Abstract
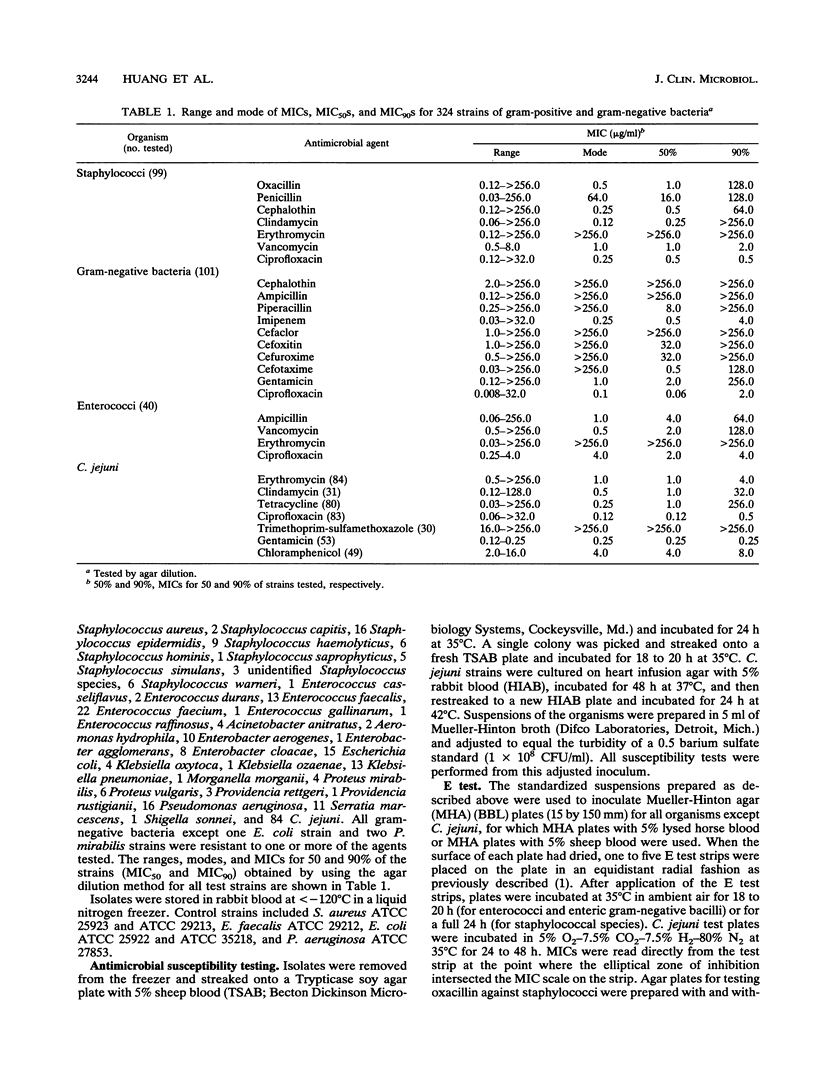
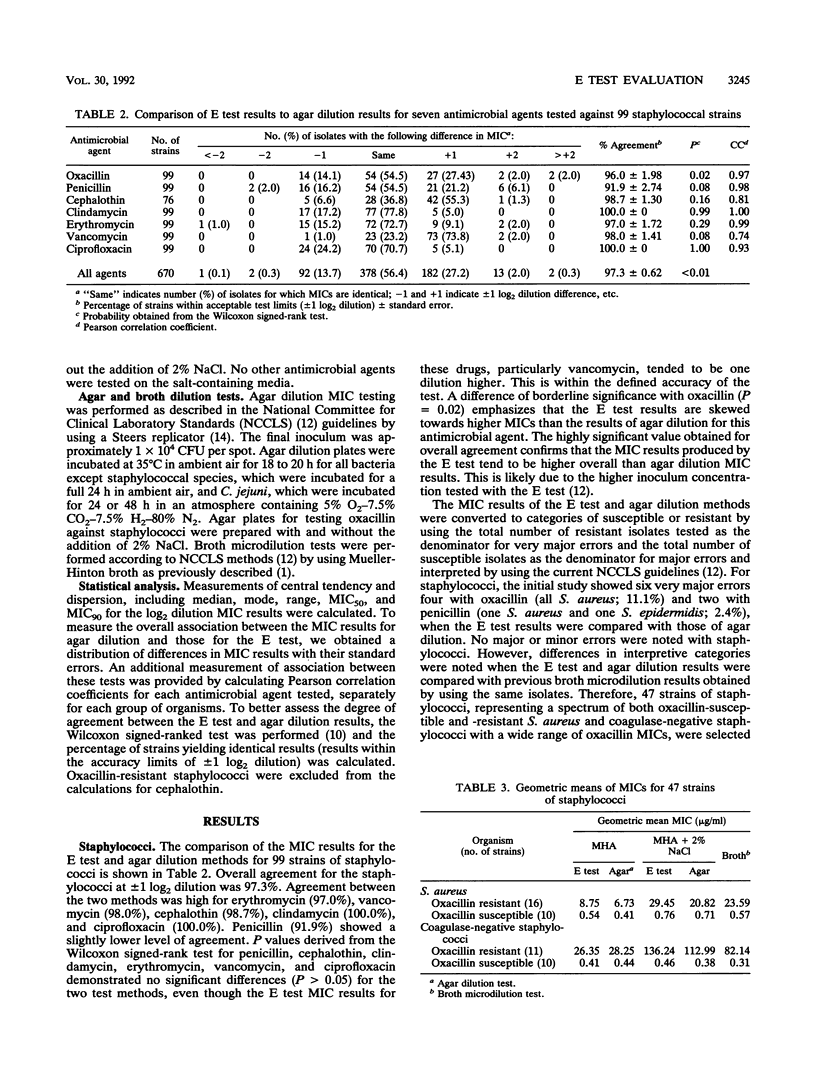
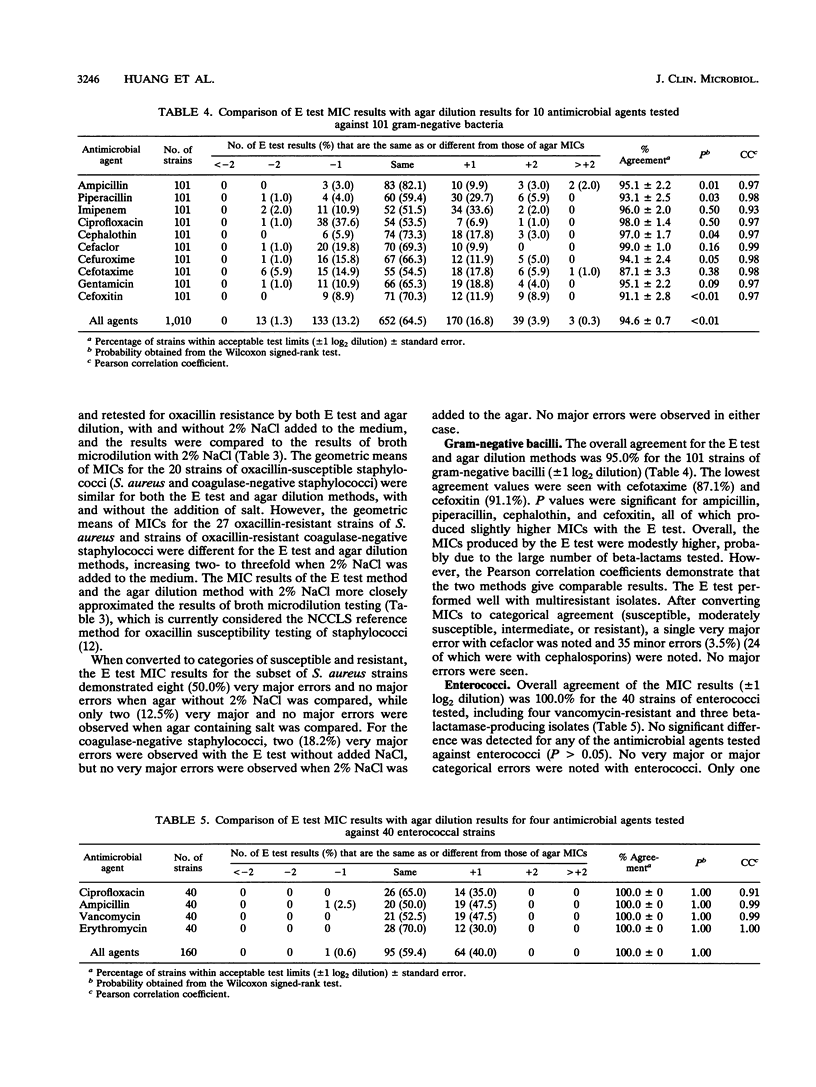
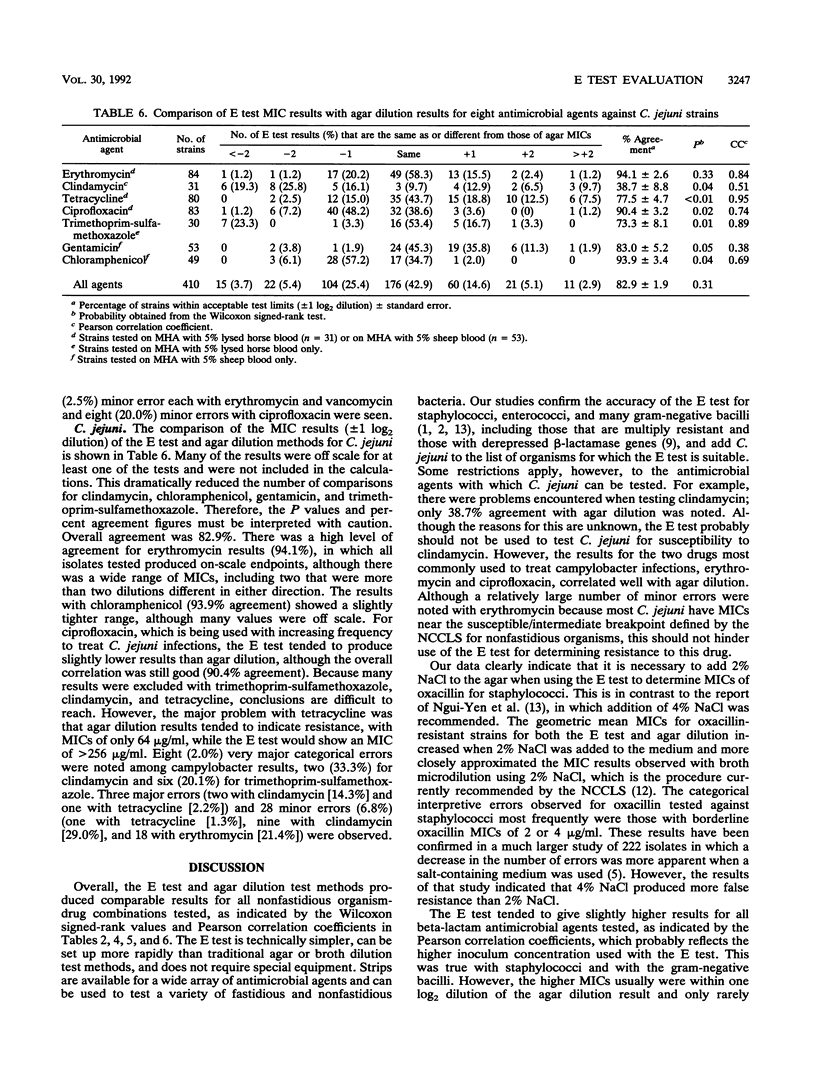
We compared the results of the E test MIC method with the results of agar dilution susceptibility testing for 18 antimicrobial agents against 324 strains of gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria, including 99 strains of staphylococci, 101 strains of antimicrobial-resistant gram-negative bacteria, 40 strains of enterococci, and 84 isolates of Campylobacter jejuni. Overall agreement of MICs (+/- 1 log2 dilution) was 97.3% for staphylococci, 94.6% for gram-negative bacilli, and 100.0% for enterococci. The MIC results for C. jejuni showed an overall agreement of only 82.9%. This was due primarily to a number of offscale values that limited the number of comparisons with clindamycin, trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, and tetracycline. Interpretative criteria for the results of the two test methods, however, were similar. Overall, the E test produced MIC results comparable to those of agar dilution when multiresistant organisms were tested. However, it was necessary to add 2% NaCl to the agar when testing oxacillin against staphylococci for both the E test and agar dilution to obtain results comparable to those of the broth microdilution method.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker C. N., Stocker S. A., Culver D. H., Thornsberry C. Comparison of the E Test to agar dilution, broth microdilution, and agar diffusion susceptibility testing techniques by using a special challenge set of bacteria. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Mar;29(3):533–538. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.3.533-538.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D. F., Brown L. Evaluation of the E test, a novel method of quantifying antimicrobial activity. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1991 Feb;27(2):185–190. doi: 10.1093/jac/27.2.185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Citron D. M., Ostovari M. I., Karlsson A., Goldstein E. J. Evaluation of the E test for susceptibility testing of anaerobic bacteria. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Oct;29(10):2197–2203. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.10.2197-2203.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glupczynski Y., Labbé M., Hansen W., Crokaert F., Yourassowsky E. Evaluation of the E test for quantitative antimicrobial susceptibility testing of Helicobacter pylori. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Sep;29(9):2072–2075. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.9.2072-2075.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs M. R., Bajaksouzian S., Appelbaum P. C., Bolmström A. Evaluation of the E-Test for susceptibility testing of pneumococci. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 1992 Jul;15(5):473–478. doi: 10.1016/0732-8893(92)90093-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jorgensen J. H., Howell A. W., Maher L. A. Quantitative antimicrobial susceptibility testing of Haemophilus influenzae and Streptococcus pneumoniae by using the E-test. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Jan;29(1):109–114. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.1.109-114.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knapp C. C., Ludwig M. D., Washington J. A. In vitro activity of metronidazole against Helicobacter pylori as determined by agar dilution and agar diffusion. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1991 Jun;35(6):1230–1231. doi: 10.1128/aac.35.6.1230. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knapp C. C., Washington J. A. Comparison of the E test and microdilution for detection of beta-lactam-resistant mutants that are stably derepressed for type I beta-lactamase. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Jan;30(1):214–215. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.1.214-215.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray P. R., Niles A. C. Comparison of the E test (PDM epsilometer) and broth microdilution susceptibility tests for members of the Bacteroides fragilis group. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 1991 Nov-Dec;14(6):501–505. doi: 10.1016/0732-8893(91)90006-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ngui-Yen J. H., Bryce E. A., Porter C., Smith J. A. Evaluation of the E test by using selected gram-positive bacteria. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Aug;30(8):2150–2152. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.8.2150-2152.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



