Abstract
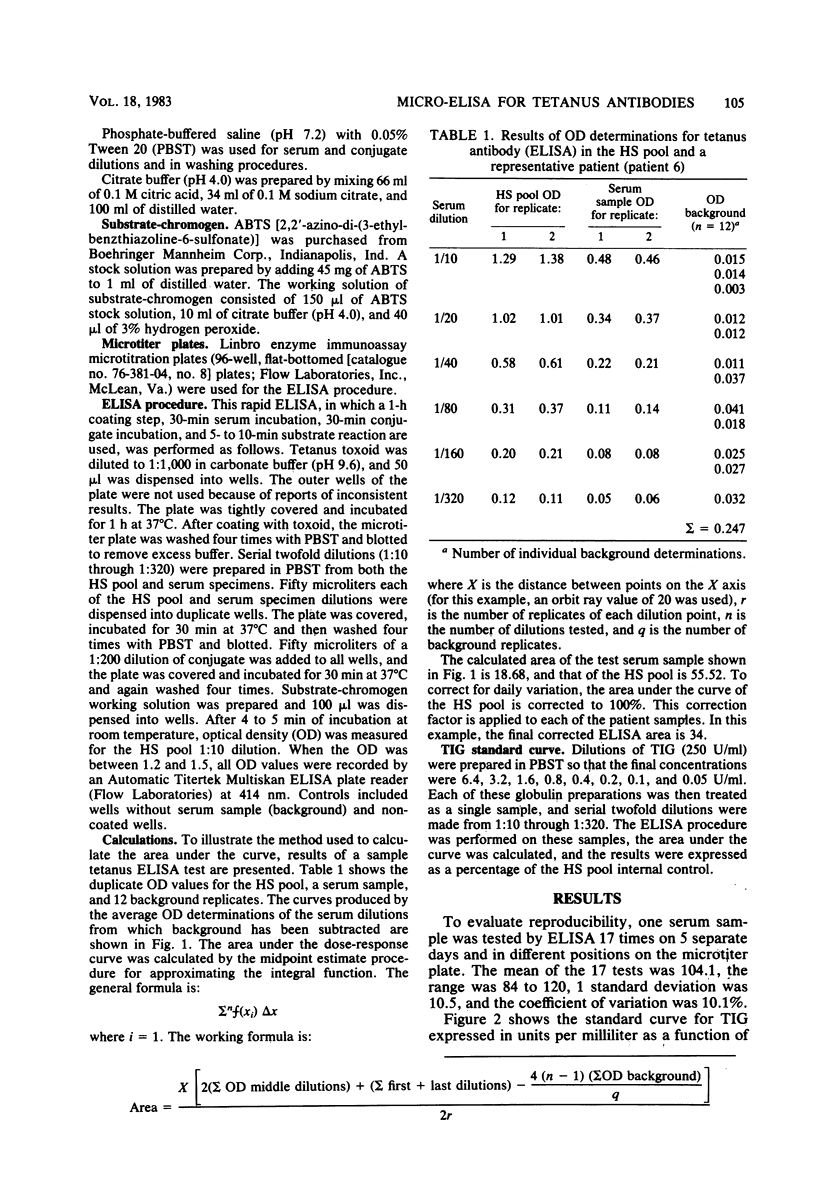
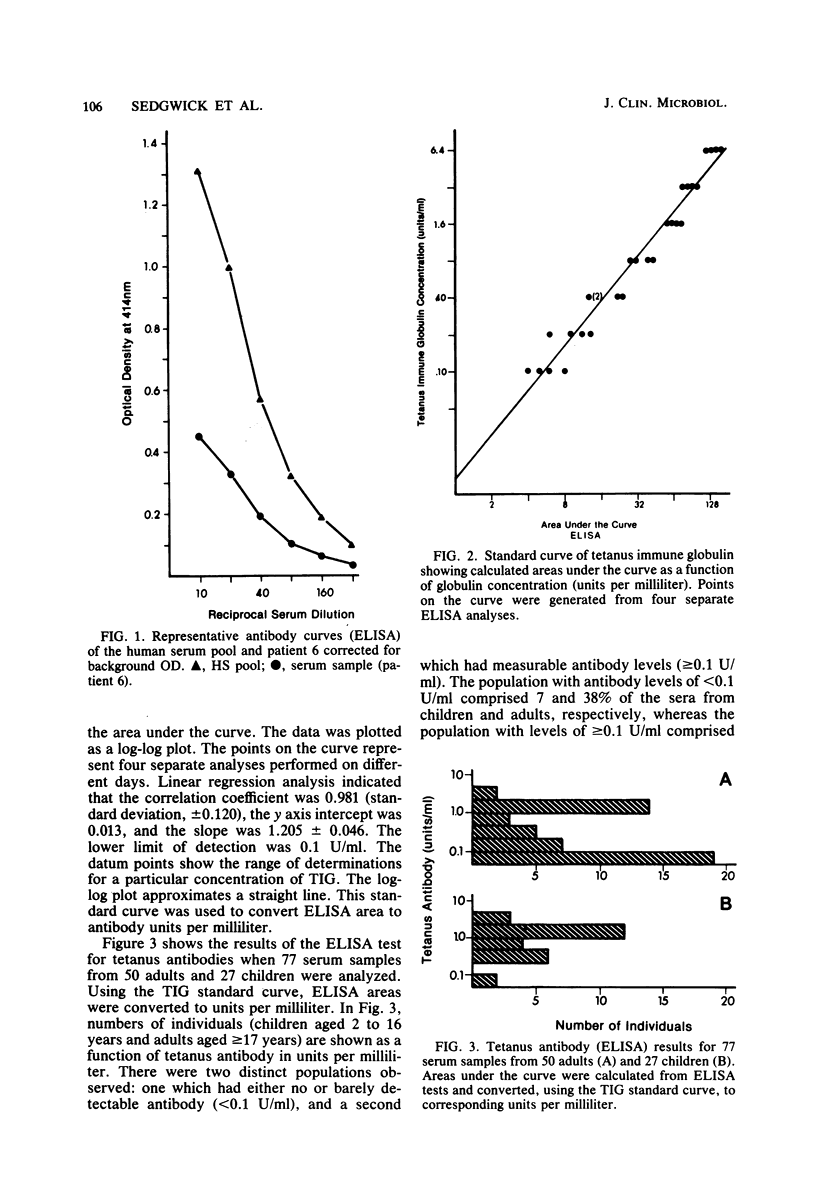
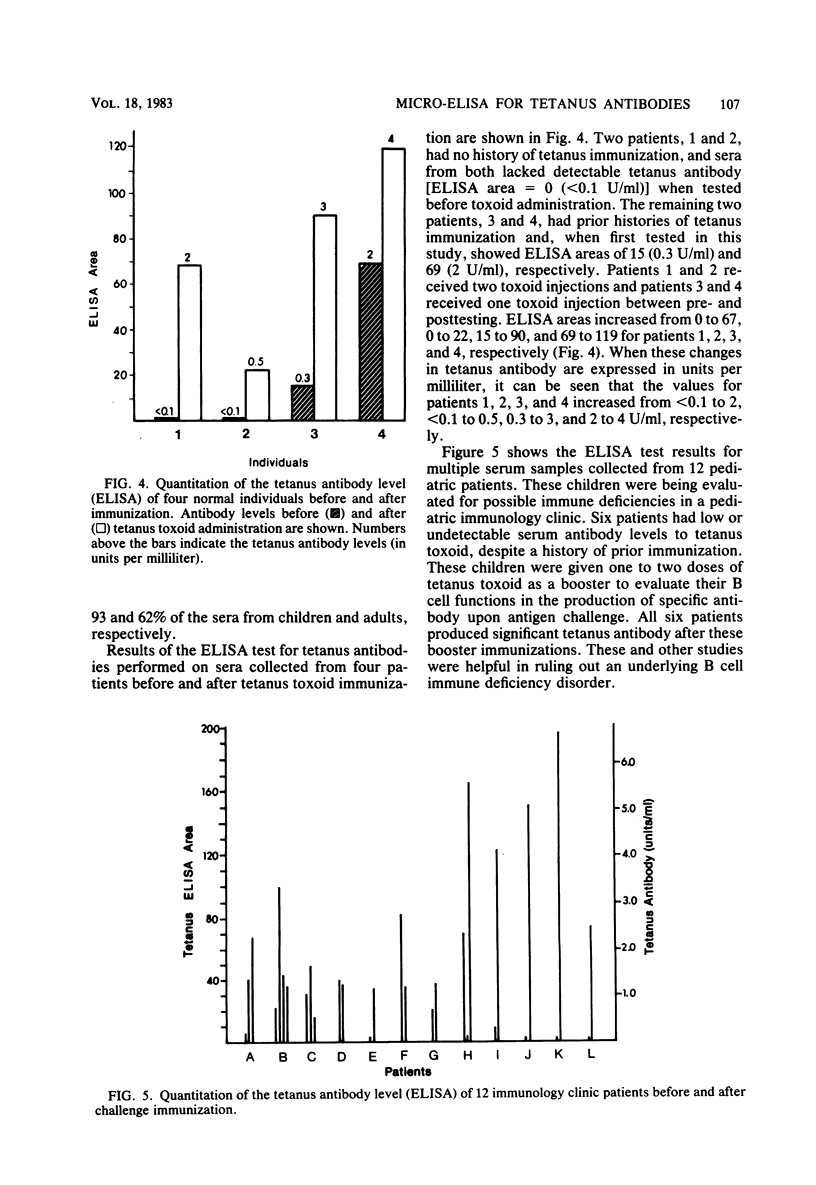
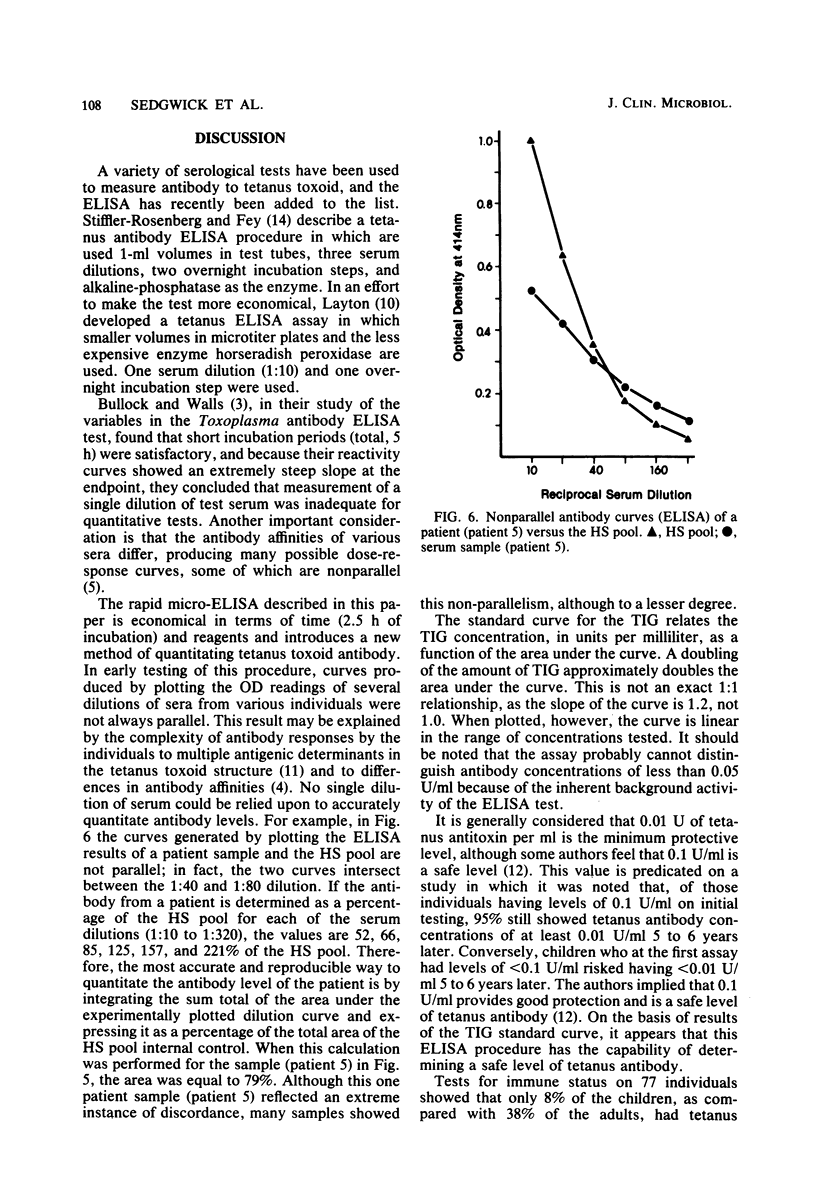
A rapid quantitative microenzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for the detection of immunoglobulin G antibodies to tetanus toxoid is described. The assay is performed in 2.5 h and detects antibody levels of between 0.1 and 6 U/ml. Quantitation of the antibody concentration is unique in that multiple serum dilutions are tested on a single patient, the results are plotted as an antibody dilution curve, and the area under the curve is integrated for a final concentration. Tests for immune status on sera from 77 individuals demonstrated tetanus antibody concentrations of greater than or equal to 0.1 U/ml in 92% of a pediatric group and 62% of an adult group. The microenzyme-linked immunosorbent assay procedure is reproducible and is useful for the determination of immune status and immunization response.