Abstract
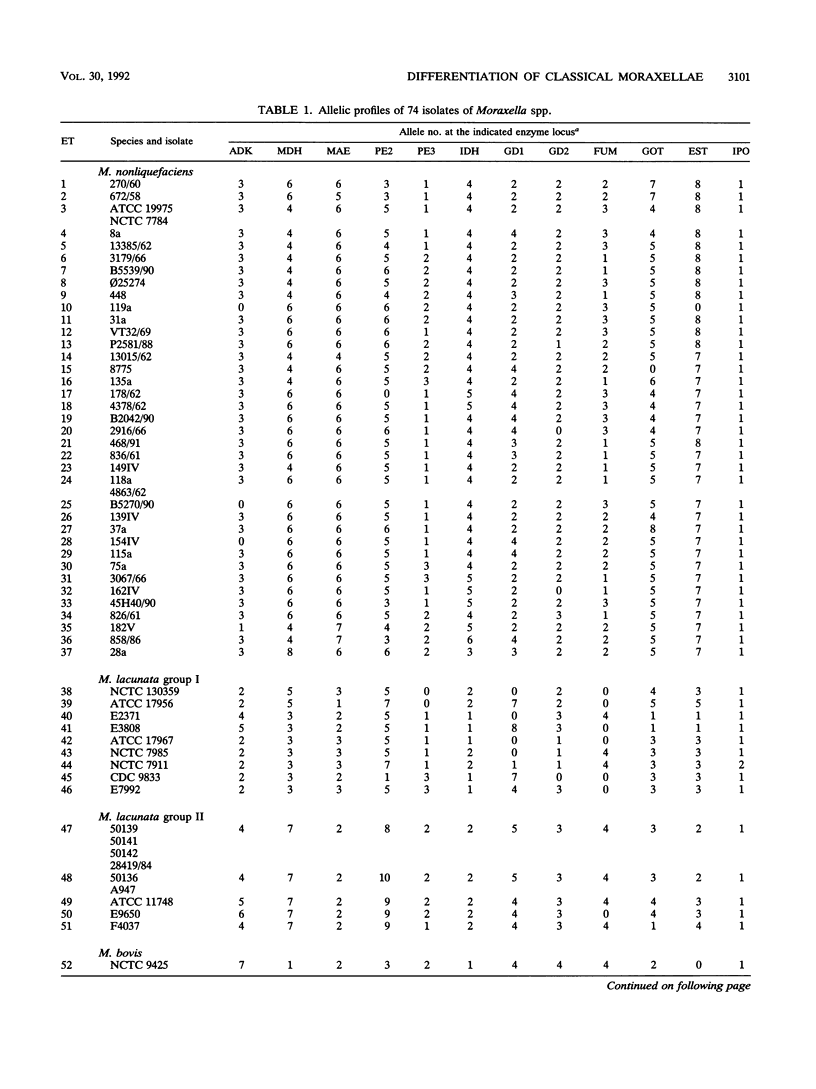
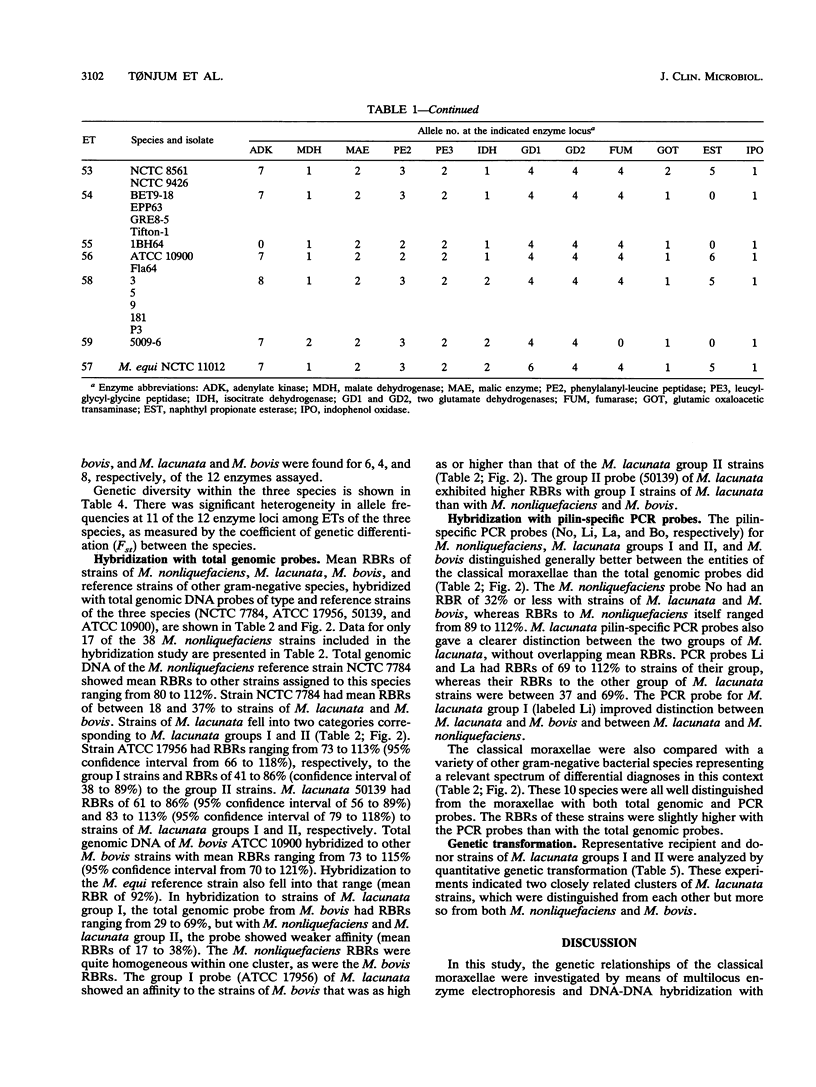
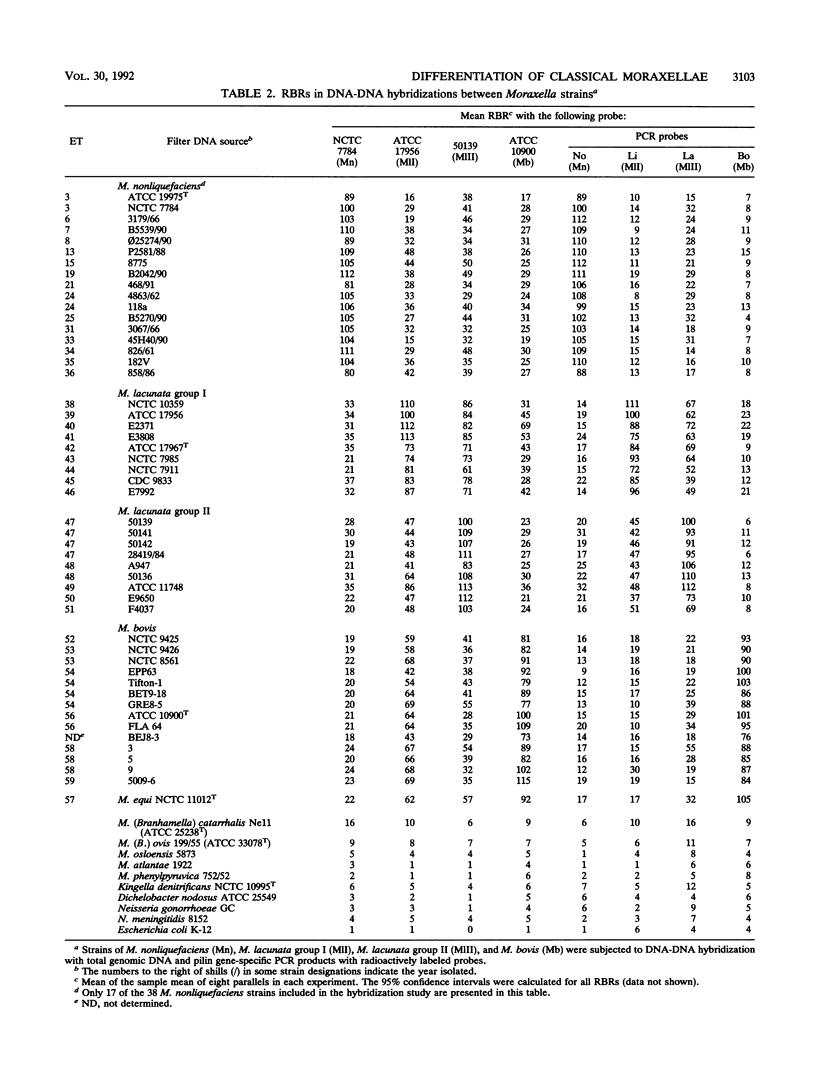
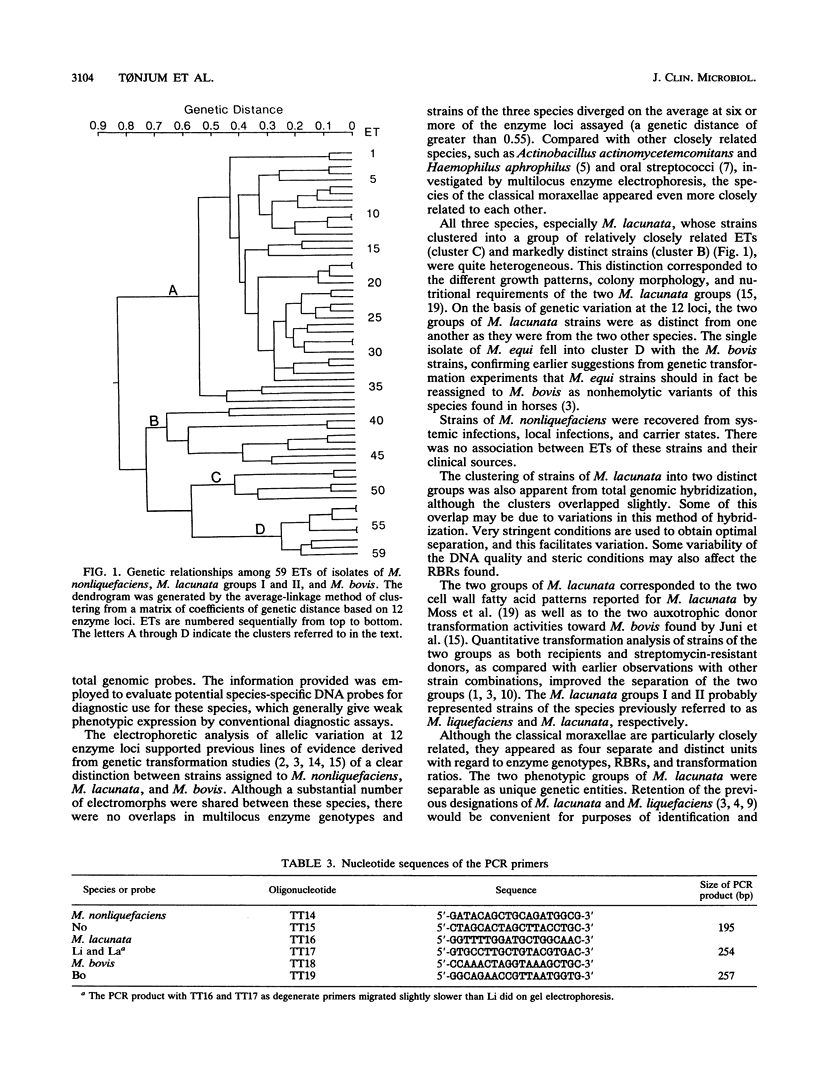
Genetic relationships among strains of Moraxella nonliquefaciens, M. lacunata, and M. bovis were studied by using multilocus enzyme electrophoresis and DNA-DNA hybridization. The 74 isolates analyzed for electrophoretic variation at 12 enzyme loci were assigned to 59 multilocus genotypes. The multilocus genotypes were grouped in four major clusters, one representing strains of M. nonliquefaciens, two representing strains of M. lacunata, and one comprising strains of M. bovis and the single strain of M. equi analyzed. DNA-DNA hybridization with total genomic probes also revealed four major distinctive entities that corresponded to those identified by multilocus enzyme electrophoresis. The two distinct clusters recognized among the M. lacunata strains apparently corresponded to the species previously designated M. lacunata and M. liquefaciens. Distinction of the four entities was improved by hybridization with polymerase chain reaction products of nonconserved parts of pilin genes as DNA probes. With these polymerase chain reaction probes, new isolates of M. nonliquefaciens, M. lacunata, M. liquefaciens, and M. bovis can be identified easily by hybridization.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bövre K. Studies on transformation in Moraxella and organisms assumed to be related to Moraxella. 5. Streptomycin resistance transformation between serum-liquefying, nonhaemolytic moraxellae, Moraxella bovis and Moraxella nonliquefaciens. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1965;65(3):435–449. doi: 10.1111/apm.1965.65.3.435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caugant D. A., Frøholm L. O., Bøvre K., Holten E., Frasch C. E., Mocca L. F., Zollinger W. D., Selander R. K. Intercontinental spread of a genetically distinctive complex of clones of Neisseria meningitidis causing epidemic disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(13):4927–4931. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.13.4927. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caugant D. A., Selander R. K., Olsen I. Differentiation between Actinobacillus (Haemophilus) actinomycetemcomitans, Haemophilus aphrophilus and Haemophilus paraphrophilus by multilocus enzyme electrophoresis. J Gen Microbiol. 1990 Oct;136(10):2135–2141. doi: 10.1099/00221287-136-10-2135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalrymple B., Mattick J. S. An analysis of the organization and evolution of type 4 fimbrial (MePhe) subunit proteins. J Mol Evol. 1987;25(3):261–269. doi: 10.1007/BF02100020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmour M. N., Whittam T. S., Kilian M., Selander R. K. Genetic relationships among the oral streptococci. J Bacteriol. 1987 Nov;169(11):5247–5257. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.11.5247-5257.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham D. R., Band J. D., Thornsberry C., Hollis D. G., Weaver R. E. Infections caused by Moraxella, Moraxella urethralis, Moraxella-like groups M-5 and M-6, and Kingella kingae in the United States, 1953-1980. Rev Infect Dis. 1990 May-Jun;12(3):423–431. doi: 10.1093/clinids/12.3.423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henriksen S. D., Bovre K. The taxonomy of the genera Moraxella and Neisseria. J Gen Microbiol. 1968 May;51(3):387–392. doi: 10.1099/00221287-51-3-387. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hermodson M. A., Chen K. C., Buchanan T. M. Neisseria pili proteins: amino-terminal amino acid sequences and identification of an unusual amino acid. Biochemistry. 1978 Feb 7;17(3):442–445. doi: 10.1021/bi00596a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes D. E., Pugh G. W., Jr A five-year study of infectious bovine keratoconjunctivitis in a beef herd. