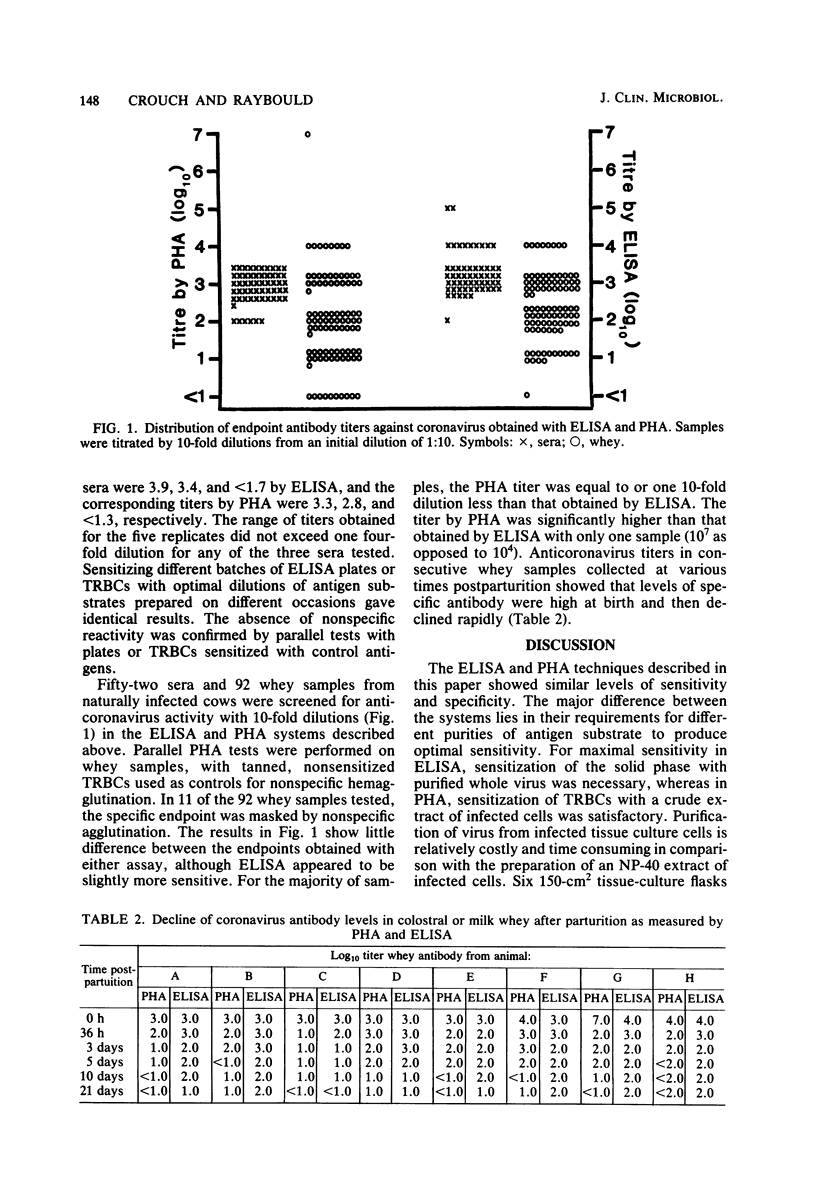
Abstract
Purified coronavirus, detergent extracts of purified coronavirus, and virus-infected Madin-Darby bovine kidney cells were evaluated as antigen substrates in enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and passive hemagglutination systems. Only detergent-extracted and -unextracted, purified viruses were reactive as antigen substrates in ELISA, whereas all three antigen preparations could be used for sensitization of erythrocytes in the passive hemagglutination assay. The passive hemagglutination system with infected cell extracts exhibited a similar level of sensitivity and specificity to the ELISA system employing purified coronavirus but enabled 300 times more tests to be performed per volume of virus-infected cell culture.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Caul E. O., Paver W. K., Clarke S. K. Letter: Coronavirus particles in faeces from patients with gastroenteritis. Lancet. 1975 May 24;1(7917):1192–1192. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(75)93176-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chasey D., Cartwright S. F. Virus-like particles associated with porcine epidemic diarrhoea. Res Vet Sci. 1978 Sep;25(2):255–256. doi: 10.1016/S0034-5288(18)32994-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dea S., Roy R. S., Elazhary M. A. Coronavirus-like Particles in the Feces of a Cat with Diarrhea. Can Vet J. 1982 May;23(5):153–155. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engvall E., Perlmann P. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, Elisa. 3. Quantitation of specific antibodies by enzyme-labeled anti-immunoglobulin in antigen-coated tubes. J Immunol. 1972 Jul;109(1):129–135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mebus C. A. Pathogenesis of coronaviral infection in calves. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1978 Sep 1;173(5 Pt 2):631–632. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mebus C. A., Stair E. L., Rhodes M. B., Twiehaus M. J. Pathology of neonatal calf diarrhea induced by a coronavirus-like agent. Vet Pathol. 1973;10(1):45–64. doi: 10.1177/030098587301000105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naqi S. A., Panigrahy B., Hall C. F. Purification and concentration of viruses associated with transmissible (coronaviral) enteritis of turkeys (bluecomb). Am J Vet Res. 1975 Apr;36(4 Pt 2):548–552. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pass D. A., Penhale W. J., Wilcox G. E., Batey R. G. Intestinal coronavirus-like particles in sheep with diarrhoea. Vet Rec. 1982 Jul 31;111(5):106–107. doi: 10.1136/vr.111.5.106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pensaert M. B., de Bouck P. A new coronavirus-like particle associated with diarrhea in swine. Arch Virol. 1978;58(3):243–247. doi: 10.1007/BF01317606. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROWE W. P., HARTLEY J. W., CAPPS W. I. Mouse hepatitis virus infection as a highly contagious, prevalent, enteric infection of mice. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1963 Jan;112:161–165. doi: 10.3181/00379727-112-27980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodak L., Babiuk L. A., Acres S. D. Detection by radioimmunoassay and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay of coronavirus antibodies in bovine serum and lacteal secretions. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Jul;16(1):34–40. doi: 10.1128/jcm.16.1.34-40.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sequeira P. J., Eldridge A. E. Treponemal haemagglutination test. Br J Vener Dis. 1973 Jun;49(3):242–248. doi: 10.1136/sti.49.3.242. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugiyama K., Amano Y. Hemagglutination and structural polypeptides of a new coronavirus associated with diarrhea in infant mice. Arch Virol. 1980;66(2):95–105. doi: 10.1007/BF01314978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tajima M. Morphology of transmissible gastroenteritis virus of pigs. A possible member of coronaviruses. Brief report. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1970;29(1):105–108. doi: 10.1007/BF01253886. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voller A., Bidwell D. E. A simple method for detecting antibodies to rubella. Br J Exp Pathol. 1975 Aug;56(4):338–339. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woode G. N., Jones J., Bridger J. Levels of colostral antibodies against neonatal calf diaahoea virus. Vet Rec. 1975 Aug 23;97(8):148–149. doi: 10.1136/vr.97.8.148. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



