Abstract
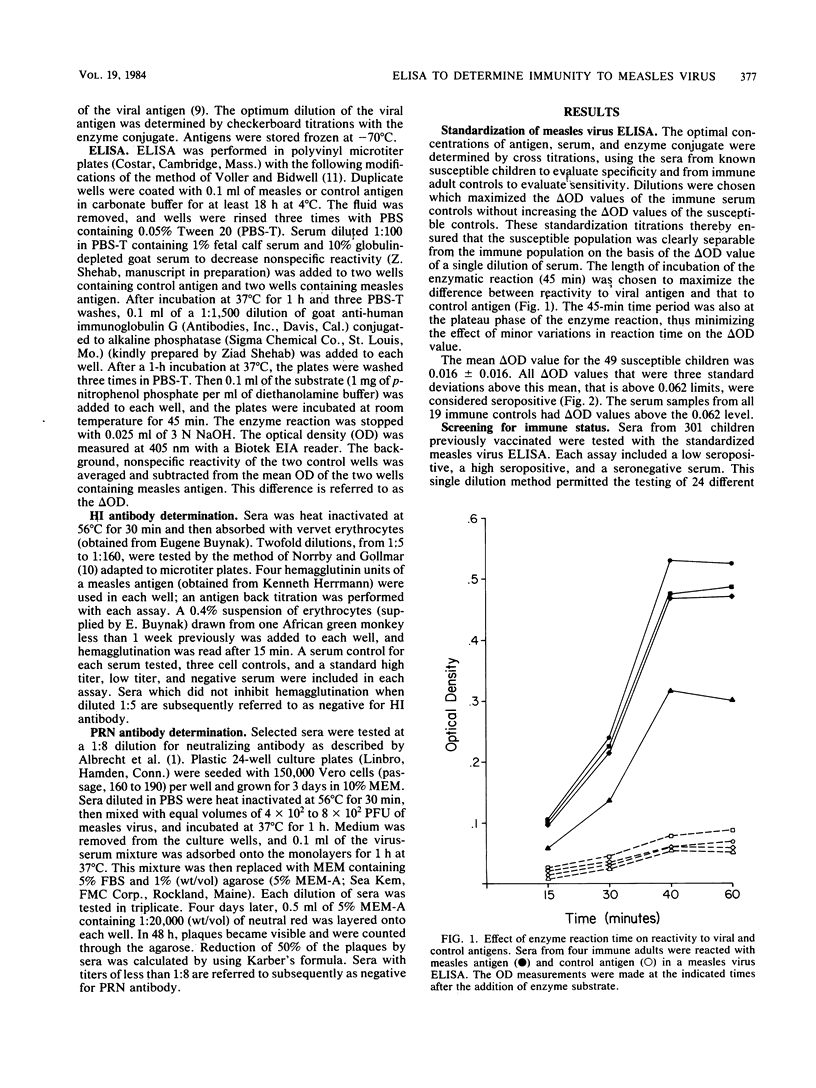
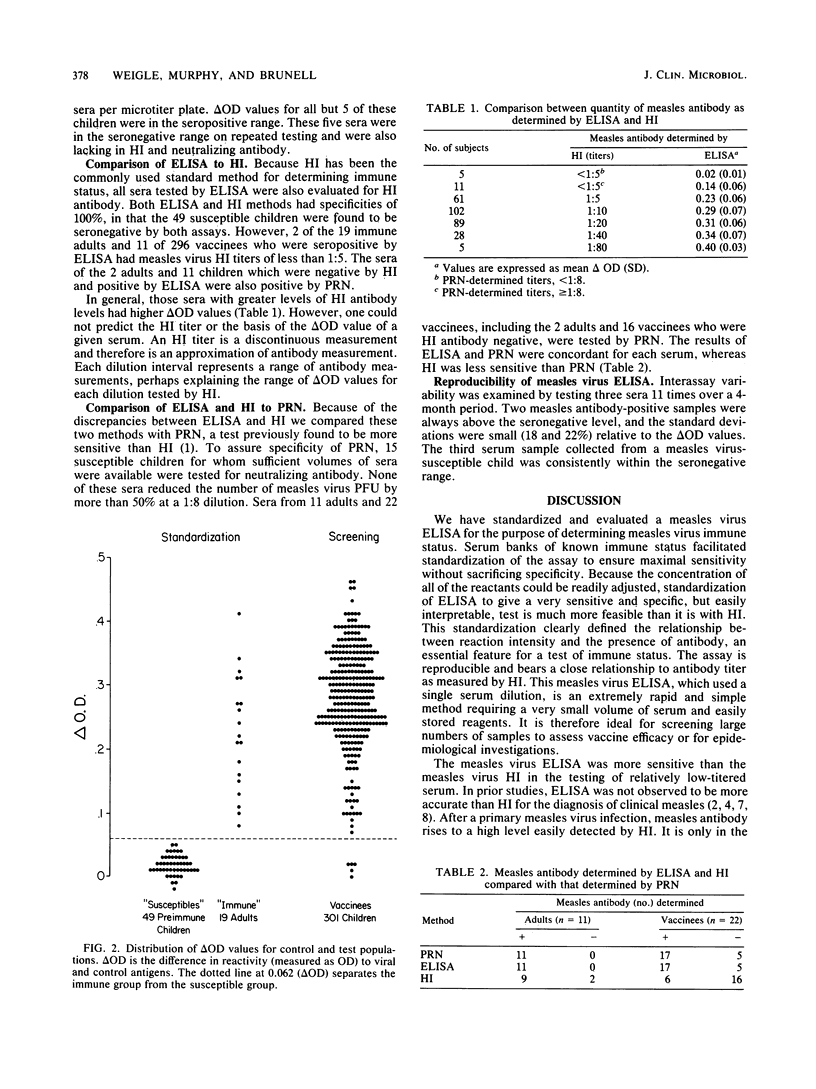
An enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for the determination of immunity to measles virus was developed and standardized; it was compared to the hemagglutination inhibition and plaque reduction neutralization methods for sensitivity and specificity. The conditions of the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay were adjusted such that groups of susceptible and immune individuals were clearly separable on the basis of the reactivity of a single (1:100) dilution of their sera to viral and control antigens. The range of values corresponding to susceptibility and immunity was defined by using the distribution of values observed from testing sera obtained from susceptible and immune control groups. The enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay was then applied in a study of measles vaccinees and found to be more sensitive than the hemagglutination inhibition method and equal in sensitivity to the plaque reduction neutralization method. The three methods were equal in specificity. Thus, the measles virus enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay is a rapid, reproducible, sensitive, and specific method for screening for the presence of measles antibody.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albrecht P., Herrmann K., Burns G. R. Role of virus strain in conventional and enhanced measles plaque neutralization test. J Virol Methods. 1981 Dec;3(5):251–260. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(81)90062-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blomberg J., Nilsson I., Andersson M. Viral antibody screening system that uses a standardized single dilution immunoglobulin G enzyme immunoassay with multiple antigens. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Jun;17(6):1081–1091. doi: 10.1128/jcm.17.6.1081-1091.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boteler W. L., Luipersbeck P. M., Fuccillo D. A., O'Beirne A. J. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for detection of measles antibody. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 May;17(5):814–818. doi: 10.1128/jcm.17.5.814-818.