Abstract
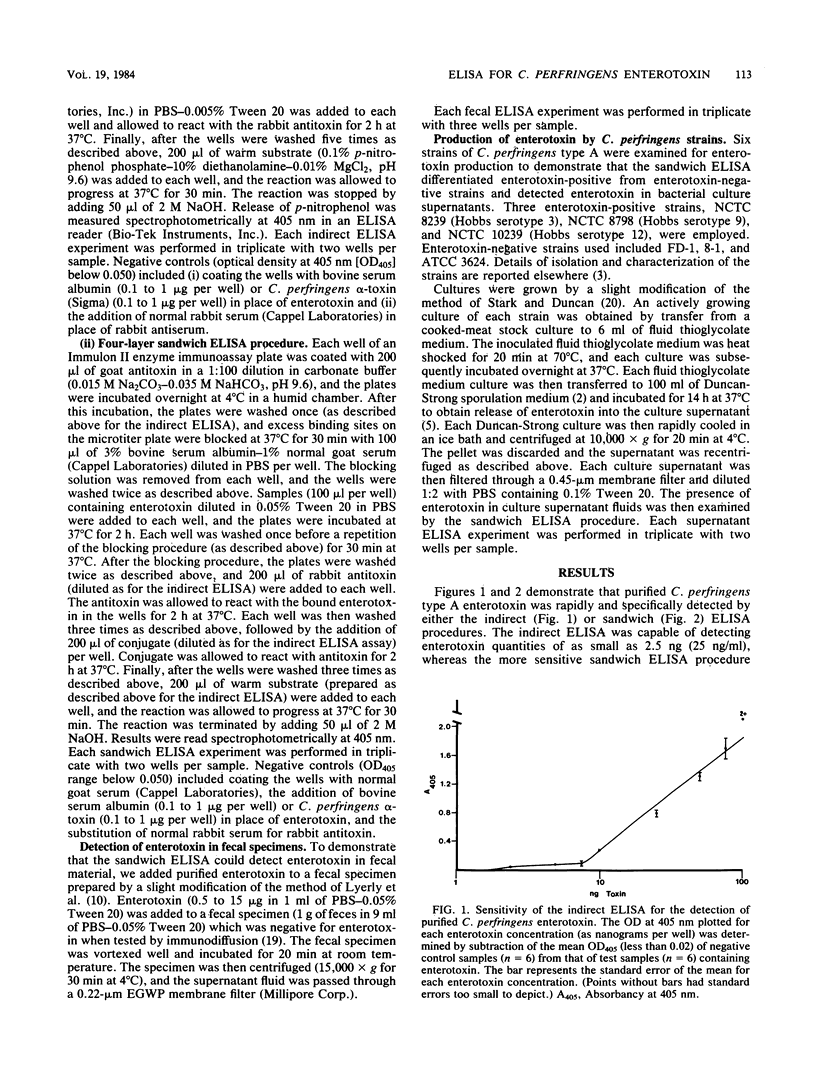
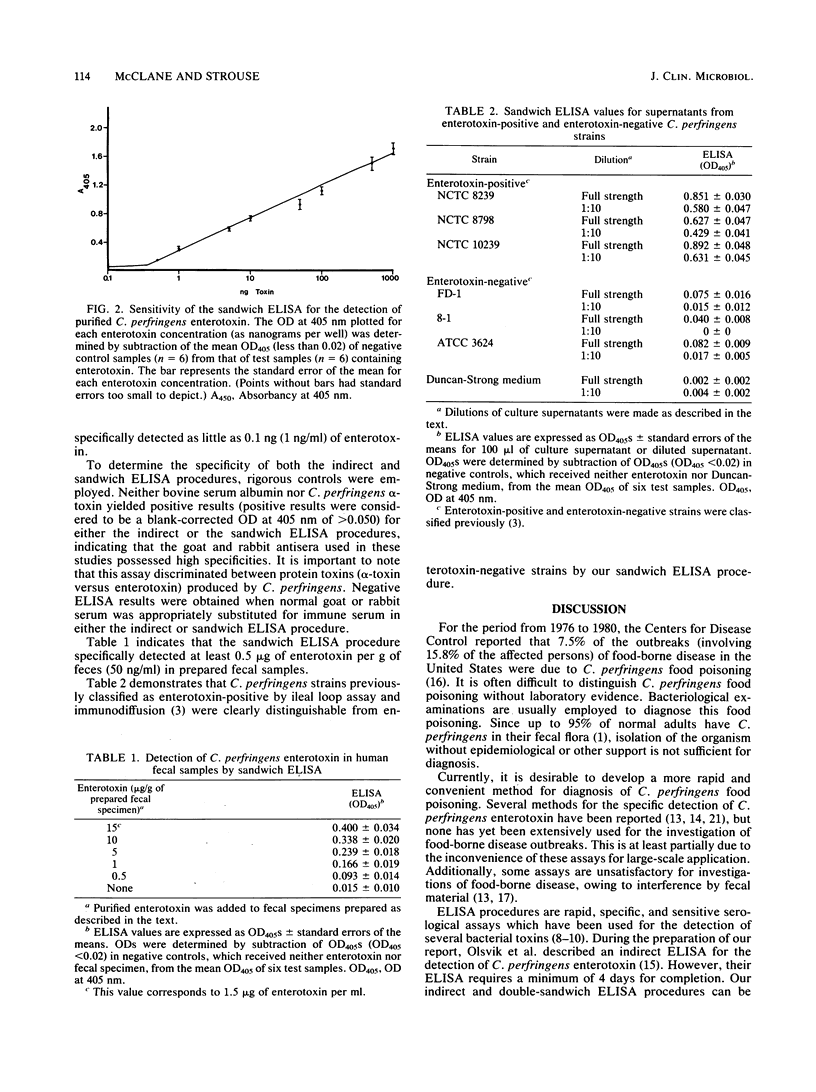
Clostridium perfringens type A enterotoxin was specifically detected and readily quantified by indirect and four-layer sandwich enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISAs). With the indirect ELISA, enterotoxin was detected in quantities of as low as 2.5 ng (25 ng/ml). When the more sensitive sandwich ELISA procedures was used, 100 pg (1 ng/ml) of enterotoxin was detected. The sandwich ELISA procedure specifically detected enterotoxin in human fecal extracts. Additionally, the sandwich ELISA specifically differentiated enterotoxin-positive strains from enterotoxin-negative strains of C. perfringens. Both the indirect and sandwich ELISA procedures described for C. perfringens enterotoxin in this report are rapid, specific, sensitive, and easily adaptable for large-scale use by clinical or research laboratories.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Duncan C. L., Strong D. H. Improved medium for sporulation of Clostridium perfringens. Appl Microbiol. 1968 Jan;16(1):82–89. doi: 10.1128/am.16.1.82-89.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan C. L., Strong D. H., Sebald M. Sporulation and enterotoxin production by mutants of Clostridium perfringens. J Bacteriol. 1972 Apr;110(1):378–391. doi: 10.1128/jb.110.1.378-391.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRABAR P., WILLIAMS C. A. Méthode permettant l'étude conjuguée des proprietés électrophorétiques et immunochimiques d'un mélange de protéines; application au sérum sanguin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1953 Jan;10(1):193–194. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(53)90233-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garel J. R., Labouesse B. The time dependence of the activity of delta-chymotrypsin at high pH. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Nov 1;39(1):293–300. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb03126.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Genigeorgis C. Public health importance of Clostridium perfringens. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1975 Nov 1;167(9):821–827. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granum P. E., Whitaker J. R. Improved method for purification of enterotoxin from Clostridium perfringens type A. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Jun;39(6):1120–1122. doi: 10.1128/aem.39.6.1120-1122.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kétyi I., Pácsa A. S. Estimation of Vibrio cholerae and Escherichia coli heat-labile enterotoxin by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Acta Microbiol Acad Sci Hung. 1980;27(1):89–97. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis G. E., Jr, Kulinski S. S., Reichard D. W., Metzger J. F. Detection of Clostridium botulinum type G toxin by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Dec;42(6):1018–1022. doi: 10.1128/aem.42.6.1018-1022.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyerly D. M., Sullivan N. M., Wilkins T. D. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for Clostridium difficile toxin A. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Jan;17(1):72–78. doi: 10.1128/jcm.17.1.72-78.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClane B. A., McDonel J. L. Protective effects of osmotic stabilizers on morphological and permeability alterations induced in Vero cells by Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Mar 6;641(2):401–409. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(81)90496-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonel J. L. Clostridium perfringens toxins (type A, B, C, D, E). Pharmacol Ther. 1980;10(3):617–655. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(80)90031-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonel J. L., McClane B. A. Highly sensitive assay for Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin that uses inhibition of plating efficiency of Vero cells grown in culture. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 May;13(5):940–946. doi: 10.1128/jcm.13.5.940-946.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naik H. S., Duncan C. L. Rapid detection and quantitation of Clostridium perfringens enterostoxin by counterimmunoelectrophoresis. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 Aug;34(2):125–128. doi: 10.1128/aem.34.2.125-128.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsvik O., Granum P. E., Berdal B. P. Detection of Clostridium perfringens type A enterotoxin by ELISA. Acta Pathol Microbiol Immunol Scand B. 1982 Dec;90(6):445–447. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1982.tb00144.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shandera W. X., Tacket C. O., Blake P. A. Food poisoning due to Clostridium perfringens in the United States. J Infect Dis. 1983 Jan;147(1):167–170. doi: 10.1093/infdis/147.1.167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skjelkvåle R., Uemura T. Detection of enterotoxin in faeces and anti-enterotoxin in serum after Clostridium perfringens food-poisoning. J Appl Bacteriol. 1977 Jun;42(3):355–363. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1977.tb00703.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skjelkvåle R., Uemura T. Experimental Diarrhoea in human volunteers following oral administration of Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin. J Appl Bacteriol. 1977 Oct;43(2):281–286. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1977.tb00752.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stark R. L., Duncan C. L. Biological characteristics of Clostridium perfringens type A enterotoxin. Infect Immun. 1971 Aug;4(2):89–96. doi: 10.1128/iai.4.2.89-96.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stark R. L., Duncan C. L. Purification and biochemical properties of Clostridium perfringens type A enterotoxin. Infect Immun. 1972 Nov;6(5):662–673. doi: 10.1128/iai.6.5.662-673.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uemura T., Sakaguchi G., Riemann H. P. In vitro production of Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin and its detection by reversed passive hemagglutination. Appl Microbiol. 1973 Sep;26(3):381–385. doi: 10.1128/am.26.3.381-385.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



