Abstract
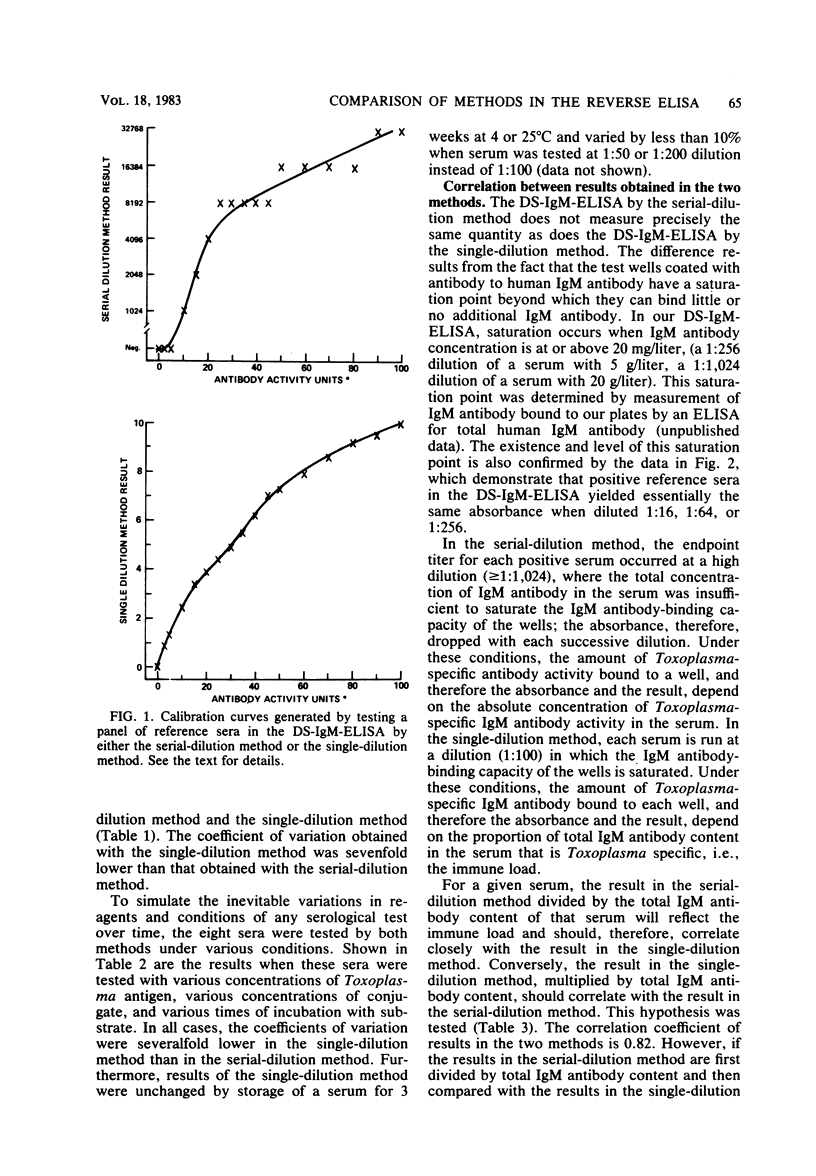
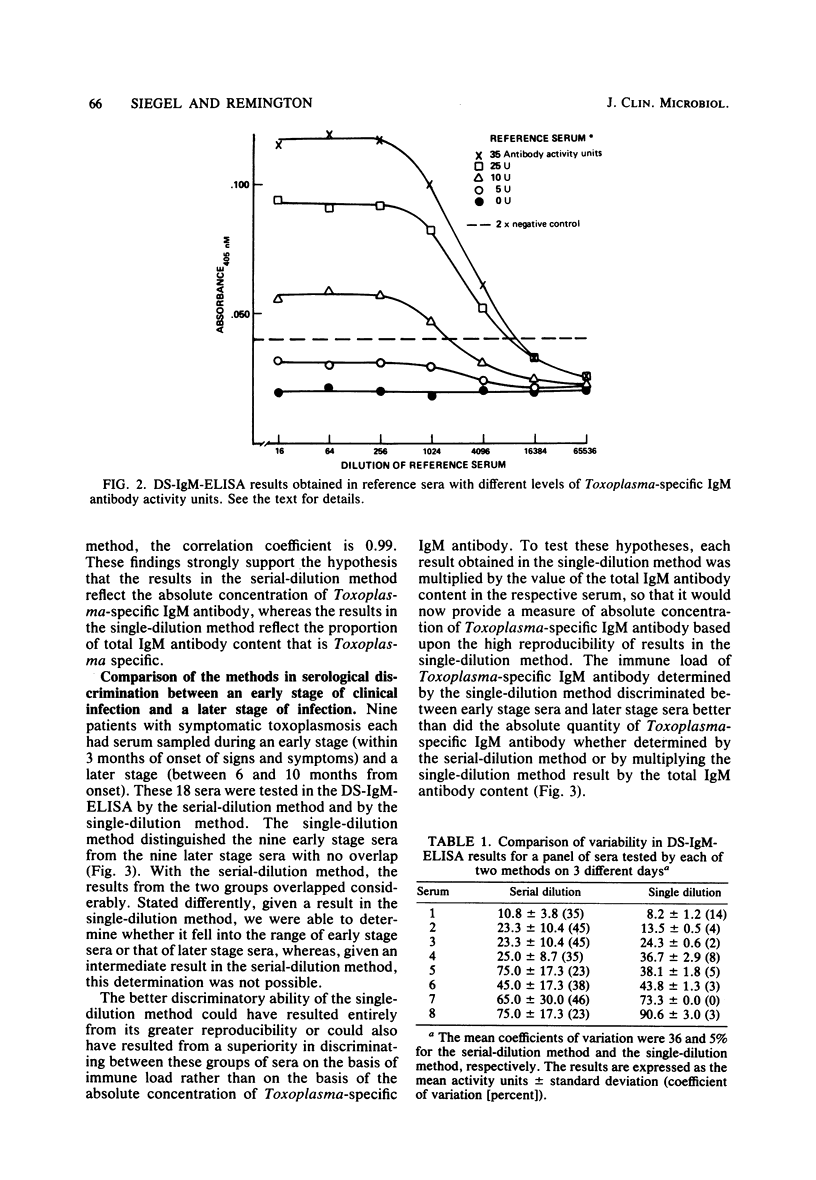
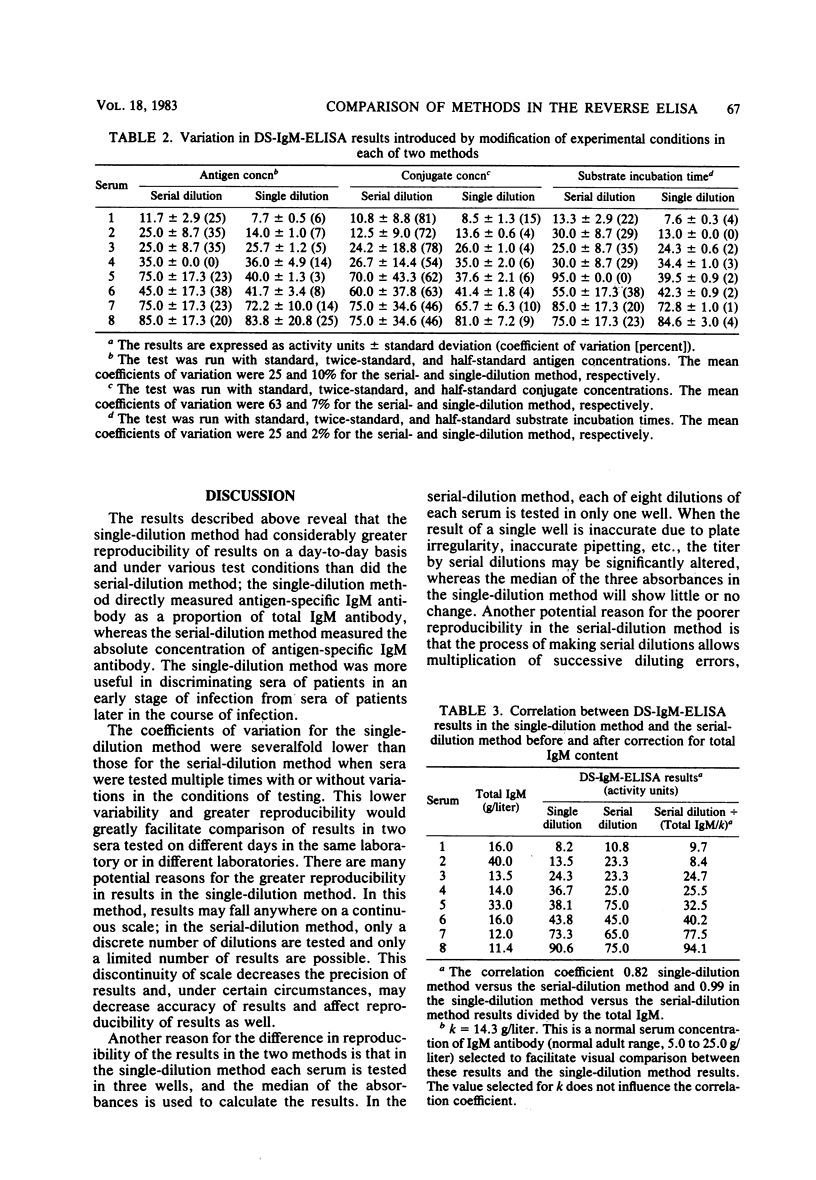
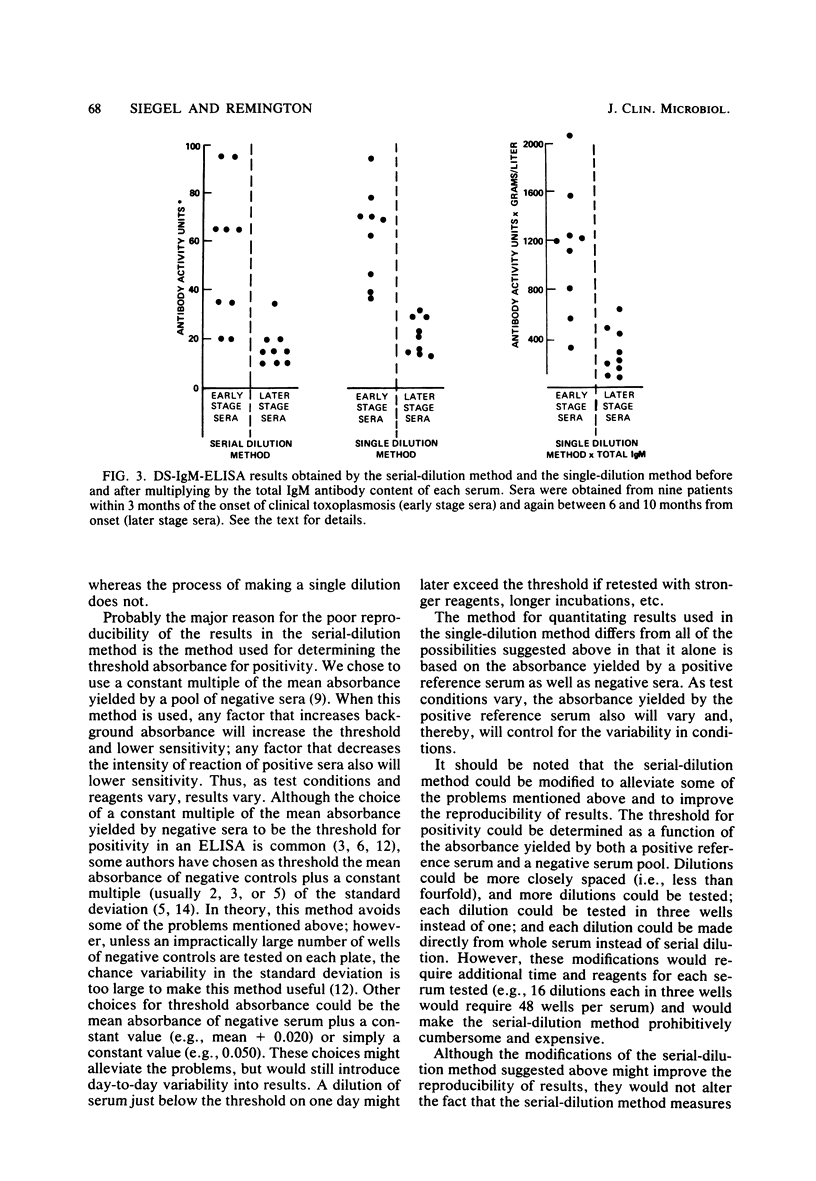
We compared two methods for quantitating antigen-specific antibody by a reverse enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. In the serial-dilution method, the result was determined to be the highest dilution of a serum yielding an absorbance above an established threshold. In the single-dilution method, the result was determined by comparing the absorbance yielded by the test serum at a standard dilution to that yielded by positive and negative reference sera at the same dilution. The results in the single-dilution method reflected the antigen-specific immunoglobulin M antibody activity as a proportion of total immunoglobulin M antibody in a serum, i.e., the immune load, whereas the results in the serial-dilution method reflected the absolute concentration of antigen-specific immunoglobulin M antibody activity. Compared with results in the serial-dilution method, results in the single-dilution method had considerably greater reproducibility on a day-to-day basis and under various test conditions. The single-dilution method was more useful in discriminating between sera from patients in an early stage of clinical infection due to Toxoplasma gondii and sera from patients in a later stage of infection.