Abstract
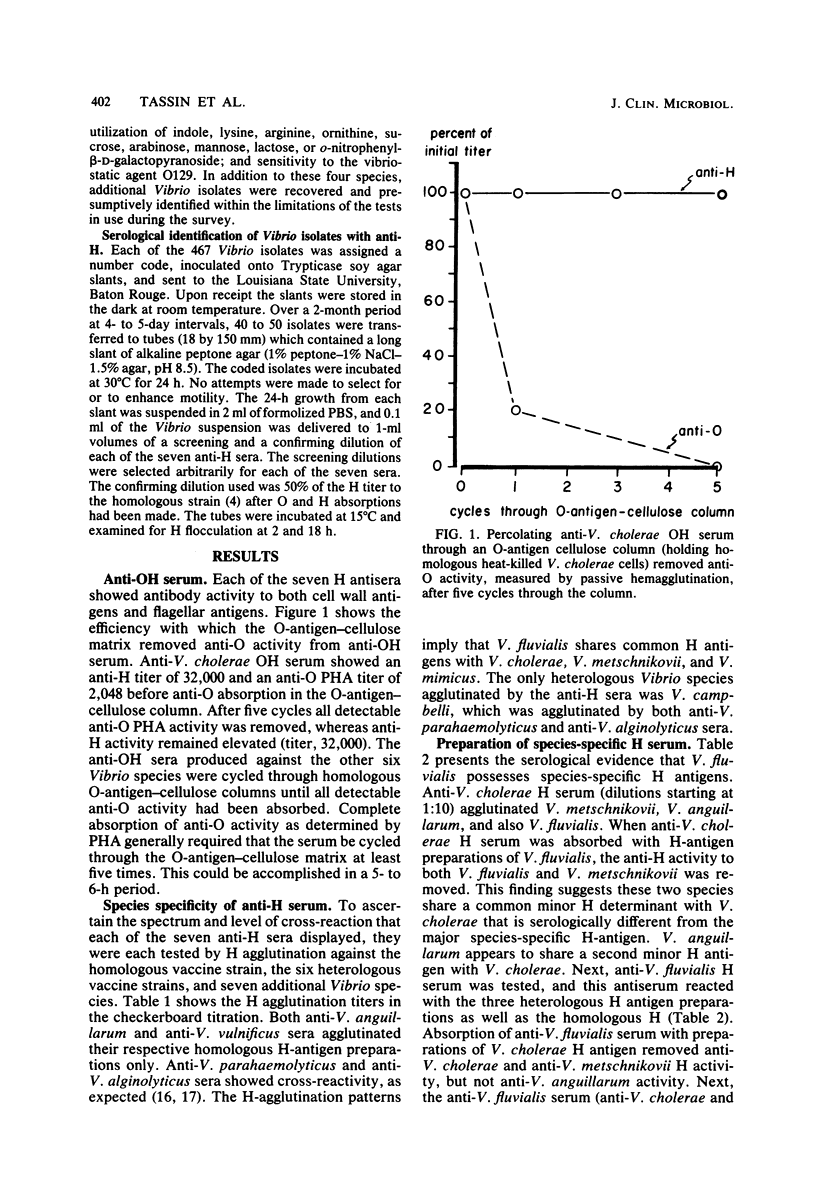
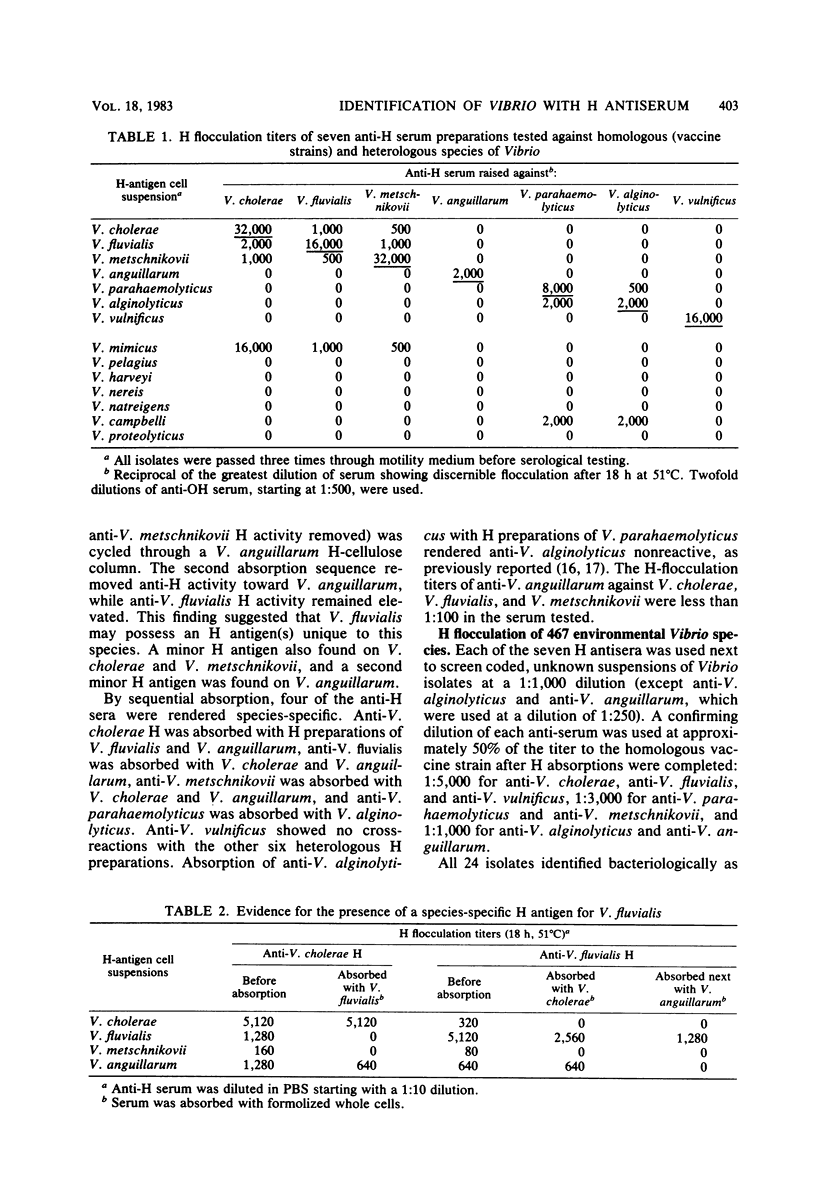
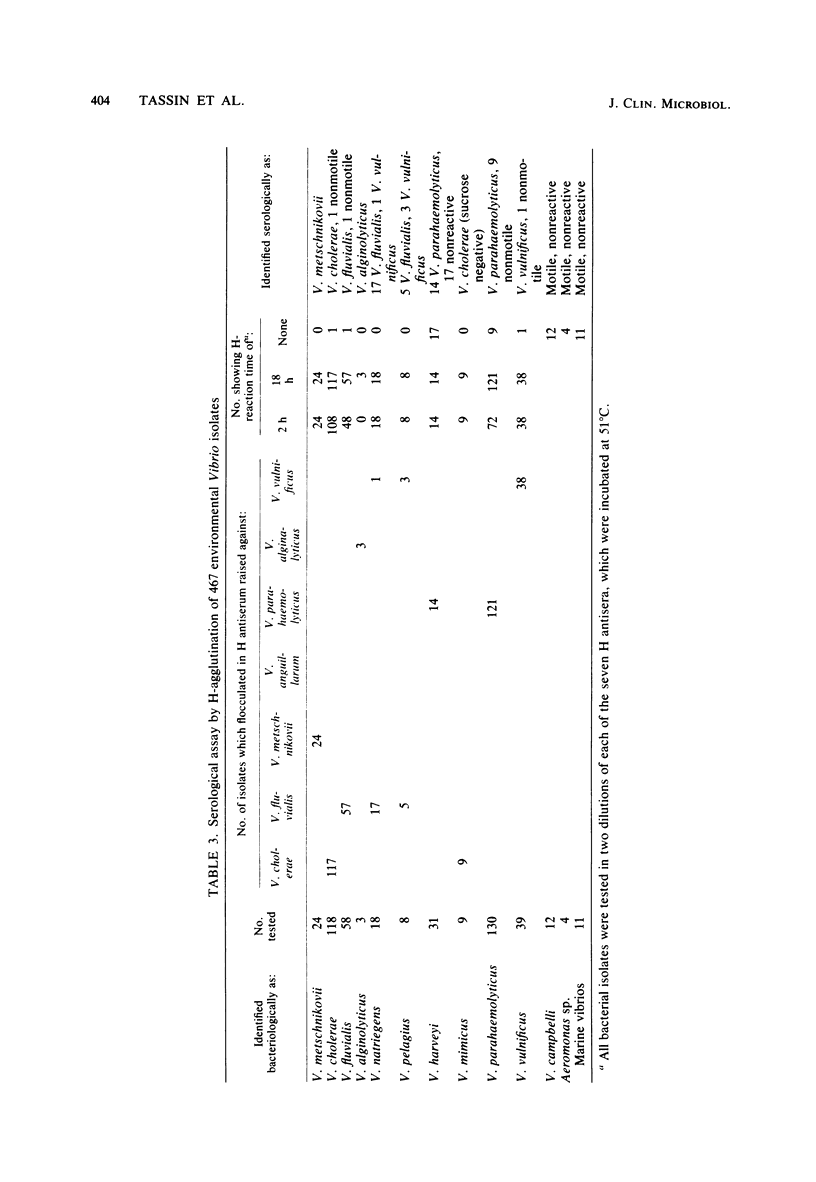
Species in the genus Vibrio exhibit flagellar (H) antigens unique to the species. Thus, species-specific H antiserum could be a valuable reagent with which to screen serologically large numbers of Vibrio isolates. Antisera against V. cholerae, V. fluvialis, V. anguillarum, V. metschnikovii, V. parahaemolyticus, V. alginolyticus, and V. vulnificus H antigens was produced in rabbits by repeated injections of Formalin-preserved whole cells. Anti-O activity and anti-H activity against common H antigens was absorbed from each antiserum, V. fluvialis was shown to possess an H antigen unique to the species and also to share minor H antigens with V. cholerae, V. metschnikovii, and V. anguillarum. V. vulnificus also exhibits a species-unique H antigen. A comprehensive serological screening system based on species-specific H antiserum was developed to identify pathogenic Vibrio species one step beyond primary isolation. Vibrio species were correctly identified with accuracies ranging from 93 to 100%. Some isolates were either nonmotile or poorly so and thus did not flocculate in H antiserum.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Auzins I. A comparative assay of O-somatic antigen 5 of Salmonellae. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1968 Feb;46(1):93–105. doi: 10.1038/icb.1968.8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhattacharyya F. K., Mukerjee S. Serological analysis of the flagellar or H agglutining antigens of cholera and NAG vibrios. Ann Microbiol (Paris) 1974 Feb-Mar;125A(2):167–181. