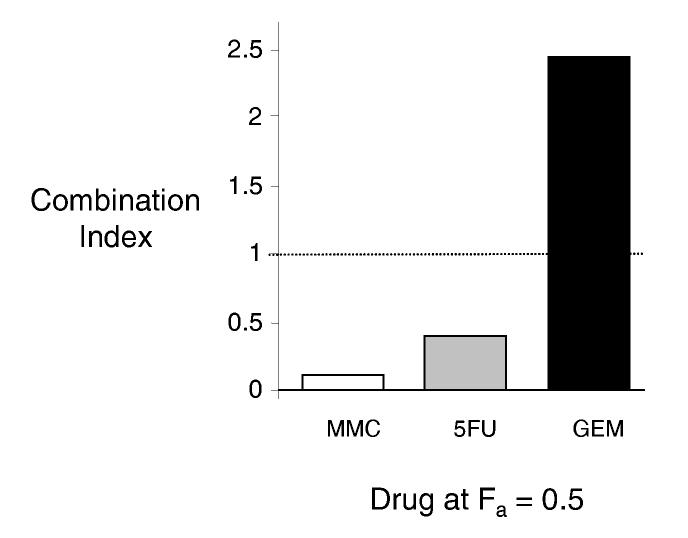
Understanding the effects of tannic acid on drug efficacy is essential prior to using tannic acid as an adjunct agent to chemotherapy. We therefore assessed the effect of tannic acid on drug-induced cytotoxicity. The nature of the interaction between tannic acid and chemotherapeutic drugs was quantitated by using the median effects analysis to derive a combination index. A combination index (CI) of 1 indicates an additive effect, whereas a CI > 1 indicates an antagonistic effect, and a CI < 1 indicates a synergistic effect. The results of the median effects analysis are depicted in Figure 2. Combinations of tannic acid with either mitomycin C or 5-fluorouracil were synergistic with a CI at an effective dose for 50% inhibition (ED50) of 0.1 ± 0.4 for mitomycin C and a CI at ED50 of 0.4 ± 0.2 for 5-fluorouracil. The synergistic effect of tannic acid on cytotoxicity by mitomycin C persisted at higher dose-effect combinations (data not shown). In contrast, the combination of tannic acid with gemcitabine had a CI at ED50 of 2.4 ± 0.9. Taken together these observations confirm that tannic acid has a selective synergistic effect to both mitomycin C and 5-fluorouracil, but not with gemcitabine.
Figure 2.
Interaction between tannic acid and chemotherapeutic drugs. The effect of tannic acid on chemotherapeutic effect was assessed in Mz-ChA-1 cells. A median effect analysis was performed and a combination index was derived for each two drug combination. A combination index <1, 1 or >1 indicates a synergistic, additive, or antagonistic interaction. Panel A. Individual plots of combination index against fractional effect for tannic acid in combination with mitomycin (MMC), 5-fluorouracil (5FU) or gemcitabine (GEM). Panel B. Plot of combination index for combinations of tannic acid with the indicated chemotherapeutic agents at their respective effective dose for 50% toxicity (fractional effect, Fa=0.5). The combination of MMC or 5FU with tannic acid was highly synergistic, but the combination of tannic acid and gemcitabine was not. Similar changes are noted over a broad range of fractional effect levels.
To examine the potential synergistic effect of other structurally related polyphenols, we performed a similar analysis using gallic acid. In contrast to the findings with tannic acid, gallic acid was not synergistic with any one of the three chemotherapeutic drugs. At an ED50, the CI for gallic acid in combination with mitomycin C was 5.7 ± 9.2, with 5-fluoro-uracil was 3.2 ± 2.7 and with gemcitabine was 4.5 ± 2.3. Similarly, the combination of mitomycin C with two other polyphenols, ellagic acid and quercetin was not synergistic either, with a CI at ED50 of mitomycin C of 5.1 ± 2.2 and 3.5 ± 3.2 respectively.
A similar analysis was performed using TFK-1 and CC-LP-1 cells. The growth inhibitory effects of tannic acid on these cell lines is similar to that observed with Mz-ChA-1 cells (Fig 1). In both these cell lines, the combination of tannic acid with 5-fluoro-uracil was synergistic. For TFK-1 cells, the CI at ED50 was 0.6 ± 0.2 whereas for CC-LP-1, the CI at ED50 was 0.5 ± 0.2. Thus, the synergistic effect of tannic acid is observed in cholangiocarcinoma cells originating from anatomically distinct sites.
