Abstract
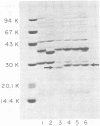
Over a 12-month period we obtained throat cultures from 1,448 children less than 5 years of age attending well-child clinics and identified 24 carriers of Haemophilus influenzae type b (1.7%). The outer membrane protein subtypes of the strains from the carriers were compared to the subtypes of isolates from 50 patients with Haemophilus type b disease hospitalized in St. Louis, Mo., during the same period (1981 to 1982), and the latter were compared to the subtypes of isolates from 51 patients hospitalized between 1977 and 1980. There were no significant differences in the frequencies of the five most common subtypes (1L, 1H, 2L, 2H, and 3L), comparing isolates from the carriers to those from the patients. However, 5 of the 24 throat isolates had the unusual 13L subtype compared with only 1 of the 50 invasive isolates (P = 0.02). The lower frequency of 13L strains among the invasive isolates suggests that type b isolates with this subtype may be less pathogenic than type b isolates with other subtypes. Subtype 2L strains accounted for only 2% of recent cerebrospinal fluid or blood isolates, compared with 22% of those from 1977 to 1980 (P = 0.02). Subtype 1H and 3L strains together accounted for 73%, compared with 47% of the earlier ones (P = 0.02). Thus, temporal shifts may also occur in the subtype distribution of Haemophilus type b strains causing invasive disease in a community.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albritton W. L., Penner S., Slaney L., Brunton J. Biochemical characteristics of Haemophilus influenzae in relationship to source of isolation and antibiotic resistance. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Jun;7(6):519–523. doi: 10.1128/jcm.7.6.519-523.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barenkamp S. J., Granoff D. M., Munson R. S., Jr Outer-membrane protein subtypes of Haemophilus influenzae type b and spread of disease in day-care centers. J Infect Dis. 1981 Sep;144(3):210–217. doi: 10.1093/infdis/144.3.210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barenkamp S. J., Munson R. S., Jr, Granoff D. M. Comparison of outer-membrane protein subtypes and biotypes of isolates of Haemophilus influenzae type b. J Infect Dis. 1981 Nov;144(5):480–480. doi: 10.1093/infdis/144.5.480. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barenkamp S. J., Munson R. S., Jr, Granoff D. M. Outer membrane protein and biotype analysis of pathogenic nontypable Haemophilus influenzae. Infect Immun. 1982 May;36(2):535–540. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.2.535-540.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barenkamp S. J., Munson R. S., Jr, Granoff D. M. Subtyping isolates of Haemophilus influenzae type b by outer-membrane protein profiles. J Infect Dis. 1981 May;143(5):668–676. doi: 10.1093/infdis/143.5.668. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barton L. L., Granoff D. M., Barenkamp S. J. Nosocomial spread of Haemophilus influenzae type b infection documented by outer membrane protein subtype analysis. J Pediatr. 1983 Jun;102(6):820–824. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(83)80005-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broud D. D., Griffiss J. M., Baker C. J. Heterogenity of serotypes of Neisseria meningitidis that cause endemic disease. J Infect Dis. 1979 Oct;140(4):465–470. doi: 10.1093/infdis/140.4.465. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilian M. A taxonomic study of the genus Haemophilus, with the proposal of a new species. J Gen Microbiol. 1976 Mar;93(1):9–62. doi: 10.1099/00221287-93-1-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lugtenberg B., Meijers J., Peters R., van der Hoek P., van Alphen L. Electrophoretic resolution of the "major outer membrane protein" of Escherichia coli K12 into four bands. FEBS Lett. 1975 Oct 15;58(1):254–258. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80272-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michaels R. H., Poziviak C. S., Stonebraker F. E., Norden C. W. Factors affecting pharyngeal Haemophilus influenzae type b colonization rates in children. J Clin Microbiol. 1976 Nov;4(5):413–417. doi: 10.1128/jcm.4.5.413-417.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michaels R. H., Stonebraker F. E., Robbins J. B. Use of antiserum agar for detection of Haemophilus influenzae type b in the pharynx. Pediatr Res. 1975 May;9(5):513–516. doi: 10.1203/00006450-197505000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mpairwe Y. Observations on the nasopharyngeal carriage of Haemophilus influenzae type b in children in Kampala, Uganda. J Hyg (Lond) 1970 Jun;68(2):337–341. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400028783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shackelford P. G., Campbell J., Feigin R. D. Countercurrent immunoelectrophoresis in the evaluation of childhood infections. J Pediatr. 1974 Oct;85(4):478–481. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(74)80448-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward J. I., Siber G. R., Scheifele D. W., Smith D. H. Rapid diagnosis of Hemophilus influenzae type b infections by latex particle agglutination and counterimmunoelectrophoresis. J Pediatr. 1978 Jul;93(1):37–42. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(78)80596-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]