Abstract
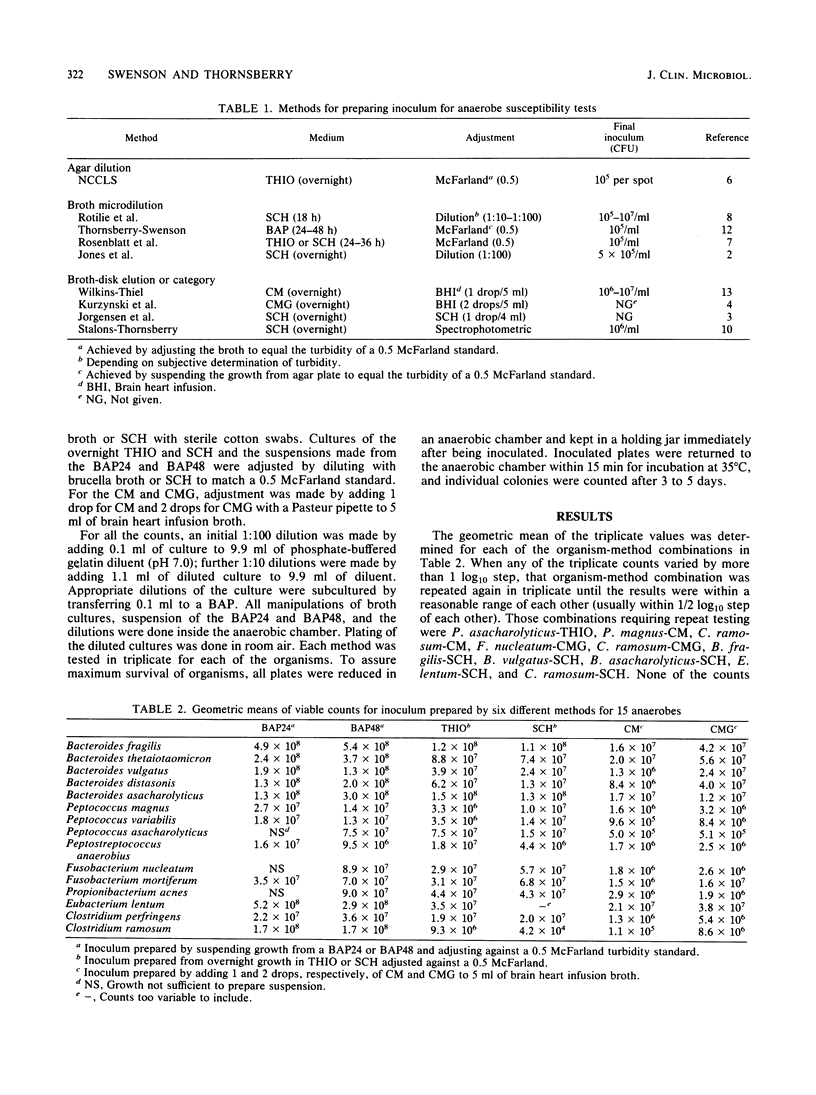
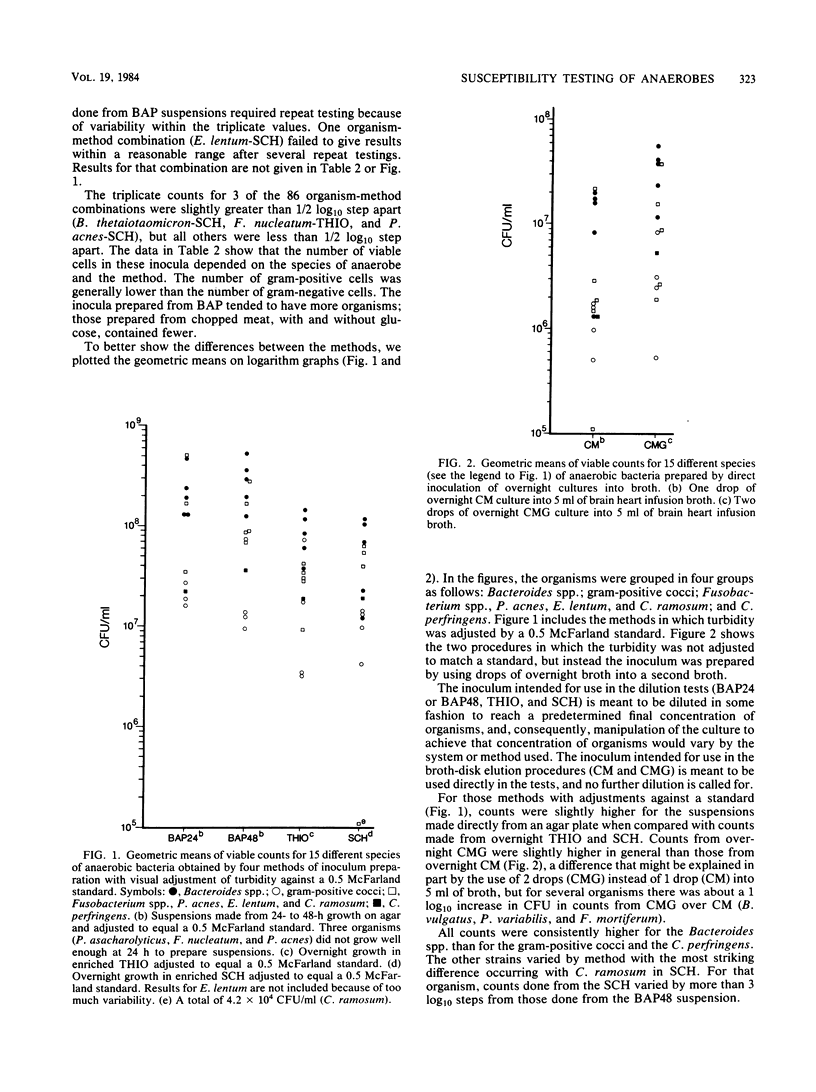
We studied six methods for preparation of inoculum to use in susceptibility tests of anaerobic bacteria to determine viable counts of 15 different species of anaerobes. We counted viable bacteria for each method-organism combination. Methods studied included those used for the more routine tests (broth microdilution and broth-disk elution) and for the National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards standard reference agar method. Inocula prepared from broth suspensions of organisms from 24- and 48-h anaerobe blood agar plates and adjusted to the turbidity of a 0.5 McFarland standard gave the most consistent counts for all organisms and also the highest numbers. Counts from these suspensions were higher than those from overnight growth in thioglycolate or Schaedler broth when all were adjusted against the same turbidity standard. Preparing inoculum directly from agar plates may also speed up the sometimes lengthy process of susceptibility testing of anaerobes and thus make results more clinically useful.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker C. N., Thornsberry C., Hawkinson R. W. Inoculum standardization in antimicrobial susceptibility testing: evaluation of overnight agar cultures and the Rapid Inoculum Standardization System. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Mar;17(3):450–457. doi: 10.1128/jcm.17.3.450-457.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jorgensen J. H., Alexander G. A., Johnson J. E. Practical anaerobic broth-disk elution susceptibility test. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Apr;17(4):740–742. doi: 10.1128/aac.17.4.740. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurzynski T. A., Yrios J. W., Helstad A. G., Field C. R. Aerobically incubated thioglycolate broth disk method for antibiotic susceptibility testing of anaerobes. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Oct;10(4):727–732. doi: 10.1128/aac.10.4.727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenblatt J. E., Murray P. R., Sonnenwirth A. C., Joyce J. L. Comparison of anaerobic susceptibility results obtained by different methods. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Mar;15(3):351–355. doi: 10.1128/aac.15.3.351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotilie C. A., Fass R. J., Prior R. B., Perkins R. L. Microdilution technique for antimicrobial susceptibility testing of anaerobic bacteria. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1975 Mar;7(3):311–315. doi: 10.1128/aac.7.3.311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sottile W., 2nd, Zabransky R. J. Comparative growth rates of selected anaerobic species in four commonly used broth media. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 Mar;11(3):482–490. doi: 10.1128/aac.11.3.482. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stalons D. R., Thornsberry C. Broth-dilution method for determining the antibiotic susceptibility of anaerobic bacteria. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1975 Jan;7(1):15–21. doi: 10.1128/aac.7.1.15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stalons D. R., Thornsberry C., Dowell V. R., Jr Effect of culture medium and carbon dioxide concentration on growth of anaerobic bacteria commonly encountered in clinical specimens. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Jun;27(6):1098–1104. doi: 10.1128/am.27.6.1098-1104.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkins T. D., Thiel T. Modified broth-disk method for testing the antibiotic susceptibility of anaerobic bacteria. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1973 Mar;3(3):350–356. doi: 10.1128/aac.3.3.350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