The dose-reduction effect of tannic acid is similar to that of gemcitabine in combination with 5-fluorouracil or mitomycin C
Synergism between therapeutic agents allows for the reduction of doses used to minimize unwanted adverse effects while maintaining therapeutic efficacy. Thus we calculated the dose-reduction index (DRI) of combinations of tannic acid with 5-fluorouracil, mitomycin C and gemcitabine. A DRI > 1 correlates with a synergistic interaction. The most effective combination was that of mitomycin C + gemcitabine followed by mitomycin C + 5-fluorouracil and subsequently 5-fluorouracil + gemcitabine. Since our observations raise the possibility that tannic acid may be useful as an adjunct therapy with either mitomycin C or 5-fluorouracil, we next quantitated the effect of either tannic acid or gemcitabine in combination with mitomycin C or 5FU (Table 1). Combinations of tannic acid with mitomycin C or 5-fluorouracil allowed for a dose-reduction at their ED50 of 9.7-fold with mitomycin C and 3.2-fold with 5-fluorouracil. However, the dose reduction index for gemcitabine and TA was 0.43. The dose-reduction effects of TA in combination with 5FU or mitomycin C were similar to those observed with a combination of either one of these drugs with gemcitabine. The DRI of combinations with gemcitabine with 5-fluorouracil was decreased by 2.7-fold, whereas the DRI with mitomycin C was decreased by 4.4-fold. In addition, the DRI for mitomycin C and gallic acid was only 0.18 consistent with our observations that gallic acid did not have a synergistic effect on chemotherapeutic drug effect.
Tannic acid increases drug-induced apoptosis
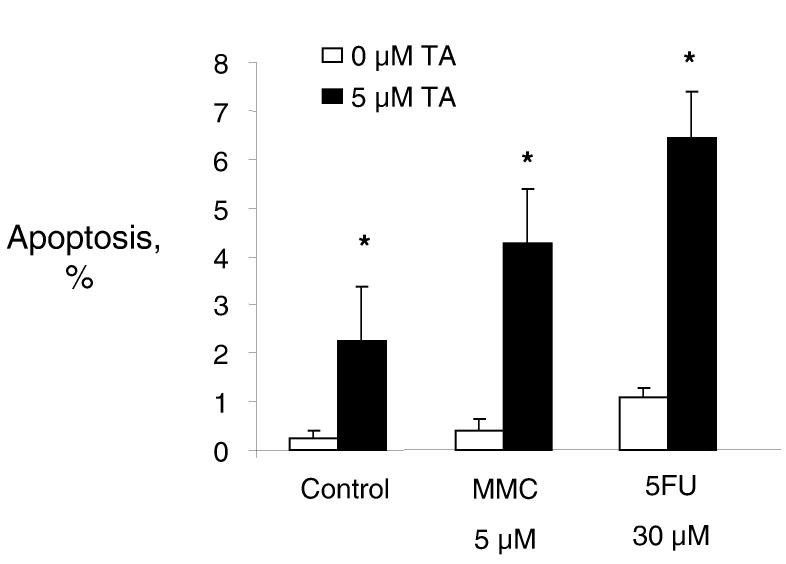
Induction of apoptosis is a mechanism by which chemotherapeutic drugs induce cytotoxicity. Although tannic acid does not directly induce apoptosis at the concentrations used, co-incubation with tannic acid increased apoptosis by either 5-fluorouracil or mitomycin C (Fig 4). Thus, tannic acid may enhance cytotoxicity by increasing drug-induced apoptosis. Although tannic acid can inhibit cell cycle progression, a synergistic effect with the alkylating agent mitomycin C that cross-links DNA and is cell-cycle independent, and the divergent effects of tannic acid on the cell-cycle dependent agents 5-fluorouracil and gemcitabine indicates that apoptosis is unlikely to occur solely as a result of abrogated cell cycle progression.
Figure 4.