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Araujo F. G., Remington J. S. Antigenemia in recently acquired acute toxoplasmosis. J Infect Dis. 1980 Feb;141(2):144–150. doi: 10.1093/infdis/141.2.144. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duermeyer W., Wielaard F., van der Veen J. A new principle for the detection of specific IgM antibodies applied in an ELISA for hepatitis A. J Med Virol. 1979;4(1):25–32. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890040104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duermeyer W., van der Veen J. Specific detection of IgM-antibodies by ELISA, applied in hepatitis-A. Lancet. 1978 Sep 23;2(8091):684–685. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(78)92802-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engvall E., Perlmann P. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Quantitative assay of immunoglobulin G. Immunochemistry. 1971 Sep;8(9):871–874. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(71)90454-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fields H. A., Davis C. L., Dreesman G. R., Bradley D. W., Maynard J. E. Enzyme potentiated radioimmunoassay (EPRIA): a sensitive third-generation test for the detection of hepatitis B surface antigen. J Immunol Methods. 1981;47(2):145–159. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(81)90115-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerlich W. H., Lüer W. Selective detection of IgM-antibody against core antigen of the hepatitis B virus by a modified enzyme immune assay. J Med Virol. 1979;4(3):227–238. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890040308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naot Y., Barnett E. V., Remington J. S. Method for avoiding false-positive results occurring in immunoglobulin M enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays due to presence of both rheumatoid factor and antinuclear antibodies. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Jul;14(1):73–78. doi: 10.1128/jcm.14.1.73-78.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naot Y., Desmonts G., Remington J. S. IgM enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay test for the diagnosis of congenital Toxoplasma infection. J Pediatr. 1981 Jan;98(1):32–36. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(81)80528-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naot Y., Guptill D. R., Remington J. S. Duration of IgM antibodies to Toxoplasma gondii after acute acquired toxoplasmosis. J Infect Dis. 1982 May;145(5):770–770. doi: 10.1093/infdis/145.2.770. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naot Y., Remington J. S. An enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for detection of IgM antibodies to Toxoplasma gondii: use for diagnosis of acute acquired toxoplasmosis. J Infect Dis. 1980 Nov;142(5):757–766. doi: 10.1093/infdis/142.5.757. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Weemen B. K., Schuurs A. H.W.M. Immunoassay using antigen-enzyme conjugates. FEBS Lett. 1971 Jun 24;15(3):232–236. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(71)80319-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yolken R. H., Leister F. J. Enzyme immunoassays for measurement of cytomegalovirus immunoglobulin M antibody. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Oct;14(4):427–432. doi: 10.1128/jcm.14.4.427-432.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Loon A. M., van der Veen J. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for quantitation of toxoplasma antibodies in human sera. J Clin Pathol. 1980 Jul;33(7):635–639. doi: 10.1136/jcp.33.7.635. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


