Abstract
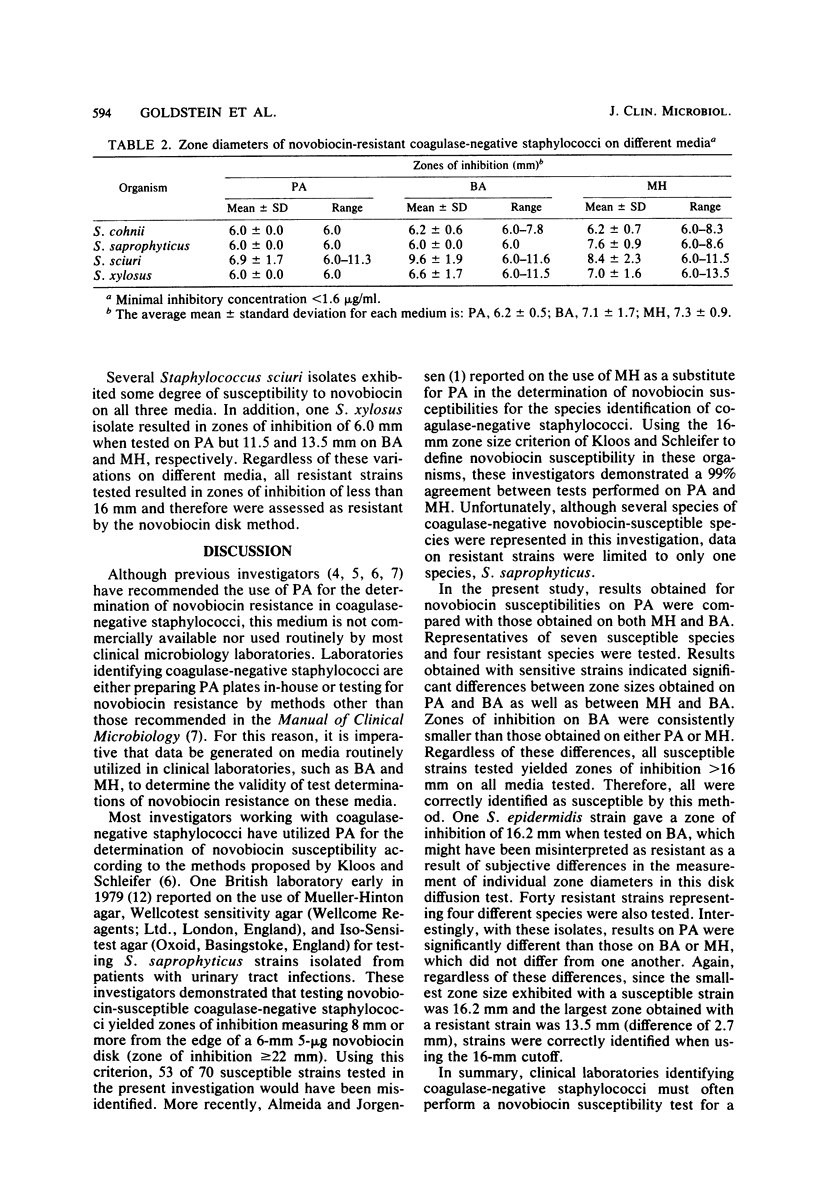
Species identification of coagulase-negative staphylococci often requires the determination of novobiocin susceptibility. Although previous investigators have recommended the use of P agar for this purpose, most clinical laboratories do not routinely utilize this medium. For this reason, studies were performed to compare novobiocin susceptibility results obtained with 11 different species of staphylococci (10 isolates of each species), using P agar, Trypticase soy agar with 5% sheep blood, and Mueller-Hinton agar. Tests performed on 70 susceptible isolates (minimal inhibitory concentration less than 1.6 micrograms/ml) resulted in zones of inhibition around 5-micrograms novobiocin disks ranging from 19.6 to 33.9, 16.2 to 26.6, and 21.3 to 36.4 mm on P agar, Trypticase soy agar with 5% sheep blood, and Mueller-Hinton agar, respectively. Forty resistant isolates (minimal inhibitory concentration greater than or equal to 1.6 micrograms/ml) exhibited zones of inhibition ranging from 6.0 to 11.3 mm on P agar, 6.0 to 11.6 mm on Trypticase soy agar with 5% sheep blood, and 6.0 to 13.5 mm on Mueller-Hinton agar. Using the established cut off of 16 mm to define novobiocin resistance for the identification of coagulase-negative staphylococci, we correctly identified 100% of the strains tested, regardless of the media utilized.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Almeida R. J., Jorgensen J. H. Use of Mueller-Hinton agar to determine novobiocin susceptibility of coagulase-negative staphylococci. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Dec;16(6):1155–1156. doi: 10.1128/jcm.16.6.1155-1156.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Archer G. L. Antimicrobial susceptibility and selection of resistance among Staphylococcus epidermidis isolates recovered from patients with infections of indwelling foreign devices. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Sep;14(3):353–359. doi: 10.1128/aac.14.3.353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eng R. H., Wang C., Person A., Kiehn T. E., Armstrong D. Species identification of coagulase-negative staphylococcal isolates from blood cultures. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Mar;15(3):439–442. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.3.439-442.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- John J. F., Jr, Gramling P. K., O'Dell N. M. Species identification of coagulase-negative staphylococci from urinary tract isolates. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Oct;8(4):435–437. doi: 10.1128/jcm.8.4.435-437.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kloos W. E., Schleifer K. H. Simplified scheme for routine identification of human Staphylococcus species. J Clin Microbiol. 1975 Jan;1(1):82–88. doi: 10.1128/jcm.1.1.82-88.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kloos W. E., Wolfshohl J. F. Identification of Staphylococcus species with the API STAPH-IDENT system. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Sep;16(3):509–516. doi: 10.1128/jcm.16.3.509-516.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis J. F., Brake S. R., Anderson D. J., Vredeveld G. N. Urinary tract infection due to coagulase-negative staphylococcus. Am J Clin Pathol. 1982 Jun;77(6):736–739. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/77.6.736. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liekweg W. G., Jr, Greenfield L. J. Vascular prosthetic infections: collected experience and results of treatment. Surgery. 1977 Mar;81(3):335–342. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shrestha T. L., Darrell J. H. Urinary infection with coagulase-negative staphylococci in a teaching hospital. J Clin Pathol. 1979 Mar;32(3):299–302. doi: 10.1136/jcp.32.3.299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tselenis-Kotsowilis A. D., Koliomichalis M. P., Papavassiliou J. T. Acute pyelonephritis caused by Staphylococcus xylosus. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Sep;16(3):593–594. doi: 10.1128/jcm.16.3.593-594.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


