Abstract
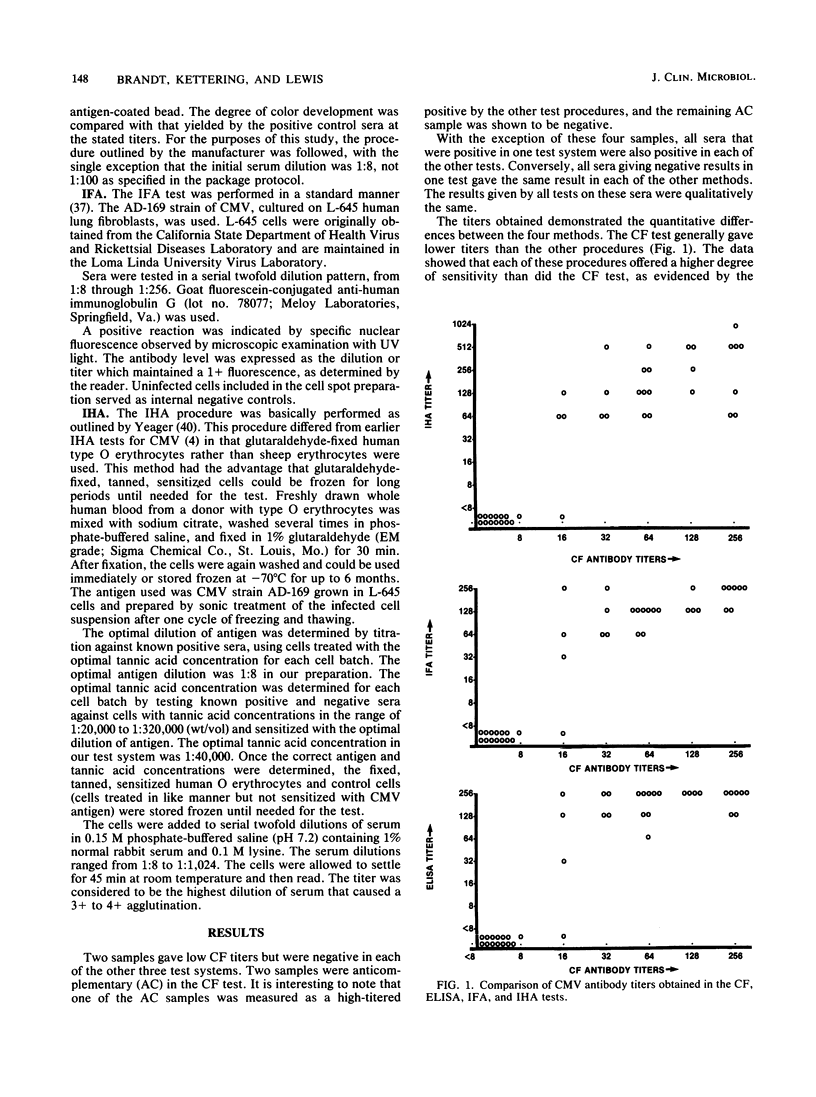
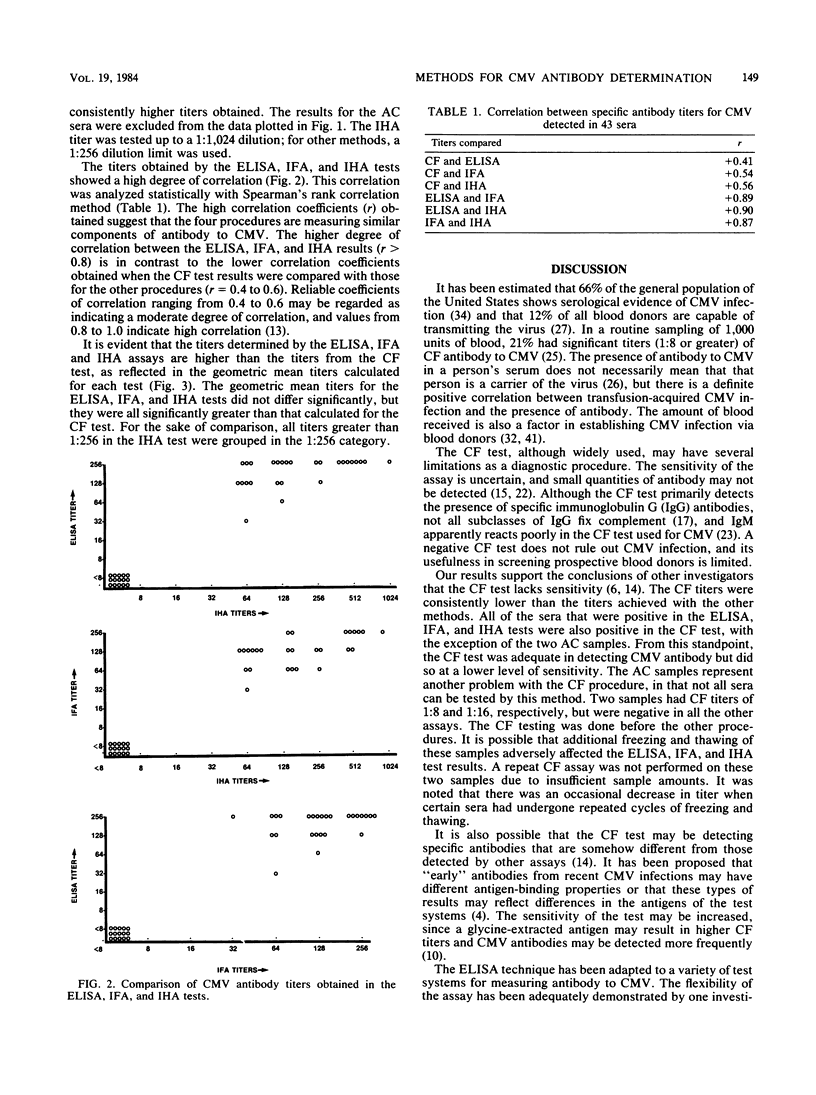
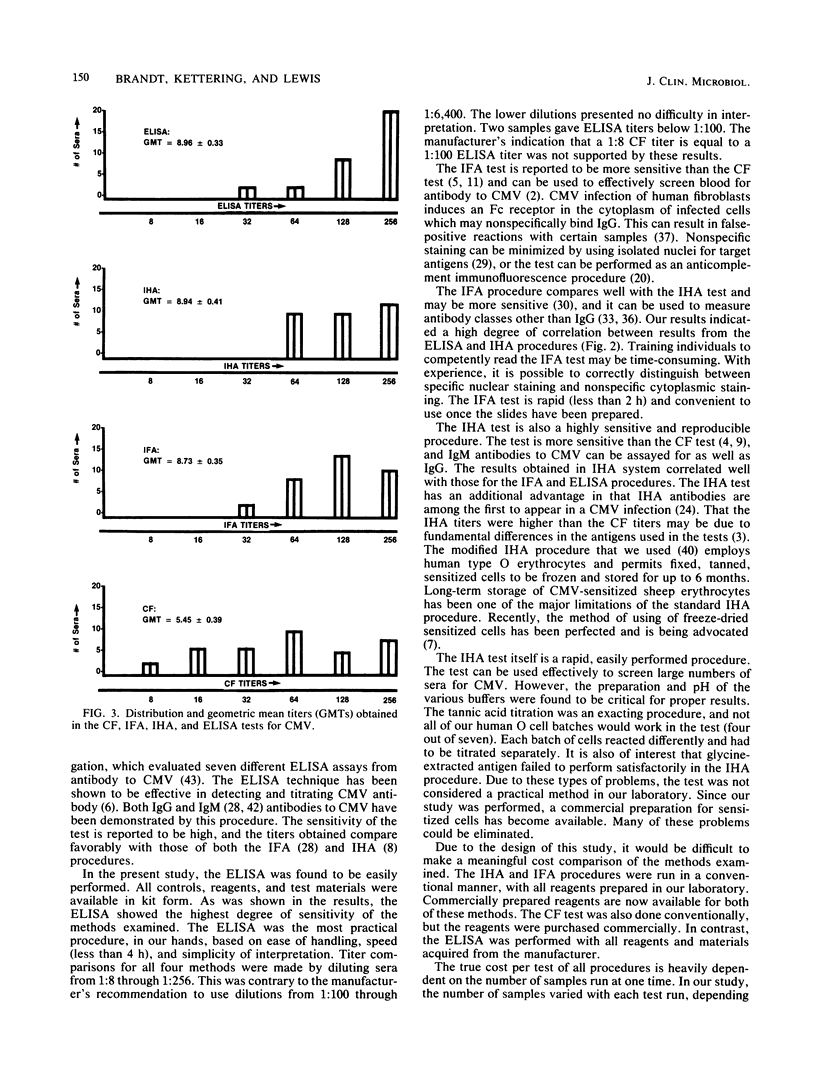
The complement fixation test is currently the test employed most frequently to determine the presence of antibody to human cytomegalovirus. Several other techniques have been adapted for this purpose. A comparison of cytomegalovirus antibody titers was made between the complement fixation test, a commercially available enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, an indirect immunofluorescent technique, and a modified indirect hemagglutination test. Forty-three serum samples were tested for antibodies by each of the above procedures. The enzyme-linked immunosorbent, immunofluorescent, and indirect hemagglutination assays were in close agreement on all samples tested; the titers obtained with these methods were all equal to or greater than the complement fixation titer for 38 of the 41 samples (92.6%). Two samples were anticomplementary in the complement fixation test but gave readable results in the other tests. The complement fixation test was the least sensitive of the procedures examined. The commercial enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay system was the most practical method and offered the highest degree of sensitivity in detecting antibodies to cytomegalovirus.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Armstrong D., Ely M., Steger L. Post-transfusion cytomegaloviremia and persistence of cytomegalovirus in blood. Infect Immun. 1971 Jan;3(1):159–163. doi: 10.1128/iai.3.1.159-163.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benson J. W., Bodden S. J., Tobin J. O. Cytomegalovirus and blood transfusion in neonates. Arch Dis Child. 1979 Jul;54(7):538–541. doi: 10.1136/adc.54.7.538. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benyesh-Melnick M., Vonka V., Probstmeyer F., Wimberly I. Human cytomegalovirus: properties of the complement-fixing antigen. J Immunol. 1966 Feb;96(2):261–267. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein M. T., Stewart J. A. Indirect hemagglutination test for detection of antibodies to Cytomegalovirus. Appl Microbiol. 1971 Jan;21(1):84–89. doi: 10.1128/am.21.1.84-89.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Betts R. F., George S. D., Rundell R. B., Freeman R. B., Douglas R. G., Jr Comparative activity of immunofluorescent antibody and complement-fixing antibody in cytomegalovirus infection. J Clin Microbiol. 