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1970 Aug 15;157(4):443–451. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hull R. A., Gill R. E., Hsu P., Minshew B. H., Falkow S. Construction and expression of recombinant plasmids encoding type 1 or D-mannose-resistant pili from a urinary tract infection Escherichia coli isolate. Infect Immun. 1981 Sep;33(3):933–938. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.3.933-938.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Juni E., Heym G. A., Maurer M. J., Miller M. L. Combined genetic transformation and nutritional assay for identification of Moraxella nonliquefaciens. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Sep;25(9):1691–1694. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.9.1691-1694.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Juni E., Heym G. A., Newcomb R. D. Identification of Moraxella bovis by qualitative genetic transformation and nutritional assays. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 May;54(5):1304–1306. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.5.1304-1306.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marrs C. F., Schoolnik G., Koomey J. M., Hardy J., Rothbard J., Falkow S. Cloning and sequencing of a Moraxella bovis pilin gene. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jul;163(1):132–139. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.1.132-139.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss C. W., Wallace P. L., Hollis D. G., Weaver R. E. Cultural and chemical characterization of CDC groups EO-2, M-5, and M-6, Moraxella (Moraxella) species, Oligella urethralis, Acinetobacter species, and Psychrobacter immobilis. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Mar;26(3):484–492. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.3.484-492.