Abstract
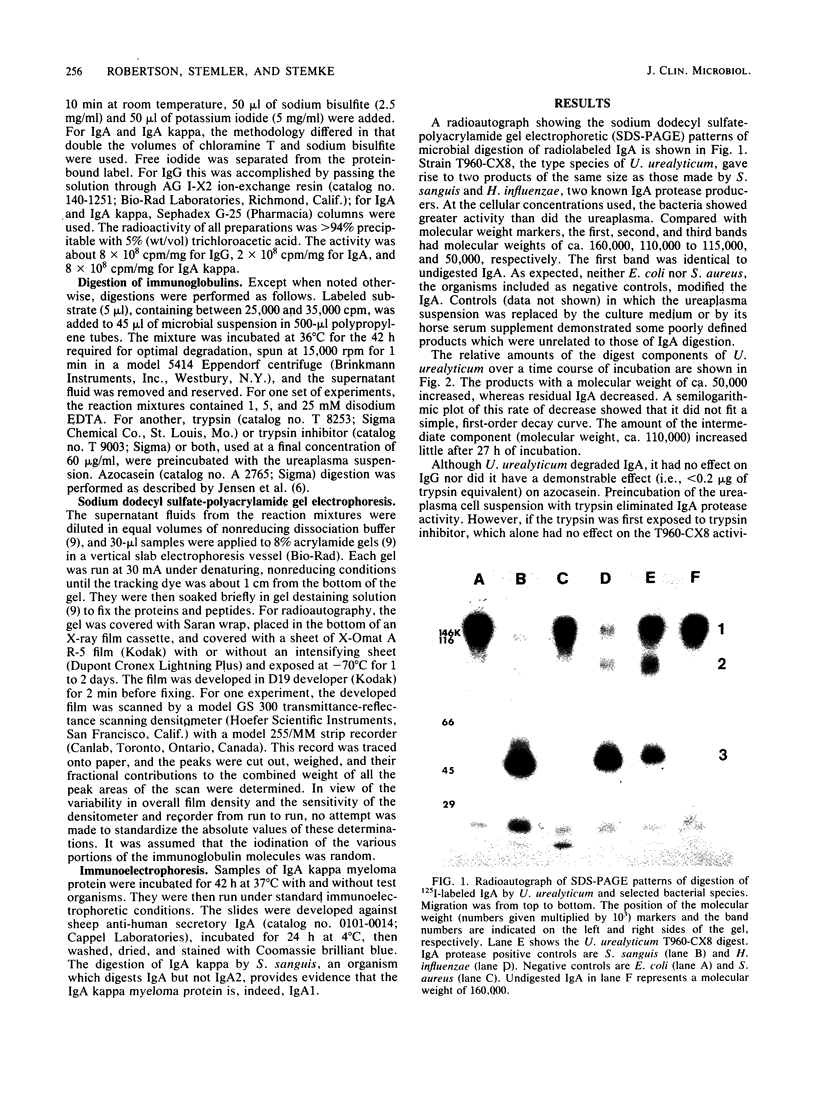
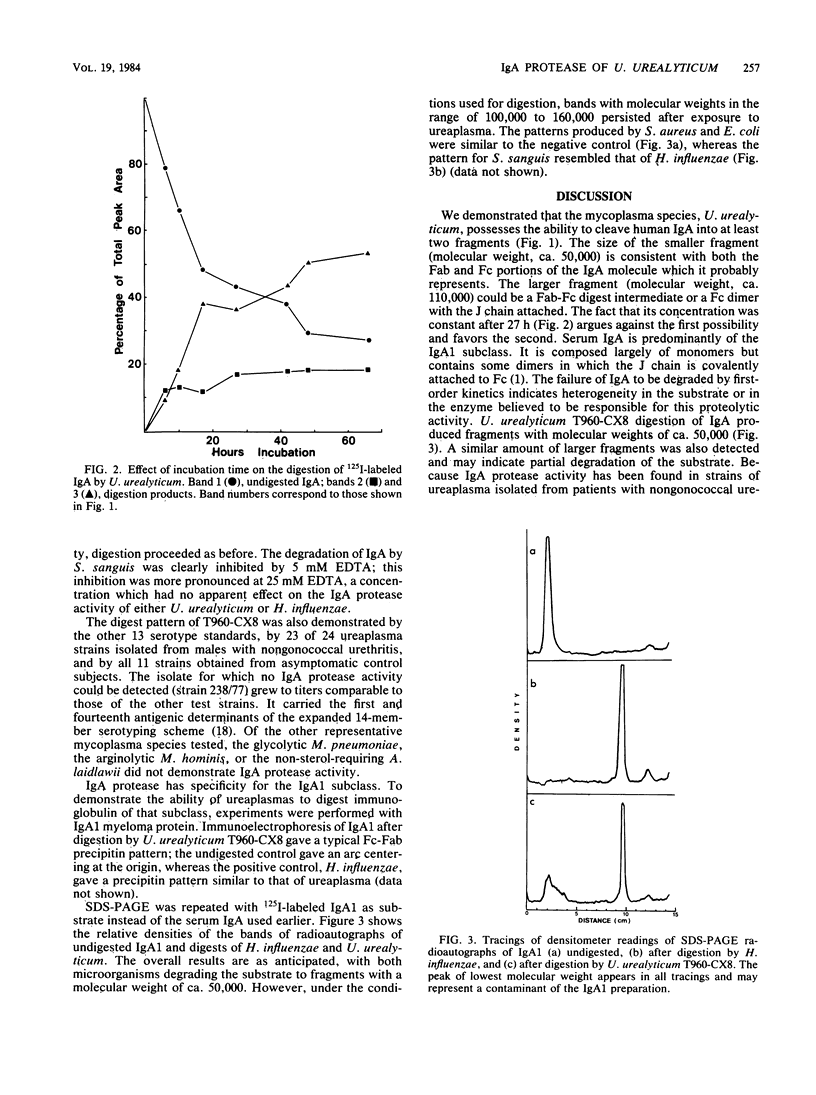
All of 14 serotype standards and 34 of 35 wild-type strains of Ureaplasma urealyticum isolated from humans demonstrated an immunoglobulin A (IgA) protease activity. This activity degraded radiolabeled human IgA including IgA1 but not IgG or azocasein. The IgA fragments were detected by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, followed by radioautography, and they had molecular weights of about 110,000 and 50,000. The IgA protease activity persisted in 25 mM EDTA but was sensitive to trypsin; it was presumed to be protein. This is the fourth microbial genus and the first myocoplasma species in which an IgA protease activity has been identified. Such activity was absent in Mycoplasma pneumoniae, Mycoplasma hominis, and Acholeplasma laidlawii.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Garcia-Pardo A., Lamm M. E., Plaut A. G., Frangione B. J chain is covalently bound to both monomer subunits in human secretory IgA. J Biol Chem. 1981 Nov 25;256(22):11734–11738. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Genco R. J., Plaut A. G., Moellering R. C., Jr Evaluation of human oral organisms and pathogenic Streptococcus for production of IgA protease. J Infect Dis. 1975 May;131 (Suppl):S17–S21. doi: 10.1093/infdis/131.supplement.s17. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goudswaard J., van der Donk J. A., Noordzij A., van Dam R. H., Vaerman J. P. Protein A reactivity of various mammalian immunoglobulins. Scand J Immunol. 1978;8(1):21–28. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1978.tb00492.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen S. E., Phillippe L., Teng Tseng J., Stemke G. W., Campbell J. N. Purification and characterization of exocellular proteases produced by a clinical isolate and a laboratory strain of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Can J Microbiol. 1980 Jan;26(1):77–86. doi: 10.1139/m80-012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilian M., Mestecky J., Schrohenloher R. E. Pathogenic species of the genus Haemophilus and Streptococcus pneumoniae produce immunoglobulin A1 protease. Infect Immun. 1979 Oct;26(1):143–149. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.1.143-149.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornfeld S. J., Plaut A. G. Secretory immunity and the bacterial IgA proteases. Rev Infect Dis. 1981 May-Jun;3(3):521–534. doi: 10.1093/clinids/3.3.521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Male C. J. Immunoglobulin A1 protease production by Haemophilus influenzae and Streptococcus pneumoniae. Infect Immun. 1979 Oct;26(1):254–261. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.1.254-261.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mehta S. K., Plaut A. G., Calvanico N. J., Tomasi T. B., Jr Human immunoglobulin A: production of an Fc fragment by an enteric microbial proteolytic enzyme. J Immunol. 1973 Oct;111(4):1274–1276. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulks M. H., Kornfeld S. J., Plaut A. G. Specific proteolysis of human IgA by Streptococcus pneumoniae and Haemophilus influenzae. J Infect Dis. 1980 Apr;141(4):450–456. doi: 10.1093/infdis/141.4.450. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulks M. H., Plaut A. G. IgA protease production as a characteristic distinguishing pathogenic from harmless neisseriaceae. N Engl J Med. 1978 Nov 2;299(18):973–976. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197811022991802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plaut A. G., Gilbert J. V., Artenstein M. S., Capra J. D. Neisseria gonorrhoeae and neisseria meningitidis: extracellular enzyme cleaves human immunoglobulin A. Science. 1975 Dec 12;190(4219):1103–1105. doi: 10.1126/science.810892. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plaut A. G. Microbial IgA proteases. N Engl J Med. 1978 Jun 29;298(26):1459–1463. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197806292982608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson J. A. Bromothymol blue broth: improved medium for detection of Ureaplasma urealyticum (T-strain mycoplasma). J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Feb;7(2):127–132. doi: 10.1128/jcm.7.2.127-132.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson J. A., Stemke G. W. Expanded serotyping scheme for Ureaplasma urealyticum strains isolated from humans. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 May;15(5):873–878. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.5.873-878.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shepard M. C., Howard D. R. Identification of "T" mycoplasmas in primary agar cultures by means of a direct test for urease. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1970 Oct 30;174(2):809–819. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1970.tb45598.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stemke G. W., Robertson J. A. Modified colony indirect epifluorescence test for serotyping Ureaplasma urealyticum and an adaptation to detect common antigenic specificity. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Nov;14(5):582–584. doi: 10.1128/jcm.14.5.582-584.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor-Robinson D., McCormack W. M. The genital mycoplasmas (second of two parts). N Engl J Med. 1980 May 8;302(19):1063–1067. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198005083021905. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vinther O., Black F. T. Aminopeptidase activity of Ureaplasma urealyticum. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1974 Dec;82(6):917–918. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1974.tb02393.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe T., Mishima K., Horikawa T. Proteolytic activities of human mycoplasmas. Jpn J Microbiol. 1973 Mar;17(2):151–153. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1973.tb00719.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]