Tannic acid increases chemotherapy-induced apoptosis. Mz-ChA-1 cells were incubated with either MMC or 5FU used at its ED50, alone (white bars) with or without 5 μM tannic acid (black bars). After 6 hours, cells were stained with 1 μM DAPI, visualized using a fluorescence microscope, and the number of apoptotic cells were counted. At least 250 cells were counted for each condition. The percentage of cells with morphological features of apoptosis are plotted on the vertical axis. Compared to controls, the addition of tannic acid increases drug-induced apoptosis. Data represents mean and 95% confidence intervals of data from five separate studies. * p<0.05 compared to apoptosis in the absence of tannic acid.
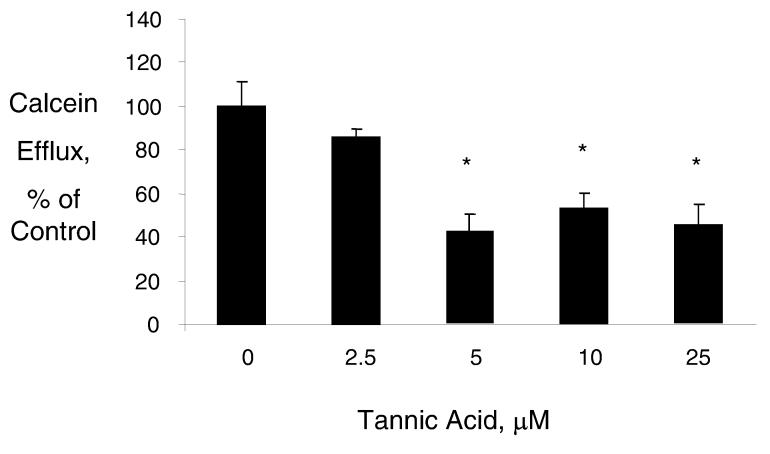
Tannic acid decreases cellular calcein efflux
Drug-induced cytotoxicity could be enhanced by mechanisms that increase intracellular concentrations due to decreased drug efflux from cancer cells. Thus, we assessed the effect of tannic acid on cellular efflux pathways in malignant cholangiocytes. Cells were loaded with calcein-AM and activity of cellular efflux pathways assessed by determining the loss of intracellular calcein fluorescence. Incubation with tannic acid decreased calcein efflux, with a dramatic effect noted at a concentration of 5 μM tannic acid which decreased calcein efflux to 41 ± 7% of controls (Fig 5). In contrast, calcein efflux was increased by 5 μM gallic acid to 288 ± 48% of control, and was unchanged by 30 μM quercetin at 98 ± 8% of control. These findings correlate with the observations made regarding the interactions of these polyphenol compounds on chemotherapy drug action. Taken together, these results suggest that inhibition of drug efflux mechanisms is a mechanism by which tannic acid could enhance chemotherapy drug toxicity in malignant cholangiocytes.
Figure 5.
Tannic acid decreases calcein efflux. Mz-ChA-1 cells were incubated with the indicated concentrations of tannic acid for 48 hours, prior to loading with calcein. The loss of intracellular calcein was assessed as a marker of drug efflux and determined as the rate of loss of calcein fluorescence over 6 hours. Calcein efflux was expressed relative to untreated controls. Incubation with tannic acid decreased calcein efflux. Data represent mean and standard error of six separate studies. * p< 0.05 relative to untreated controls.
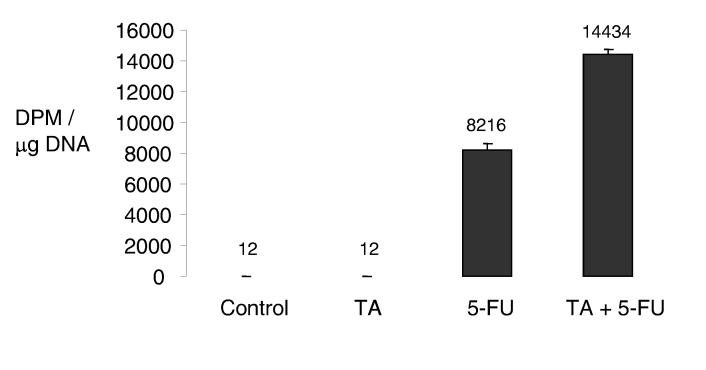
To verify the presence of such a mechanism, we assessed DNA incorporation of 5-FU as a measure of intracellular 5-FU concentrations (16). Mz-ChA-1 cells were pre-incubated with tannic acid for 48 hours prior to the addition on radio-labeled 5-FU. The incorporation of 5-FU in DNA was then assessed after 24 hours. Consistent with our previous findings, tannic acid significantly increased 5-FU DNA incorporation (Fig 6).
