Abstract
During an outbreak of infections caused by methicillin-resistant (MR) Staphylococcus aureus in our burn unit, we conducted an extensive 10-week study to define the environmental epidemiology of the organism. The inanimate environment in patient rooms and adjacent areas was examined by using volumetric air samplers and Rodac plates. Airborne and surface level contamination with MR S. aureus was quantitated, and overall, MR S. aureus comprised 16, 31, and 40% of all bacterial growth from air, elevated surfaces, and floor surfaces, respectively. Mean air, elevated surface, and floor surface MR S. aureus contamination in rooms of MR S. aureus-infected burn patients were 1.9 MR S. aureus per ft3 (ca. 0.028 m3), 20 MR S. aureus per Rodac plate and 48 MR S. aureus per Rodac plate, respectively. Peak patient room environmental contamination levels were 6.9 MR S. aureus per ft3 of air, 70 MR S. aureus per Rodac plate per elevated surface and 138 MR S. aureus per Rodac plate per floor surface. Environmental contamination levels in the adjacent work areas were considerably lower than in infected patient rooms. There was ample opportunity for contamination of personnel through the inanimate environment in this unit.
Full text
PDF
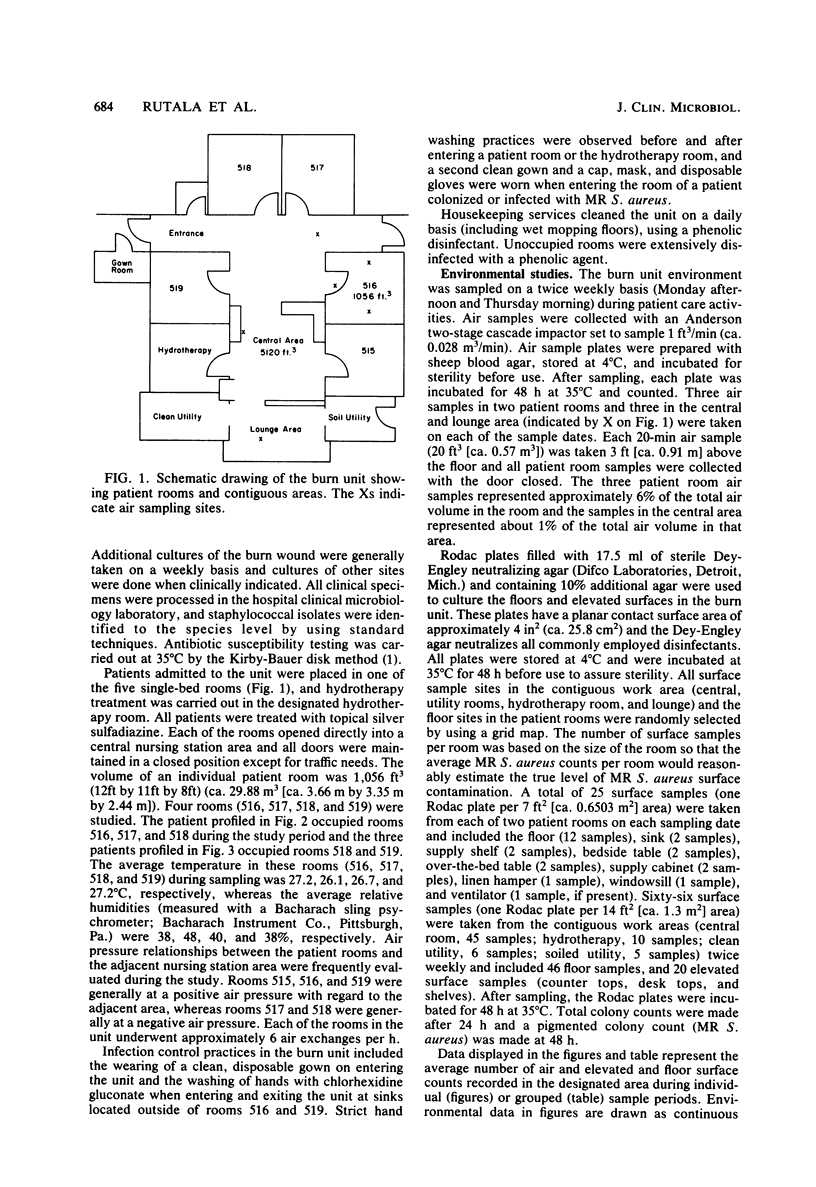
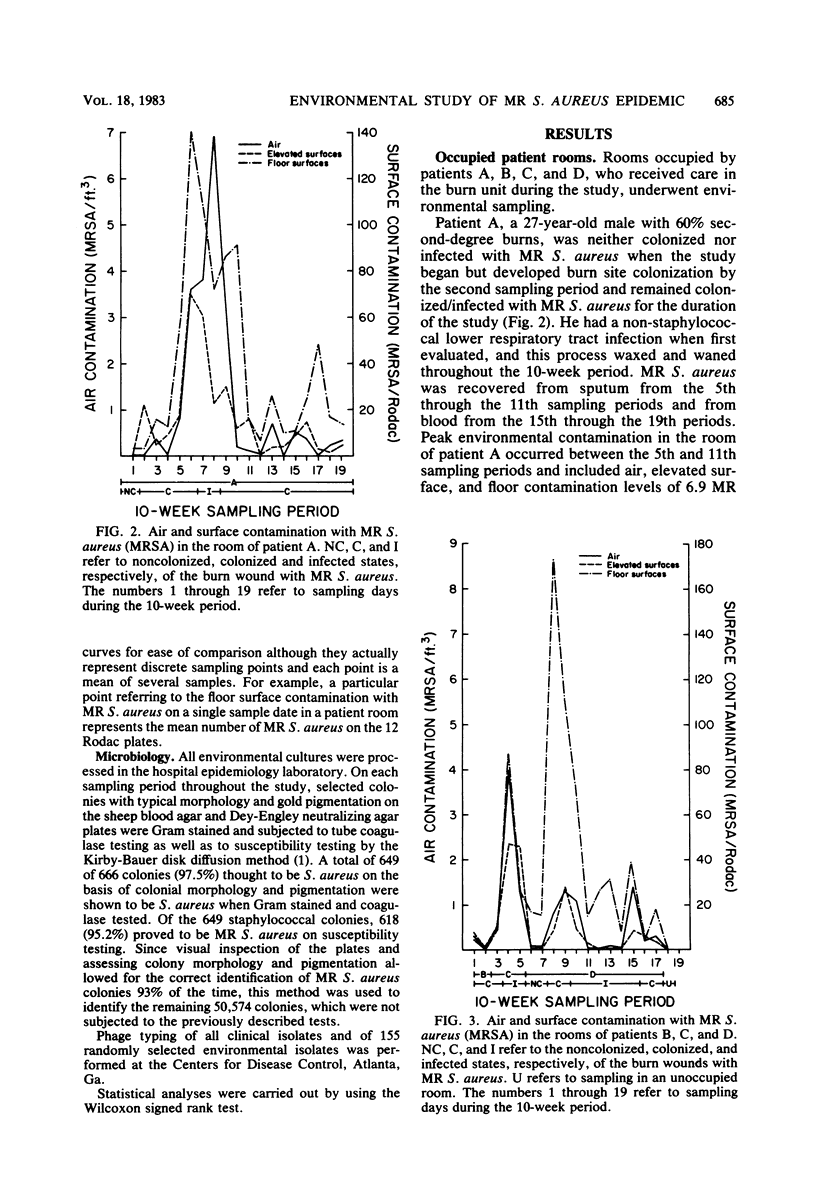



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bauer A. W., Kirby W. M., Sherris J. C., Turck M. Antibiotic susceptibility testing by a standardized single disk method. Am J Clin Pathol. 1966 Apr;45(4):493–496. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyce J. M., Landry M., Deetz T. R., DuPont H. L. Epidemiologic studies of an outbreak of nosocomial methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infections. Infect Control. 1981 Mar-Apr;2(2):110–116. doi: 10.1017/s0195941700053881. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crossley K., Landesman B., Zaske D. An outbreak of infections caused by strains of Staphylococcus aureus resistant to methicillin and aminoglycosides. II. Epidemiologic studies. J Infect Dis. 1979 Mar;139(3):280–287. doi: 10.1093/infdis/139.3.280. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crossley K., Loesch D., Landesman B., Mead K., Chern M., Strate R. An outbreak of infections caused by strains of Staphylococcus aureus resistant to methicillin and aminoglycosides. I. Clinical studies. J Infect Dis. 1979 Mar;139(3):273–279. doi: 10.1093/infdis/139.3.273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Everett E. D., McNitt T. R., Rahm A. E., Jr, Stevens D. L., Peterson H. E. Epidemiologic investigation of methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus in a burn unit. Mil Med. 1978 Mar;143(3):165–167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haley R. W., Hightower A. W., Khabbaz R. F., Thornsberry C., Martone W. J., Allen J. R., Hughes J. M. The emergence of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infections in United States hospitals. Possible role of the house staff-patient transfer circuit. Ann Intern Med. 1982 Sep;97(3):297–308. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-97-3-297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hambraeus A. Studies on transmission of Staphylococcus aureus in an isolated ward for burned patients. J Hyg (Lond) 1973 Mar;71(1):171–183. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400046349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klimek J. J., Marsik F. J., Bartlett R. C., Weir B., Shea P., Quintiliani R. Clinical, epidemiologic and bacteriologic observations of an outbreak of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus at a large community hospital. Am J Med. 1976 Sep;61(3):340–345. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(76)90370-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mortimer E. A., Jr, Wolinsky E., Gonzaga A. J., Rammelkamp C. H., Jr Role of airborne transmission in staphylococcal infections. Br Med J. 1966 Feb 5;1(5483):319–322. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5483.319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peacock J. E., Jr, Marsik F. J., Wenzel R. P. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: introduction and spread within a hospital. Ann Intern Med. 1980 Oct;93(4):526–532. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-93-4-526. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson R. L., Cabezudo I., Wenzel R. P. Epidemiology of nosocomial infections caused by methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Ann Intern Med. 1982 Sep;97(3):309–317. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-97-3-309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


