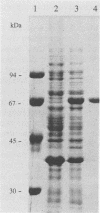
Abstract
A recombinantly expressed protein, recEh-P1, representing part of an immunodominant surface antigen of pathogenic Entamoeba histolytica, was used for serodiagnosis of invasive amebiasis. Expression was performed under the control of a T7-RNA promoter by using a modified procaryotic expression vector, designated pHisT7. This vector allowed high-yield expression of recEh-P1 fused to a stretch of sequence containing eight histidine residues, which facilitated purification by metal chelate affinity chromatography on Ni2+ columns under highly denatured conditions. Purified recEh-P1 was found to be water soluble after prolonged dialysis and was used as the antigen for the detection of antiamebic serum antibodies by immunoblotting and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. In both tests all sera of patients with invasive amebiasis reacted to recEh-P1 whereas none of those collected from healthy controls, including individuals with noninvasive amebiasis, or from patients suffering from bacterial or protozoan infections unrelated to E. histolytica did so.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Clark C. G., Diamond L. S. Ribosomal RNA genes of 'pathogenic' and 'nonpathogenic' Entamoeba histolytica are distinct. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1991 Dec;49(2):297–302. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(91)90073-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edman U., Meraz M. A., Rausser S., Agabian N., Meza I. Characterization of an immuno-dominant variable surface antigen from pathogenic and nonpathogenic Entamoeba histolytica. J Exp Med. 1990 Sep 1;172(3):879–888. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.3.879. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garfinkel L. I., Giladi M., Huber M., Gitler C., Mirelman D., Revel M., Rozenblatt S. DNA probes specific for Entamoeba histolytica possessing pathogenic and nonpathogenic zymodemes. Infect Immun. 1989 Mar;57(3):926–931. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.3.926-931.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Healy G. R. Immunologic tools in the diagnosis of amebiasis: epidemiology in the United States. Rev Infect Dis. 1986 Mar-Apr;8(2):239–246. doi: 10.1093/clinids/8.2.239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann B. J., Torian B. E., Vedvick T. S., Petri W. A., Jr Sequence of a cysteine-rich galactose-specific lectin of Entamoeba histolytica. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 15;88(8):3248–3252. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.8.3248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ravdin J. I., Jackson T. F., Petri W. A., Jr, Murphy C. F., Ungar B. L., Gathiram V., Skilogiannis J., Simjee A. E. Association of serum antibodies to adherence lectin with invasive amebiasis and asymptomatic infection with pathogenic Entamoeba histolytica. J Infect Dis. 1990 Sep;162(3):768–772. doi: 10.1093/infdis/162.3.768. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg A. H., Lade B. N., Chui D. S., Lin S. W., Dunn J. J., Studier F. W. Vectors for selective expression of cloned DNAs by T7 RNA polymerase. Gene. 1987;56(1):125–135. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90165-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley S. L., Jr, Jackson T. F., Reed S. L., Calderon J., Kunz-Jenkins C., Gathiram V., Li E. Serodiagnosis of invasive amebiasis using a recombinant Entamoeba histolytica protein. JAMA. 1991 Oct 9;266(14):1984–1986. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tachibana H., Ihara S., Kobayashi S., Kaneda Y., Takeuchi T., Watanabe Y. Differences in genomic DNA sequences between pathogenic and nonpathogenic isolates of Entamoeba histolytica identified by polymerase chain reaction. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Oct;29(10):2234–2239. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.10.2234-2239.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tannich E., Burchard G. D. Differentiation of pathogenic from nonpathogenic Entamoeba histolytica by restriction fragment analysis of a single gene amplified in vitro. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Feb;29(2):250–255. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.2.250-255.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tannich E., Ebert F., Horstmann R. D. Primary structure of the 170-kDa surface lectin of pathogenic Entamoeba histolytica. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 1;88(5):1849–1853. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.5.1849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tannich E., Horstmann R. D., Knobloch J., Arnold H. H. Genomic DNA differences between pathogenic and nonpathogenic Entamoeba histolytica. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(13):5118–5122. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.13.5118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh J. A. Problems in recognition and diagnosis of amebiasis: estimation of the global magnitude of morbidity and mortality. Rev Infect Dis. 1986 Mar-Apr;8(2):228–238. doi: 10.1093/clinids/8.2.228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]