Figure 6.
Tannic acid increases DNA incorporation of 5-fluourouracil. Mz-ChA-1 cells (1 × 105 / 60 mm plate) were pre-incubated with diluent or 10 μM tannic acid for 48 hours prior to the addition of 5μM 3H-5-fluorouracil or diluent. After 24 hours, cells were harvested and DNA was isolated and quantitated. Incorporation of radiolabeled 5-FU in DNA was assessed using a liquid scintillation analyzer and expressed as disintegrations per microgram DNA. Data represent mean and 95% confidence intervals of four studies. * p<0.05 relative to diluent controls.
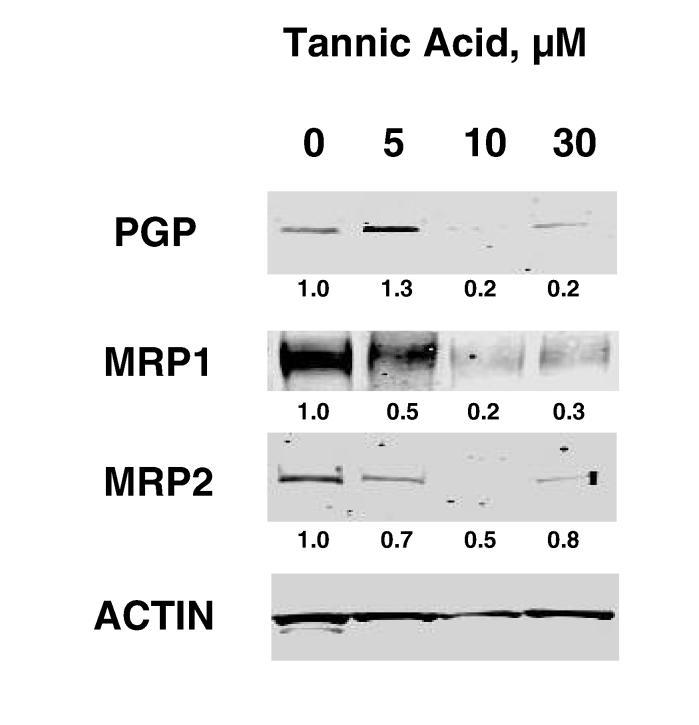
Tannic acid decreases expression of drug-efflux transporters, PGP and MRP 1,2
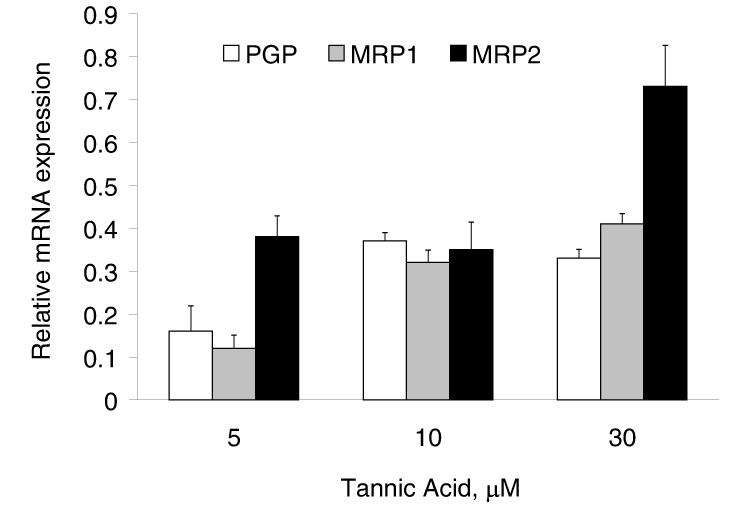
To assess the mechanism by which tannic acid modulates cellular efflux pathways, we evaluated the expression of specific membrane pumps involved in cellular efflux. The P-glycoprotein (PGP) and multidrug resistance proteins (MRP) 1 and 2 are membrane pumps that have been shown to be expressed in cholangiocytes (17-20). Moreover, over-expression of these proteins has been shown to be associated with drug resistance. Incubation with tannic acid decreased protein expression of PGP, MRP-1 and MRP-2 after 48 hours (Fig 7). To verify that tannic acid could modulate gene expression, mRNA expression was assessed using real-time PCR. Indeed, a reduction of expression of all three membrane pumps was observed with tannic acid. In contrast, gallic acid did not alter MRP-1 but did decrease PGP and MRP-2 mRNA expression (data not shown). The greatest decrease in mRNA expression was observed at a concentration of 5 μM tannic acid. Since the calcein efflux assay is a functional assay, there is a possibility that tannic acid could act by mechanisms other than modulation of expression of drug efflux proteins such as by directly inhibiting the activity of efflux pumps. Indeed, tannic acid has also been shown to act as a direct inhibitor of the glutathione conjugate export pump, or multidrug resistance protein. Thus, our data support alterations in the expression or function of drug efflux pathways as a mechanism by which tannic acid can modulate the response to chemotherapy.