1976 Aug;4(2):151–156. doi: 10.1128/jcm.4.2.151-156.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Booth J. C., Hannington G., Aziz T. A., Stern H. Comparison of enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) technique and complement-fixation test for estimation of cytomegalovirus IgG antibody. J Clin Pathol. 1979 Feb;32(2):122–127. doi: 10.1136/jcp.32.2.122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cabau N., Crainic R., Duros C., Denoyel G., Gaspar A., Bronnert C., Boué A., Horodniceanu F. Freeze-dried erythrocytes for an indirect hemagglutination test for detection of cytomegalovirus antibodies. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Jun;13(6):1026–1030. doi: 10.1128/jcm.13.6.1026-1030.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castellano G. A., Hazzard G. T., Madden D. L., Sever J. L. Comparison of the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and the indirect hemagglutination test for detection of antibody to cytomegalovirus. J Infect Dis. 1977 Oct;136 (Suppl):S337–S340. doi: 10.1093/infdis/136.supplement_2.s337. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cremer N. E., Hoffman M., Lennette E. H. Analysis of antibody assay methods and classes of viral antibodies in serodiagnosis of cytomegalovirus infection. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Aug;8(2):153–159. doi: 10.1128/jcm.8.2.153-159.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cremer N. E., Schmidt N. J., Jensen F., Hoffman M., Oshiro L. S., Lennette E. H. Complement-fixing antibody in human sera reactive with viral and soluble antigens of cytomegalovirus. J Clin Microbiol. 1975 Mar;1(3):262–267. doi: 10.1128/jcm.1.3.262-267.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diosi P., Moldovan E., Tomescu N. Latent cytomegalovirus infection in blood donors. Br Med J. 1969 Dec 13;4(5684):660–662. doi: 10.1136/bmj.4.5684.660. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths P. D., Buie K. J., Heath R. B. A comparison of complement fixation, indirect immunofluorescence for viral late antigens, and anti-complement immunofluorescence tests for the detection of cytomegalovirus specific serum antibodies. J Clin Pathol. 1978 Sep;31(9):827–831. doi: 10.1136/jcp.31.9.827. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horodniceanu F., Michelson S. Assessment of human cytomegalovirus antibody detection techniques. Arch Virol. 1980;64(4):287–301. doi: 10.1007/BF01320614. