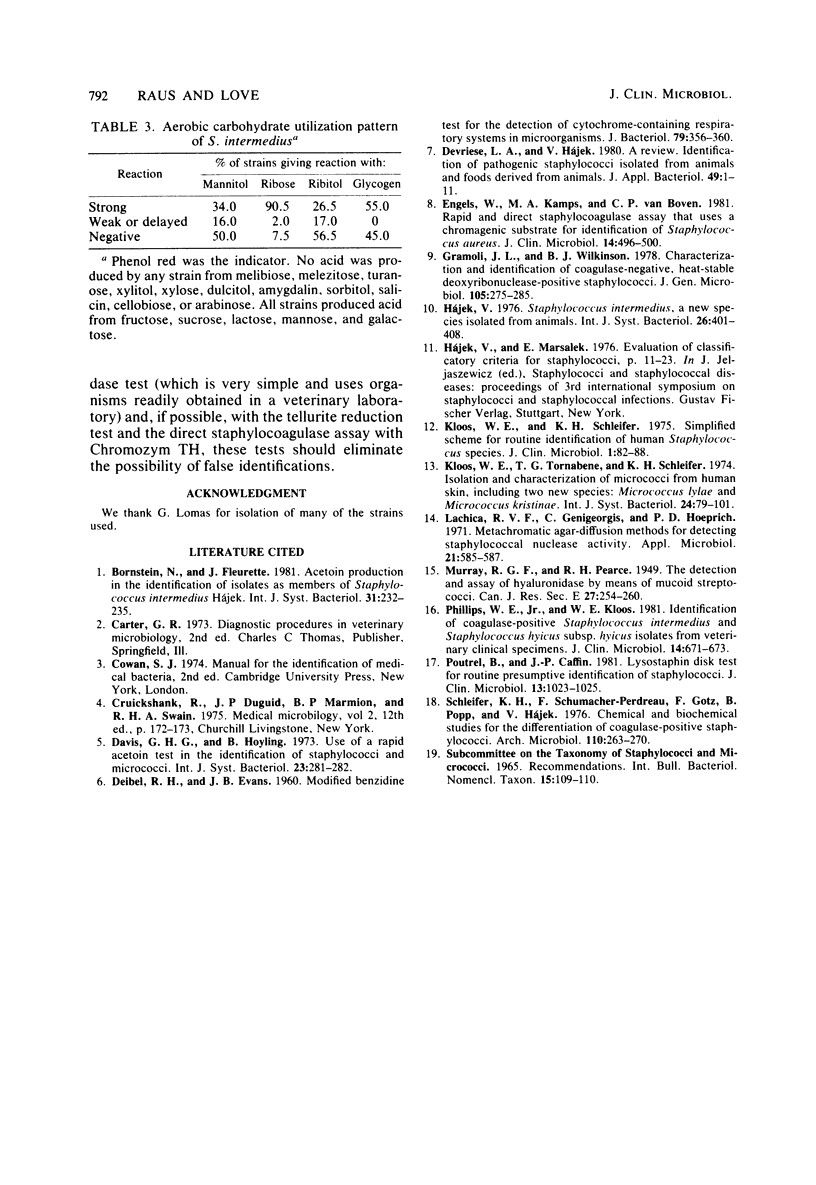
Abstract
Staphylococci were the most frequent isolates from clinical specimens submitted from a large referral and teaching veterinary hospital. In this study a total of 160 isolates were examined by a wide range of biochemical tests and modifications of basic procedures. An attempt was made to test the validity of these procedures for use in characterization of clinical isolates of coagulase-positive staphylococci. Of the isolates examined, some 27 were Staphylococcus aureus, 115 were Staphylococcus intermedius, and the rest were coagulase-negative staphylococci and were not characterized further. The most useful discriminatory tests were acid production from maltose incubated overnight on maltose purple agar (W. E. Kloos and K. H. Schleifer, J. Clin. Microbiol., 1:82-88, 1975), acetoin production detected by the Barritt method, and detection of hyaluronidase activity. These gave accurate and fast results. Supplemented with the tellurite reduction test and the direct staphylocoagulase assay using Chromozym TH (Engels et al.; J. Clin. Microbiol. 14:496-500, 1981), these tests should eliminate the possibility of false identifications of these two species.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- DEIBEL R. H., EVANS J. B. Modified benzidine test for the detection of cytochrome-containing respiratory systems in microorganisms. J Bacteriol. 1960 Mar;79:356–360. doi: 10.1128/jb.79.3.356-360.1960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devriese L. A., Hájek V. Identification of pathogenic staphylococci isolated from animals and foods derived from animals. J Appl Bacteriol. 1980 Aug;49(1):1–11. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1980.tb01038.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engels W., Kamps M. A., van Boven C. P. Rapid and direct staphylocoagulase assay that uses a chromogenic substrate for identification of Staphylococcus aureus. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Nov;14(5):496–500. doi: 10.1128/jcm.14.5.496-500.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gramoli J. L., Wilkinson B. J. Characterization and identification of coagulase-negative, heat-stable deoxyribonuclease-positive staphylococci. J Gen Microbiol. 1978 Apr;105(2):275–285. doi: 10.1099/00221287-105-2-275. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kloos W. E., Schleifer K. H. Simplified scheme for routine identification of human Staphylococcus species. J Clin Microbiol. 1975 Jan;1(1):82–88. doi: 10.1128/jcm.1.1.82-88.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lachica R. V., Genigeorgis C., Hoeprich P. D. Metachromatic agar-diffusion methods for detecting staphylococcal nuclease activity. Appl Microbiol. 1971 Apr;21(4):585–587. doi: 10.1128/am.21.4.585-587.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips W. E., Jr, Kloos W. E. Identification of coagulase-positive Staphylococcus intermedius and Staphylococcus hyicus subsp. hyicus isolates from veterinary clinical specimens. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Dec;14(6):671–673. doi: 10.1128/jcm.14.6.671-673.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poutrel B., Caffin J. P. Lysostaphin disk test for routine presumptive identification of staphylococci. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Jun;13(6):1023–1025. doi: 10.1128/jcm.13.6.1023-1025.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schleifer K. H., Schumacher-Perdreau F., Götz F., Popp B. Chemical and biochemical studies for the differentiation of coagulase-positive staphylococci. Arch Microbiol. 1976 Nov 2;110(23):263–270. doi: 10.1007/BF00690237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