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunell P. A., Weigle K., Murphy M. D., Shehab Z., Cobb E. Antibody response following measles-mumps-rubella vaccine under conditions of customary use. JAMA. 1983 Sep 16;250(11):1409–1412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forghani B., Schmidt N. J. Antigen requirements, sensitivity, and specificity of enzyme immunoassays for measles and rubella viral antibodies. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Jun;9(6):657–664. doi: 10.1128/jcm.9.6.657-664.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayden G. F. Measles vaccine failure. A survey of causes and means of prevention. Clin Pediatr (Phila) 1979 Mar;18(3):155-6, 161-3, 167. doi: 10.1177/000992287901800308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinman A. R., Eddins D. L., Kirby C. D., Orenstein W. A., Bernier R. H., Turner P. M., Jr, Bloch A. B. Progress in measles elimination. JAMA. 1982 Mar 19;247(11):1592–1595. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahane S., Goldstein V., Sarov I. Detection of IgG antibodies specific for measles virus by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Intervirology. 1979;12(1):39–46. doi: 10.1159/000149067. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleiman M. B., Blackburn C. K., Zimmerman S. E., French M. L. Comparison of enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for acute measles with hemagglutination inhibition complement fixation, and fluorescent-antibody methods. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Aug;14(2):147–152. doi: 10.1128/jcm.14.2.147-152.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norrby E., Gollmar Y. Appearance and persistence of antibodies against different virus components after regular measles infections. Infect Immun. 1972 Sep;6(3):240–247. doi: 10.1128/iai.6.3.240-247.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voller A., Bidwell D. E. Enzyme-immunoassays for antibodies in measles, cytomegalovirus infections and after rubella vaccination. Br J Exp Pathol. 1976 Apr;57(2):243–247. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeager A. S., Davis J. H., Ross L. A., Harvey B. Measles immunization. Successes and failures. JAMA. 1977 Jan 24;237(4):347–351. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