Figure 7.
Tannic acid modulates the expression of membrane pumps involved in drug efflux. Panel A. Mz-ChA-1 cells were incubated with varying concentrations of tannic acid. After 48 hours, cells were lysed and expression of PGP, MRP-1 and MRP-2 assessed by western blots. The panel shows a representative immunoblot, whereas the figures represent quantitative data for expression relative to β-actin from 3 separate blots. Panel B. MzChA-1 cells were incubated with tannic acid at the indicated concentrations. After 48 hours, RNA was isolated, and cDNA obtained by reverse transcription. Real-time PCR was performed to quantitate the mRNA expression of PGP, MRP-1 and MRP-2. For each condition, mRNA expression was normalized to β-actin and expressed relative to that of diluent alone controls. A decrease in expression of these membrane pumps was noted (p<0.05 for all conditions relative to expression in untreated controls). Data represent the mean and 95% confidence intervals from four studies.
DISCUSSION
The refractoriness of cholangiocarcinoma to conventional single-drug regimens supports the use of combination drug approaches if drug-related toxicity can be minimized. However, the use of combination therapies has not resulted in improved treatment response rates in cholangiocarcinoma. The limited efficacy of multiagent treatments for cholangiocarcinoma may reflect the lack of synergy between the agents and the dose-limiting toxicities of individual agents. We have shown that tannic acid increases drug-induced apoptosis and have a synergistic effect on cytotoxicity by either 5-fluorouracil or mitomycin C. Moreover, the dose-reduction achieved by the use of tannic acid in combination with 5-fluorouracil or mitomycin C is similar to that achieved by the use of gemcitabine. Tannic acid alters cellular efflux and decreases the expression of several membrane pumps involved in drug efflux and chemoresistance indicating that tannic acid could enhance drug induced cytotoxicity by increasing intracellular drug concentrations.
The use of a safe and synergistic agent such as tannic acid may therefore be expected to enhance treatment response rates for unresectable cholangiocarcinoma. Oral tannic acid is regarded as being safe in humans and is currently used as a food additive commercially. The addition of tannic acid to regimens of either mitomycin C or 5-fluorouracil would be expected to increase the cytotoxic effect at a given dosage level while minimizing side effect toxicity. The safety and independent anti-cancer effect of tannic acid support the use of tannic acid as an adjunct to these agents. Patient-based trials to formally evaluate the use of tannic acid either as monotherapy or as an adjunct to other chemotherapeutic regimens are justified.
Gemcitabine is a nucleoside drug that can be transported across cell membranes by facilitated diffusion and does not act as a substrate for drug efflux pumps such as PGP or MRP (21). However, gemcitabine sensitivity appears to be related to the expression of these membrane pumps. Enhanced sensitivity to gemcitabine has been described with over-expression of PGP and MRP1 in cancer cells but the mechanisms remain unknown (22). Our results showing an antagonist effect with gemcitabine with tannic acid, which decreases PGP and MRP1 expression are consistent with these reported observations and suggest that the use of tannic acid with gemcitabine may not enhance therapeutic responses.
In addition to its potential for use as an anti-cancer agent for cholangiocarcinoma, tannic acid may be potentially useful for structure-based approaches to identify and develop novel drug efflux inhibitors. Increased expression of membrane pumps such as MDR-1 enhance drug efflux and are associated with chemoresistance and subsequently with a poor clinical response. Concomitant inhibition of drug efflux along with the use of chemotherapeutic drugs is a promising strategy for highly chemo-resistant tumors. Although several structure-based inhibitors of MDR-1 have being developed, their therapeutic efficacy has been limited. The use of a natural product such as tannic acid that has both anti-cancer effects and can modulate drug efflux is more likely to yield effective agents and provides a logical basis for rational drug development.
