Abstract
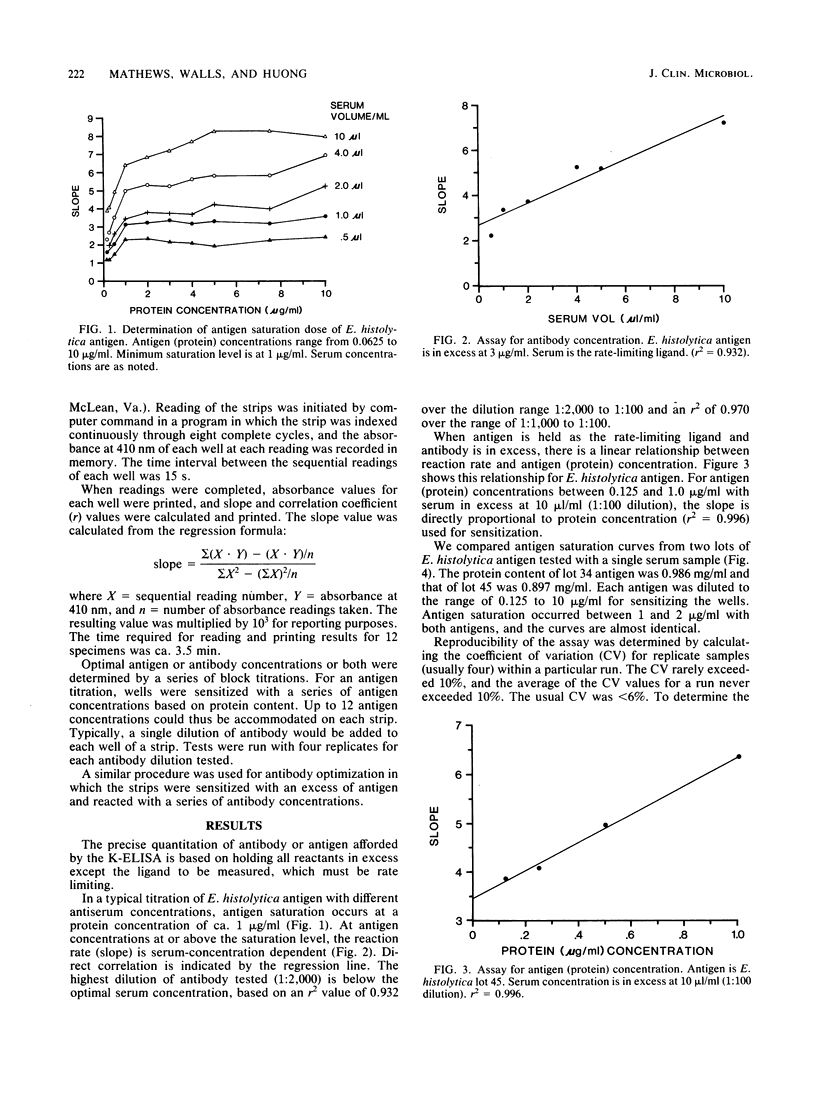
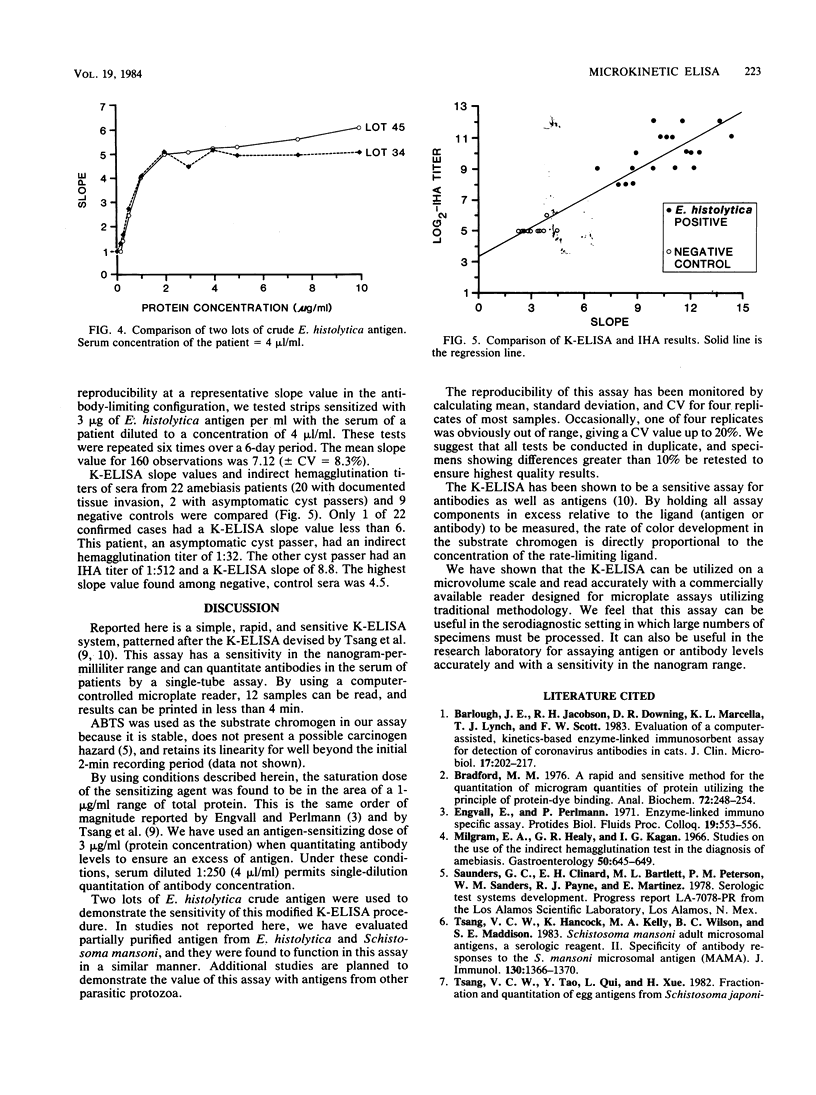
We describe a microvolume enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay based on enzyme rate kinetics. Antigens from Entamoeba histolytica were adsorbed in wells of disposable polystyrene strips containing 12 flat-bottom wells. After exposure to the serum of a patient and peroxidase-labeled anti-human immunoglobulin G, the rate of color change in specific substrate was determined by eight sequential readings of individual wells over a 2-min period with a microcomputer-controlled model MR-600 automated plate reader. The changes in absorbance readings were converted to slope values for each well by the microcomputer. Thus, 12 samples were read, and results were printed in ca. 3.5 min. Assay conditions are described and data are presented to show that this assay is quantitative for antibody and antigen concentration with a single-tube (well) dilution.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barlough J. E., Jacobson R. H., Downing D. R., Marcella K. L., Lynch T. J., Scott F. W. Evaluation of a computer-assisted, kinetics-based enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for detection of coronavirus antibodies in cats. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Feb;17(2):202–217. doi: 10.1128/jcm.17.2.202-217.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milgram E. A., Healty G. R., Kagan I. G. Studies on the use of the indirect hemagglutination test in the diagnosis of amebiasis. Gastroenterology. 1966 May;50(5):645–649. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsang V. C., Hancock K., Kelly M. A., Wilson B. C., Maddison S. E. Schistosoma mansoni adult microsomal antigens, a serologic reagent. II. Specificity of antibody responses to the S. mansoni microsomal antigen (MAMA). J Immunol. 1983 Mar;130(3):1366–1370. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsang V. C., Tsang K. R., Hancock K., Kelly M. A., Wilson B. C., Maddison S. E. Schistosoma mansoni adult microsomal antigens, a serologic reagent. I. Systematic fractionation, quantitation, and characterization of antigenic components. J Immunol. 1983 Mar;130(3):1359–1365. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsang V. C., Wilson B. C., Maddison S. E. Kinetic studies of a quantitative single-tube enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Clin Chem. 1980 Aug;26(9):1255–1260. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsang V. C., Wilson B. C., Peralta J. M. Quantitative, single-tube, kinetic-dependent enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (k-ELISA). Methods Enzymol. 1983;92:391–403. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)92033-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


