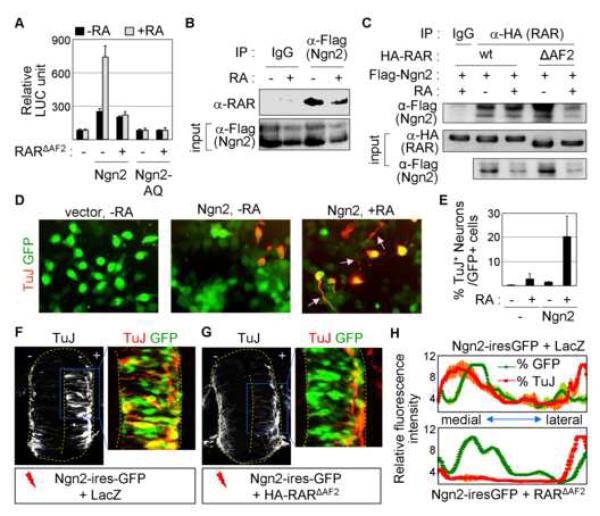
Figure 1. RA-signal stimulates Ngn2 activity through the formation of the Ngn2/RAR-complex.
(A) RA enhances the transcriptional activity of Ngn2, but not Ngn2-AQ, in E-box:LUC reporter in P19 cells. Ngn2-AQ is a Ngn2 mutant that no longer binds E-box. RARΔAF2, a RAR mutant that is unable to interact with AF2-dependent coactivators, inhibits the stimulating effect of RA on E-box:LUC. (B) Ngn2 binds RAR in a RA-independent manner in HEK293 cells, as determined by immunoprecipitation (IP) of lysates of HEK293 cells expressing Flag-Ngn2 with anti-Flag antibody followed by immunoblotting with anti-RAR antibody. (C) CoIP assays in HEK293 cells transfected with Flag-Ngn2 and either HA-RAR or HA-RARΔAF2. Both RAR and RARΔAF2 interact with Ngn2 in a RA-independent manner. (D) P19 cells transfected with vector or Ngn2-ires-GFP were treated with vehicle or RA, and analyzed for neuronal differentiation using immunostaining with anti-TuJ antibody. Arrows indicate neurite-like processes. (E) % quantification of TuJ+-neurons among GFP+-transfected P19 cells under indicated condition. (F, G) Immunohistochemical analysis of neuronal differentiation (TuJ+-cells) in HH stage 20 chick embryos electroporated with the indicated constructs on the bottom. RARΔAF2 compromises precocious neuronal differentiation triggered by Ngn2 in the medial zone of the chick neural tube. GFP+-cells mark electroporated cells. (H) Quantification of GFP (green) and TuJ (red) fluorescence intensity in the neural tube. The X-axis indicates the most medial to lateral sides of the neural tube. Coexpression of Ngn2-ires-GFP and LacZ leads to the increase in TuJ staining concomitant with GFP expression in the medial zone of the neural tube (upper panel), whereas GFP expression does not correlate with TuJ staining in the medial zone of the neural tube electroporated with Ngn2-ires-GFP and RARΔAF2 (bottom panel). (A, E) The error bars represent the standard deviation.