Abstract
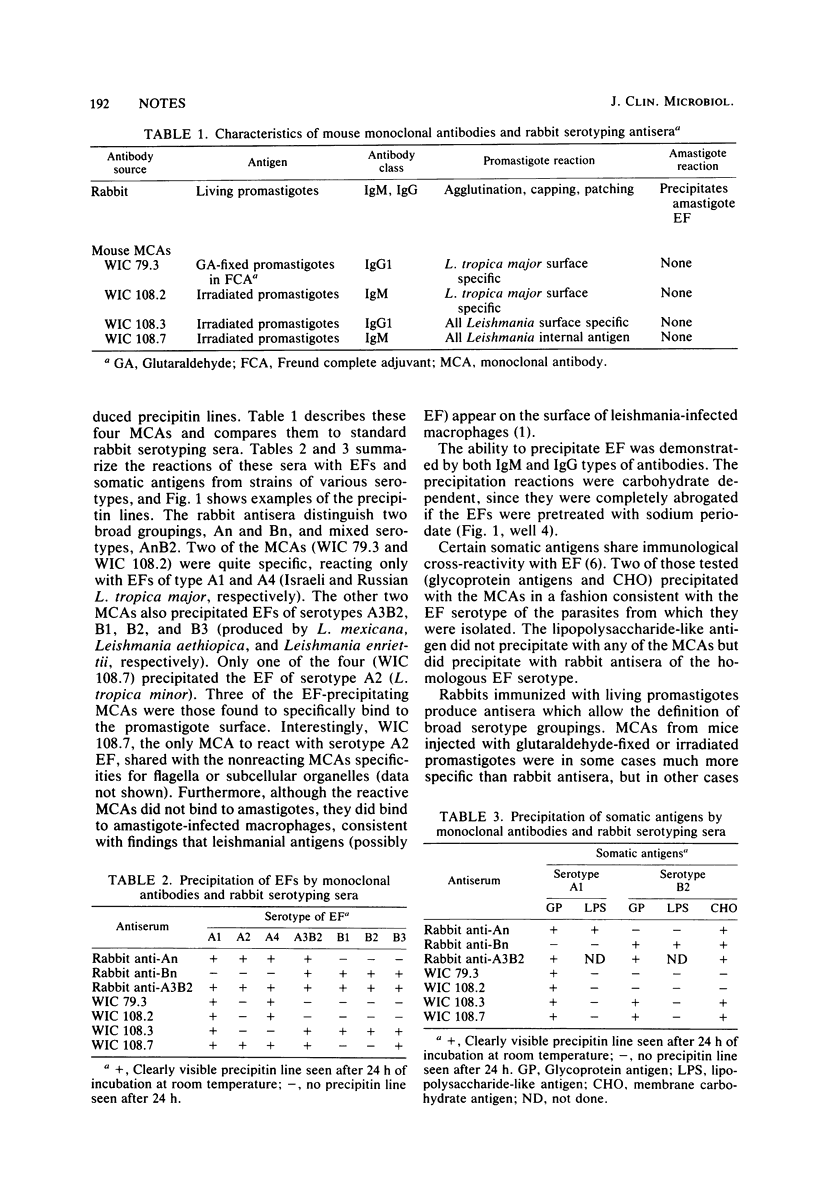
Mouse monoclonal antibodies raised against Leishmania tropica major were found to precipitate with the excreted factor produced by this and other leishmanial species. We suggest that a classification system for Leishmania, based on selective precipitation reactions between monoclonal antibodies and the excreted factor, would remove many ambiguities that currently exist.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berman J. D., Dwyer D. M. Expression of Leishmania antigen on the surface membrane of infected human macrophages in vitro. Clin Exp Immunol. 1981 May;44(2):342–348. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard J. G., Nicklin S., Hale C., Liew F. Y. Prophylactic immunization against experimental leishmaniasis: I. Protection induced in mice genetically vulnerable to fatal Leishmania tropica infection. J Immunol. 1982 Nov;129(5):2206–2212. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaneshiro E. S., Gottlieb M., Dwyer D. M. Cell surface origin of antigens shed by Leishmania donovani during growth in axenic culture. Infect Immun. 1982 Aug;37(2):558–567. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.2.558-567.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pratt D. M., David J. R. Monoclonal antibodies that distinguish between New World species of Leishmania. Nature. 1981 Jun 18;291(5816):581–583. doi: 10.1038/291581a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radin N. S. Extraction of tissue lipids with a solvent of low toxicity. Methods Enzymol. 1981;72:5–7. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(81)72003-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnur L. F., Zuckerman A., Greenblatt C. L. Leishmanial serotypes as distinguished by the gel diffusion of factors excreted in vitro and in vivo. Isr J Med Sci. 1972 Jul;8(7):932–942. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slutzky G. M., El-On J., Greenblatt C. L. Leishmanial excreted factor: protein-bound and free forms from promastigote cultures of Leishmania tropica and Leishmania donovani. Infect Immun. 1979 Dec;26(3):916–924. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.3.916-924.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slutzky G. M., Greenblatt C. L. Identification of galactose as the immunodominant sugar of leishmanial excreted factor and subsequent labeling with galactose oxidase and sodium boro[3H]hydride. Infect Immun. 1982 Jul;37(1):10–14. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.1.10-14.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snary D., Ferguson M. A., Scott M. T., Allen A. K. Cell surface antigens of Trypanosoma cruzi: use of monoclonal antibodies to identify and isolate an epimastigote specific glycoprotein. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1981 Oct;3(6):343–356. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(81)90035-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watkins W. M. Biochemistry and Genetics of the ABO, Lewis, and P blood group systems. Adv Hum Genet. 1980;10:1-136, 379-85. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-8288-5_1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Ibarra A. A., Howard J. G., Snary D. Monoclonal antibodies to Leishmania tropica major: specificities and antigen location. Parasitology. 1982 Dec;85(Pt 3):523–531. doi: 10.1017/s0031182000056304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]