Abstract
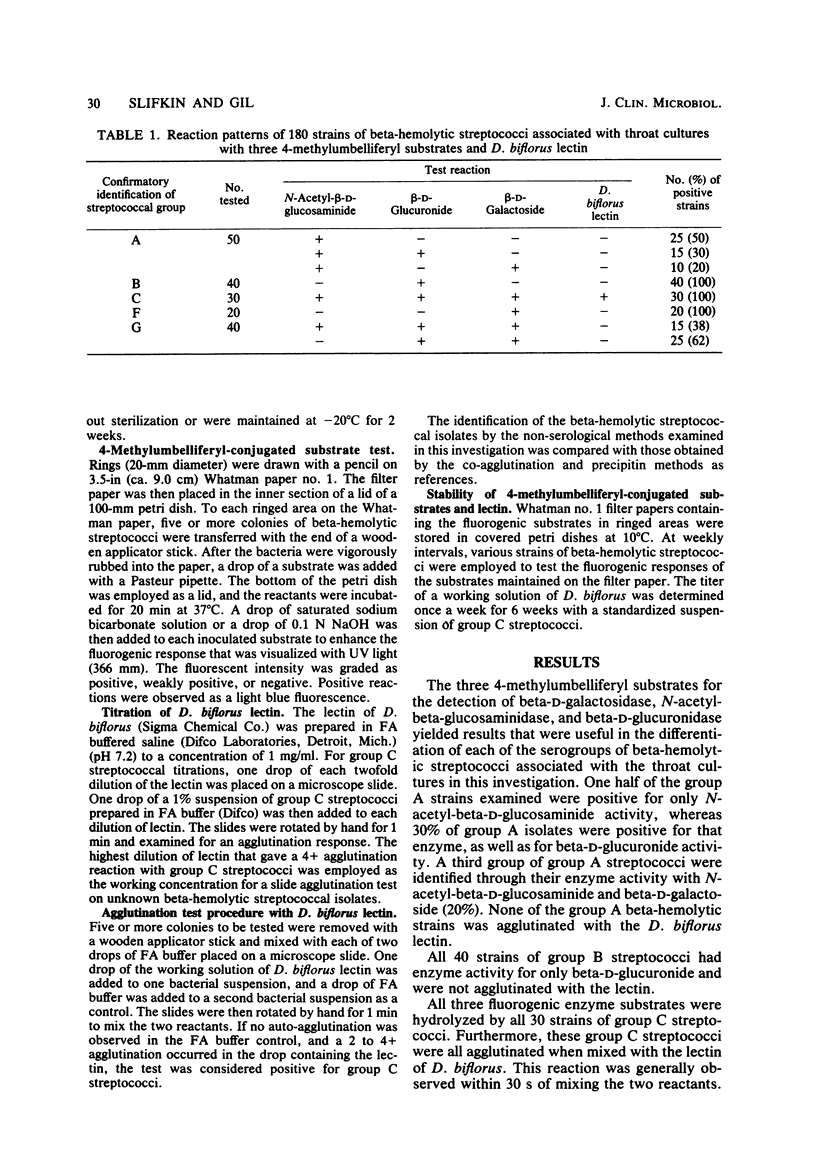
A test employing three fluorogenic 4-methylumbelliferyl substrates and the lectin of Dolichos biflorus was developed for the identification of beta-hemolytic streptococcal colonies associated with throat cultures. This non-serological method is unique in that it permits the accurate identification of groups C, F, and G streptococci, as well as groups A and B streptococci. The method is rapid, simple, and specific and appears to be a useful means to identify groups A, B, C, F, and G streptococci.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bobey D. G., Ederer G. M. Rapid detection of yeast enzymes by using 4-methylumbelliferyl substrates. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Feb;13(2):393–394. doi: 10.1128/jcm.13.2.393-394.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradbury J. M. Rapid biochemical tests for characterization of the Mycoplasmatales. J Clin Microbiol. 1977 May;5(5):531–534. doi: 10.1128/jcm.5.5.531-534.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Facklam R. R. A review of the microbiological techniques for the isolation and identification of streptococci. CRC Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci. 1976 Mar;6(4):287–317. doi: 10.3109/10408367609151573. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Facklam R. R., Padula J. F., Thacker L. G., Wortham E. C., Sconyers B. J. Presumptive identification of group A, B, and D streptococci. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Jan;27(1):107–113. doi: 10.1128/am.27.1.107-113.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Facklam R. R., Padula J. F., Wortham E. C., Cooksey R. C., Rountree H. A. Presumptive identification of group A, B, and D streptococci on agar plate media. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Jun;9(6):665–672. doi: 10.1128/jcm.9.6.665-672.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Facklam R. R., Thacker L. G., Fox B., Eriquez L. Presumptive identification of streptococci with a new test system. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Jun;15(6):987–990. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.6.987-990.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grange J. M., Clark K. Use of umbelliferone derivatives in the study of enzyme activities of mycobacteria. J Clin Pathol. 1977 Feb;30(2):151–153. doi: 10.1136/jcp.30.2.151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunn B. A. SXT and Taxo A disks for presumptive identification of group A and B streptococci in throat cultures. J Clin Microbiol. 1976 Aug;4(2):192–193. doi: 10.1128/jcm.4.2.192-193.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler W., Prokop O. Agglutinationversuche an Streptokokken mit dem Phytagglutinin aus Dolichos biflorus. Z Immunitatsforsch Allerg Klin Immunol. 1967 Jul;133(2):171–175. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler W., Prokop O., Kühnemund O. Routine identification of group-C streptococci by means of an agglutinin (protectin) from the albumen gland of the edible snail, Helix pomatia. J Med Microbiol. 1973 Feb;6(1):127–130. doi: 10.1099/00222615-6-1-127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maddocks J. L., Greenan M. J. A rapid method for identifying bacterial enzymes. J Clin Pathol. 1975 Aug;28(8):686–687. doi: 10.1136/jcp.28.8.686. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien M., Davis G. H. Enzymatic profile of Pseudomonas maltophilia. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Sep;16(3):417–421. doi: 10.1128/jcm.16.3.417-421.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ottensooser F., Nakamizo Y., Sato M., Miyamoto Y., Takizawa K. Lectins detecting group C streptococci. Infect Immun. 1974 May;9(5):971–973. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.5.971-973.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prokop O., Köhler W. Agglutinationsreaktionen von Mikroorganismen mit Helix pomatia Eiweissdrüsen-Extrakt (Anti-Ahel-Agglutinin) Z Immunitatsforsch Allerg Klin Immunol. 1967 Jul;133(2):176–179. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RANTZ L. A., RANDALL E. Use of autoclaved extracts of hemolytic streptococci for serological grouping. Stanford Med Bull. 1955 May;13(2):290–291. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruoff K. L., Ferraro M. J., Jerz M. E., Kissling J. Automated identification of gram-positive bacteria. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Dec;16(6):1091–1095. doi: 10.1128/jcm.16.6.1091-1095.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slifkin M., Interval G. Serogrouping single colonies of beta-hemolytic streptococci from primary throat culture plates with nitrous acid extraction and Phadebact streptococcal reagents. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Oct;12(4):541–545. doi: 10.1128/jcm.12.4.541-545.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