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howell C. L., Miller M. J., Martin W. J. Comparison of rates of virus isolation from leukocyte populations separated from blood by conventional and Ficoll-Paque/Macrodex methods. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Oct;10(4):533–537. doi: 10.1128/jcm.10.4.533-537.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishizaka T., Ishizaka K., Salmon S., Fudenberg H. Biologic activities of aggregated gamma-globulin. 8. Aggregated immunoglobulins of different classes. J Immunol. 1967 Jul;99(1):82–91. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kettering J. D., Schmidt N. J., Gallo D., Lennette E. H. Anti-complement immunofluorescence test for antibodies to human cytomegalovirus. J Clin Microbiol. 1977 Dec;6(6):627–632. doi: 10.1128/jcm.6.6.627-632.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Käriäinen L., Klemola E., Paloheimo J. Rise of cytomegalovirus antibodies in an infectious-mononucleosis-like syndrome after transfusion. Br Med J. 1966 May 21;1(5498):1270–1272. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5498.1270. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lang D. J., Ebert P. A., Rodgers B. M., Boggess H. P., Rixse R. S. Reduction of postperfusion cytomegalovirus-infections following the use of leukocyte depleted blood. Transfusion. 1977 Jul-Aug;17(4):391–395. doi: 10.1046/j.1537-2995.1977.17477216868.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lang D. J., Hanshaw J. B. Cytomegalovirus infection and the postperfusion syndrome. Recognition of primary infections in four patients. N Engl J Med. 1969 May 22;280(21):1145–1149. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196905222802103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lang D. J., Noren B. Cytomegaloviremia following congenital infection. J Pediatr. 1968 Dec;73(6):812–819. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(68)80233-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michelson S., Cabau N., Boue A., Horodniceanu F. Comparison of occurrence of antibodies to human cytomegalovirus as demonstrated by immunofluorescence and indirect hemagglutination techniques. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Jan;9(1):149–151. doi: 10.1128/jcm.9.1.149-151.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monif G. R., Adams W. R., Flory L. F. Complement-fixing antibodies to the AD-169 strain of cytomegalovirus in banked blood. Transfusion. 1974 Jan-Feb;14(1):58–60. doi: 10.1111/j.1537-2995.1974.tb04485.