Abstract
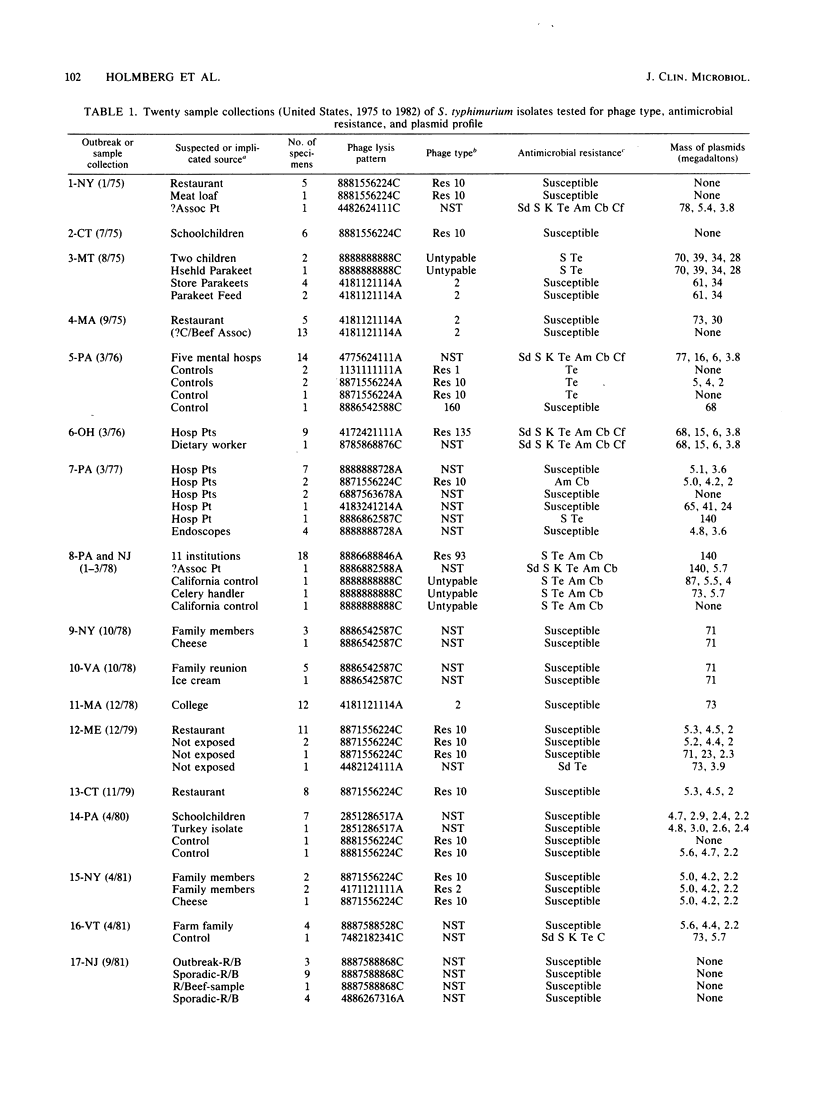
We compared the phage types, antimicrobial resistance patterns, and plasmid profiles of 20 groups of isolates received at the Centers for Disease Control from Salmonella typhimurium outbreaks between 1975 and 1982 to determine the most useful laboratory method for identifying epidemiologically related isolates of S. typhimurium. In 18 (90%) of the 20 outbreaks, epidemiologically related isolates were identified as being the same by each of the three methods. In a subgroup of nine outbreaks in which isolates unrelated to the outbreak were submitted for comparison, outbreak isolates were differentiated from such control isolates six times (67%) by phage typing alone, four times (44%) by antimicrobial susceptibility testing alone, and eight times (89%) by plasmid profile analysis alone. Epidemic isolates were multiply susceptible, nontypable, or without plasmids in 14 (70%), 1 (5%), and 3 (15%), respectively, of the 20 outbreaks. Plasmid analysis appeared to be at least as specific as phage typing in identifying epidemiologically related isolates of S. typhimurium as being the same or in differentiating them from control specimens; both techniques appeared to be superior to antimicrobial susceptibility testing.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson E. S., Ward L. R., Saxe M. J., de Sa J. D. Bacteriophage-typing designations of Salmonella typhimurium. J Hyg (Lond) 1977 Apr;78(2):297–300. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400056187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauer A. W., Kirby W. M., Sherris J. C., Turck M. Antibiotic susceptibility testing by a standardized single disk method. Am J Clin Pathol. 1966 Apr;45(4):493–496. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bezanson G., Khakhria R., Lacroix R. Involvement of plasmids in determining bacteriophage sensitivity in Salmonella typhimurium: genetic and physical analysis of phagovar 204. Can J Microbiol. 1982 Sep;28(9):993–1001. doi: 10.1139/m82-149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farmer J. J., 3rd Mnemonic for reporting bacteriocin and bacteriophage types. Lancet. 1970 Jul 11;1(7663):96–96. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(70)92663-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khakhria R., Lior H. Distribution of phagovars of Salmonella typhimurium in Canada (1969-1976). Zentralbl Bakteriol A. 1980;248(1):50–63. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyers J. A., Sanchez D., Elwell L. P., Falkow S. Simple agarose gel electrophoretic method for the identification and characterization of plasmid deoxyribonucleic acid. J Bacteriol. 1976 Sep;127(3):1529–1537. doi: 10.1128/jb.127.3.1529-1537.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riley L. W., DiFerdinando G. T., Jr, DeMelfi T. M., Cohen M. L. Evaluation of isolated cases of salmonellosis by plasmid profile analysis: introduction and transmission of a bacterial clone by precooked roast beef. J Infect Dis. 1983 Jul;148(1):12–17. doi: 10.1093/infdis/148.1.12. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor D. E., Levine J. G., Kouvelos K. L. Incidence of plasmid DNA in Salmonella strains isolated from clinical sources in Ontario, Canada, during 1979 and 1980. Can J Microbiol. 1982 Oct;28(10):1150–1157. doi: 10.1139/m82-170. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor D. N., Wachsmuth I. K., Shangkuan Y. H., Schmidt E. V., Barrett T. J., Schrader J. S., Scherach C. S., McGee H. B., Feldman R. A., Brenner D. J. Salmonellosis associated with marijuana: a multistate outbreak traced by plasmid fingerprinting. N Engl J Med. 1982 May 27;306(21):1249–1253. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198205273062101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Threlfall E. J., Ward L. R., Rowe B. Epidermic spread of a chloramphenicol-resistant strain of Salmonella typhimurium phage type 204 in bovine animals in Britain. Vet Rec. 1978 Nov 11;103(20):438–440. doi: 10.1136/vr.103.20.438. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willshaw G. A., Threlfall E. J., Ward L. R., Ashley A. S., Rowe B. Plasmid studies of drug-resistant epidemic strains of Salmonella typhimurium belonging to phage types 204 and 193. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1980 Nov;6(6):763–773. doi: 10.1093/jac/6.6.763. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