These studies justify the use of tannic acid as an adjunct to chemotherapy based regimens for the management of cholangiocarcinoma. They provide a rationale for further study of the pharmacokinetics, and pharmacodynamics of orally administered tannic acid in humans, and clinical studies to determine the effectiveness of these combinations in the treatment of this devastating cancer.
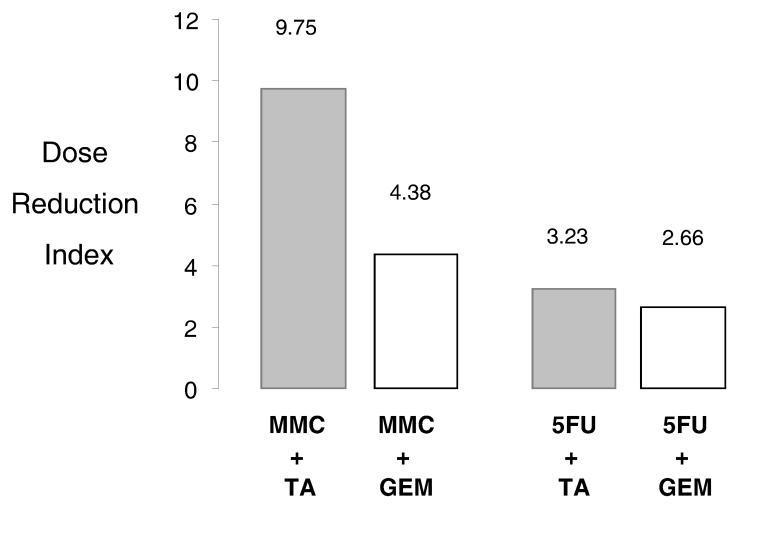
Figure 3.
Tannic acid (TA) allows dose reduction when combined with 5-fluorouracil (5FU) or mitomycin C (MMC). The dose-reduction effect is a measure of how much the dose of each drug in a synergistic combination may be reduced at a given effect level compared with the doses of each drug alone. The dose-reduction index was calculated for MMC and 5FU using the mean values of the proliferative index of four separate studies for Mz-ChA-1 cells. When TA is combined with either agent, there is a marked dose reduction possible, which is greater for MMC than for 5FU (grey bars). The use of gemcitabine (GEM) in combination with MMC allows a much lower dose-reduction for MMC, but a comparable reduction in 5FU dose compared to the combination of tannic acid with these agents (white bars).
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work was supported by the Scott & White Hospital Foundation and by Public Health Service grant DK60637 and DK69370 from the National Institute of Diabetes, Digestion and Kidney Diseases.
Abbreviations
- 5FU
5-flurouracil
- CI
Combination Index
- DRI
Dose-Reduction Index
- ED
Effective dose
- Gem
Gemcitabine
- MMC
Mitomycin C
Footnotes
Publisher's Disclaimer: This is a PDF file of an unedited manuscript that has been accepted for publication. As a service to our customers we are providing this early version of the manuscript. The manuscript will undergo copyediting, typesetting, and review of the resulting proof before it is published in its final citable form. Please note that during the production process errorsmaybe discovered which could affect the content, and all legal disclaimers that apply to the journal pertain.