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barile M. F., Hardegree M. C., Pittman M. Immunization against neonatal tetanus in New Guinea. 3. The toxin-neutralization test and the response of guinea-pigs to the toxoids as used in the immunization schedules in New Guinea. Bull World Health Organ. 1970;43(3):453–459. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Booth J. R., Nuttall P. A. A rapid automated latex screen for tetanus toxoid antibodies. Vox Sang. 1978;34(4):239–240. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1978.tb02474.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bullock S. L., Walls K. W. Evaluation of some of the parameters of the enzyme-linked immunospecific assay. J Infect Dis. 1977 Oct;136 (Suppl):S279–S285. doi: 10.1093/infdis/136.supplement_2.s279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler J. E., Feldbush T. L., McGivern P. L., Stewart N. The enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA): a measure of antibody concentration or affinity. Immunochemistry. 1978 Feb;15(2):131–136. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(78)90053-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engvall E., Perlmann P. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Quantitative assay of immunoglobulin G. Immunochemistry. 1971 Sep;8(9):871–874. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(71)90454-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Habermann E., Horváth E., Schaeg W. A radioimmunoassay for tetanus antibodies using protein A - containing Staphylococcus aureus. Med Microbiol Immunol. 1977 Dec 27;163(4):261–268. doi: 10.1007/BF02125510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Habermann E., Wiegand H. A rapid and simple radioimmunological procedure for measuring low concentrations of tetanus antibodies. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1973;276(3-4):321–326. doi: 10.1007/BF00499886. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Layton G. T. A micro-enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and radioimmunosorbent technique (RIST) for the detection of immunity to clinical tetanus. Med Lab Sci. 1980 Oct;37(4):323–329. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stiffler-Rosenberg G., Fey H. Messung von Tetanus-Antitoxin mit dem Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Schweiz Med Wochenschr. 1977 Aug 6;107(31):1101–1104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stiffler-Rosenberg G., Fey H. Radioimmunologische Messung von Tetanusantitoxin. Schweiz Med Wochenschr. 1975 Jun 21;105(25):804–810. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Weemen B. K., Schuurs A. H.W.M. Immunoassay using antigen-enzyme conjugates. FEBS Lett. 1971 Jun 24;15(3):232–236. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(71)80319-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Savigny D., Voller A. The communication of ELISA data from laboratory to clinician. J Immunoassay. 1980;1(1):105–128. doi: 10.1080/01971528008055779. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