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ochman H., Whittam T. S., Caugant D. A., Selander R. K. Enzyme polymorphism and genetic population structure in Escherichia coli and Shigella. J Gen Microbiol. 1983 Sep;129(9):2715–2726. doi: 10.1099/00221287-129-9-2715. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ringvold A., Vik E., Bevanger L. S. Moraxella lacunata isolated from epidemic conjunctivitis among teen-aged females. Acta Ophthalmol (Copenh) 1985 Aug;63(4):427–431. doi: 10.1111/j.1755-3768.1985.tb01558.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selander R. K., Caugant D. A., Ochman H., Musser J. M., Gilmour M. N., Whittam T. S. Methods of multilocus enzyme electrophoresis for bacterial population genetics and systematics. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 May;51(5):873–884. doi: 10.1128/aem.51.5.873-884.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tønjum T., Bukholm G., Bøvre K. Differentiation of some species of Neisseriaceae and other bacterial groups by DNA-DNA hybridization. APMIS. 1989 May;97(5):395–405. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1989.tb00806.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tønjum T., Bukholm G., Bøvre K. Identification of Haemophilus aphrophilus and Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans by DNA-DNA hybridization and genetic transformation. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Sep;28(9):1994–1998. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.9.1994-1998.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tønjum T., Marrs C. F., Rozsa F., Bøvre K. The type 4 pilin of Moraxella nonliquefaciens exhibits unique similarities with the pilins of Neisseria gonorrhoeae and Dichelobacter (Bacteroides) nodosus. J Gen Microbiol. 1991 Oct;137(10):2483–2490. doi: 10.1099/00221287-137-10-2483. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