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monif G. R., Daicoff G. I., Flory L. L. Blood as a potential vehicle for the cytomegaloviruses. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1976 Oct 15;126(4):445–448. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(76)90636-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prince A. M., Szmuness W., Millian S. J., David D. S. A serologic study of cytomegalovirus infections associated with blood transfusions. N Engl J Med. 1971 May 20;284(20):1125–1131. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197105202842004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitz H., Doerr H. W., Kampa D., Vogt A. Solid-phase enzyme immunoassay for immunoglobulin M antibodies to cytomegalovirus. J Clin Microbiol. 1977 Jun;5(6):629–634. doi: 10.1128/jcm.5.6.629-634.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stagno S., Reynolds D. W., Smith R. J. Use of isolated nuclei in the indirect fluorescent-antibody test for human cytomegalovirus infection: comparison with microneutralization, anticomplement, and conventional indirect fluorescent-antibody assays. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 May;7(5):486–489. doi: 10.1128/jcm.7.5.486-489.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stagno S., Reynolds D. W., Tsiantos A., Fuccillo D. A., Long W., Alford C. A. Comparative serial virologic and serologic studies of symptomatic and subclinical congenitally and natally acquired cytomegalovirus infections. J Infect Dis. 1975 Nov;132(5):568–577. doi: 10.1093/infdis/132.5.568. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens D. P., Barker L. F., Ketcham A. S., Meyer H. M., Jr Asymptomatic cytomegalovirus infection following blood transfusion in tumor surgery. JAMA. 1970 Feb 23;211(8):1341–1344. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- The T. H., Klein G., Langenhuysen M. M. Antibody reactions to virus-specific early antigens (EA) in patients with cytomegalovirus (CMV) infection. Clin Exp Immunol. 1974 Jan;16(1):1-7,9-12. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tolkoff-Rubin N. A., Rubin R. H., Keller E. E., Baker G. P., Stewart J. A., Hirsch M. S. Cytomegalovirus infection in dialysis patients and personnel. Ann Intern Med. 1978 Nov;89(5 Pt 1):625–628. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-89-5-625. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torrey E. F., Yolken R. H., Winfrey C. J. Cytomegalovirus antibody in cerebrospinal fluid of schizophrenic patients detected by enzyme immunoassay. Science. 