References
- 1.Patel T. Cholangiocarcinoma. Nat Clin Pract Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2006 Jan;3(1):33–42. doi: 10.1038/ncpgasthep0389. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Sirica AE. Cholangiocarcinoma: molecular targeting strategies for chemoprevention and therapy. Hepatology. 2005 Jan;41(1):5–15. doi: 10.1002/hep.20537. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Lazaridis KN, Gores GJ. Cholangiocarcinoma. Gastroenterology. 2005 May;128(6):1655–1667. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2005.03.040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Khan SA, Thomas HC, Davidson BR, Taylor-Robinson SD. Cholangiocarcinoma. Lancet. 2005 Oct 8;366(9493):1303–1314. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(05)67530-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Patel T. Increasing incidence and mortality of primary intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma in the United States. Hepatology. 2001 Jun;33(6):1353–1357. doi: 10.1053/jhep.2001.25087. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Patel T. Worldwide trends in mortality from biliary tract malignancies. BMC Cancer. 2002 May 3;2(1):10. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-2-10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Khan SA, Taylor-Robinson SD, Toledano MB, Beck A, Elliott P, Thomas HC. Changing international trends in mortality rates for liver, biliary and pancreatic tumours. J Hepatol. 2002 Dec;37(6):806–813. doi: 10.1016/s0168-8278(02)00297-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Taylor-Robinson SD, Toledano MB, Arora S, Keegan TJ, Hargreaves S, Beck A, et al. Increase in mortality rates from intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma in England and Wales 1968-1998. Gut. 2001 Jun;48(6):816–820. doi: 10.1136/gut.48.6.816. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Marienfeld C, Tadlock L, Yamagiwa Y, Patel T. Inhibition of cholangiocarcinoma growth by tannic acid. Hepatology. 2003 May;37(5):1097–1104. doi: 10.1053/jhep.2003.50192. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Direct Food Substances Affirmed as Generally Recognized as Safe. 2002;(Pt 84) Report No.: Title 21 (1989) [Google Scholar]
- 11.Yamagiwa Y, Meng F, Patel T. Interleukin-6 decreases senescence and increases telomerase activity in malignant human cholangiocytes. Life Sci. 2005 Dec 3; doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2005.10.015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Chou TC, Talalay P. Quantitative analysis of dose-effect relationships: the combined effects of multiple drugs or enzyme inhibitors. Adv Enzyme Regul. 1984;22:27–55. doi: 10.1016/0065-2571(84)90007-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Park J, Tadlock L, Gores GJ, Patel T. Inhibition of interleukin 6-mediated mitogen-activated protein kinase activation attenuates growth of a cholangiocarcinoma cell line. Hepatology. 1999 Nov;30(5):1128–1133. doi: 10.1002/hep.510300522. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Yamagiwa Y, Marienfeld C, Meng F, Holcik M, Patel T. Translational regulation of x-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein by interleukin-6: a novel mechanism of tumor cell survival. Cancer Res. 2004 Feb 15;64(4):1293–1298. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.can-03-2517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Tadlock L, Yamagiwa Y, Hawker J, Marienfeld C, Patel T. Transforming growth factor-beta inhibition of proteasomal activity: a potential mechanism of growth arrest. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2003 Aug;285(2):C277–C285. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00550.2002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.De Angelis PM, Svendsrud DH, Kravik KL, Stokke T. Cellular response to 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) in 5-FU-resistant colon cancer cell lines during treatment and recovery. Mol Cancer. 2006 May 18;5(1):20. doi: 10.1186/1476-4598-5-20. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Gigliozzi A, Fraioli F, Sundaram P, Lee J, Mennone A, Alvaro D, et al. Molecular identification and functional characterization of Mdr1a in rat cholangiocytes. Gastroenterology. 2000 Oct;119(4):1113–1122. doi: 10.1053/gast.2000.18156. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Rost D, Konig J, Weiss G, Klar E, Stremmel W, Keppler D. Expression and localization of the multidrug resistance proteins MRP2 and MRP3 in human gallbladder epithelia. Gastroenterology. 2001 Nov;121(5):1203–1208. doi: 10.1053/gast.2001.28648. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Courtois A, Payen L, Lagadic D, Guillouzo A, Fardel O. Evidence for a multidrug resistance-associated protein 1 (MRP1)-related transport system in cultured rat liver biliary epithelial cells. Life Sci. 1999;64(9):763–774. doi: 10.1016/s0024-3205(98)00618-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Cao L, Duchrow M, Windhovel U, Kujath P, Bruch HP, Broll R. Expression of MDR1 mRNA and encoding P-glycoprotein in archival formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded gall bladder cancer tissues. Eur J Cancer. 1998 Sep;34(10):1612–1617. doi: 10.1016/s0959-8049(98)00142-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Mackey JR, Mani RS, Selner M, Mowles D, Young JD, Belt JA, et al. Functional nucleoside transporters are required for gemcitabine influx and manifestation of toxicity in cancer cell lines. Cancer Res. 1998 Oct 1;58(19):4349–4357. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Bergman AM, Pinedo HM, Talianidis I, Veerman G, Loves WJ, van der Wilt CL, et al. Increased sensitivity to gemcitabine of P-glycoprotein and multidrug resistance-associated protein-overexpressing human cancer cell lines. Br J Cancer. 2003 Jun 16;88(12):1963–1970. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6601011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]