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhattacharyya F. K. The agglutination reactions of cholera vibrios. Jpn J Med Sci Biol. 1977 Oct;30(5):259–268. doi: 10.7883/yoken1952.30.259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhattacharyya F. K. Vibrio cholerae flagellar antigens: a serodiagnostic test, functional implications of H-reactivity and taxonomic importance of cross-reactions within the Vibrio genus. Med Microbiol Immunol. 1975 Dec 30;162(1):29–41. doi: 10.1007/BF02123575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis B. R., Fanning G. R., Madden J. M., Steigerwalt A. G., Bradford H. B., Jr, Smith H. L., Jr, Brenner D. J. Characterization of biochemically atypical Vibrio cholerae strains and designation of a new pathogenic species, Vibrio mimicus. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Dec;14(6):631–639. doi: 10.1128/jcm.14.6.631-639.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hickman F. W., Farmer J. J., 3rd, Hollis D. G., Fanning G. R., Steigerwalt A. G., Weaver R. E., Brenner D. J. Identification of Vibrio hollisae sp. nov. from patients with diarrhea. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Mar;15(3):395–401. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.3.395-401.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miwatani T., Shinoda S. Flagellar antigen of Vibrio alginolyticus. Biken J. 1971 Dec;14(4):389–394. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miwtani T., Shinoda S., Nishimune H., Okada M., Takeda Y. A common antigenic substance of Vibrio parahaemolyticus. I. Isolation and purification. Biken J. 1969 Jun;12(2):97–106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pastoris M. C., Bhattacharyya F. K., Sil J. Evaluation of the phenol-induced flagellar agglutination test for the identification of the cholera group of vibrios. J Med Microbiol. 