1982 May 21;216(4548):892–894. doi: 10.1126/science.6281883. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WYATT J. P., HEMSATH F. A., SOASH M. D. Disseminated cytomegalic inclusion disease in an adult; with primary refractory anemia and transfusional siderosis; report of a case. Am J Clin Pathol. 1951 Jan;21(1):50–55. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/21.1.50. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waner J. L., Hopkins D. R., Weller T. H., Allred E. N. Cervical excretion cytomegalovirus: correlation with secretory and humoral antibody. J Infect Dis. 1977 Dec;136(6):805–809. doi: 10.1093/infdis/136.6.805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winston D. J., Ho W. G., Howell C. L., Miller M. J., Mickey R., Martin W. J., Lin C. H., Gale R. P. Cytomegalovirus infections associated with leukocyte transfusions. Ann Intern Med. 1980 Nov;93(5):671–675. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-93-5-671. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeager A. S., Grumet F. C., Hafleigh E. B., Arvin A. M., Bradley J. S., Prober C. G. Prevention of transfusion-acquired cytomegalovirus infections in newborn infants. J Pediatr. 1981 Feb;98(2):281–287. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(81)80662-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeager A. S. Improved indirect hemagglutination test for cytomegalovirus using human O erythrocytes in lysine. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Jul;10(1):64–68. doi: 10.1128/jcm.10.1.64-68.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yolken R. H., Leister F. J. Enzyme immunoassays for measurement of cytomegalovirus immunoglobulin M antibody. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Oct;14(4):427–432. doi: 10.1128/jcm.14.4.427-432.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yolken R. H., Stopa P. J. Comparison of seven enzyme immunoassay systems for measurement of cytomegalovirus. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Jun;11(6):546–551. doi: 10.1128/jcm.11.6.546-551.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Silva L. M., Kampfner G. L., Lister C. M., Tobin J. O. Identification of pregnancies at risk from cytomegalovirus infection. J Hyg (Lond) 1977 Dec;79(3):347–354. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400053183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


