Abstract
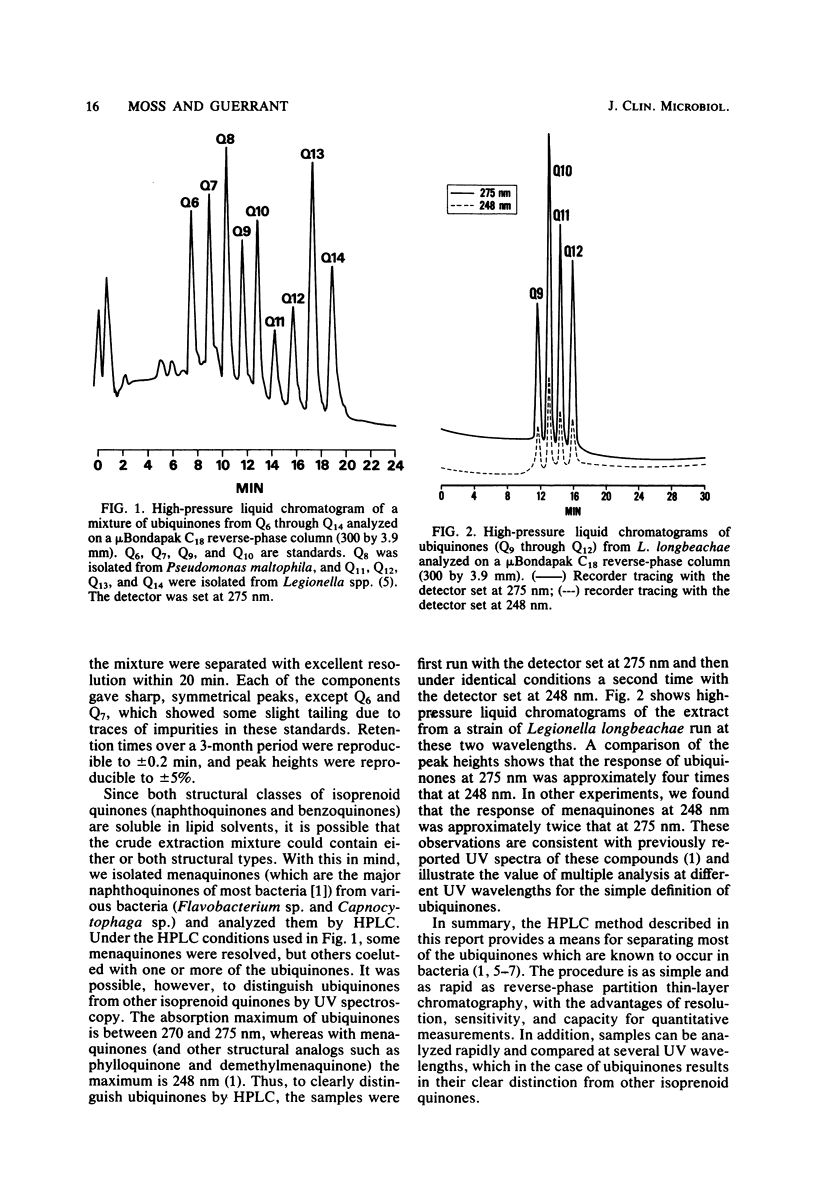
A procedure was developed for the separation of ubiquinones by high-pressure liquid chromatography on a reverse-phase C18 column. Ubiquinones Q6 through Q14 were resolved in 20 min and were distinguished from menaquinones by comparing UV spectra at 248 and 275 nm.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Collins M. D., Jones D. Distribution of isoprenoid quinone structural types in bacteria and their taxonomic implication. Microbiol Rev. 1981 Jun;45(2):316–354. doi: 10.1128/mr.45.2.316-354.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerrant G. O., Lambert M. A., Moss C. W. Analysis of short-chain acids from anaerobic bacteria by high-performance liquid chromatography. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Aug;16(2):355–360. doi: 10.1128/jcm.16.2.355-360.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karr D. E., Bibb W. F., Moss C. W. Isoprenoid quinones of the genus Legionella. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Jun;15(6):1044–1048. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.6.1044-1048.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