1980 May;13(2):362–367. doi: 10.1099/00222615-13-2-363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakazaki R., Iwanami S., Tamura K. Studies on the enteropathogenic, facultatively halophilic bacterium, Vibrio parahaemolyticus. II. Serological characteristics. Jpn J Med Sci Biol. 1968 Oct;21(5):313–324. doi: 10.7883/yoken1952.21.313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakazaki R., Tamura K., Gomez C. Z., Sen R. Serological studies on the cholera group of vibrios. Jpn J Med Sci Biol. 1970 Feb;23(1):13–20. doi: 10.7883/yoken1952.23.13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinoda S., Miwatani T., Fujino T. A common antigenic substance of Vibrio parahaemolyticus. II. Some physicochemical properties. Biken J. 1971 Mar;14(1):75–76. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinoda S., Miwatani T., Fujino T. Antigens of Vibrio parahaemolyticus. II. Existence of two different subunits in the flagella of Vibrio parahaemolyticus and their characterization. Biken J. 1970 Dec;13(4):241–247. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinoda S., Senoh T., Asano K., Nakahara N., Ono B. Differences between surface antigenic determinants of polar monotrichous flagella of Vibrio parahaemolyticus and of related species. Microbiol Immunol. 1980;24(5):409–418. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1980.tb02845.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sil J., Bhattacharyya F. K. A rapid test for the identification of all serotypes of Vibrio cholerae (including "non-agglutinating" vibrios). J Med Microbiol. 1979 Feb;12(1):63–70. doi: 10.1099/00222615-12-1-63. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sil J., Sanyal S. C., Mukerjee S. Studies on the so-called NAG vibrios. Indian J Med Res. 1975 May;63(5):724–732. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terada Y. [Serological studies of Vibrio parahaemolyticus. II. Flagellar antigens]. Nihon Saikingaku Zasshi. 1968 Nov;23(11):767–771. doi: 10.3412/jsb.23.767. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


