Abstract
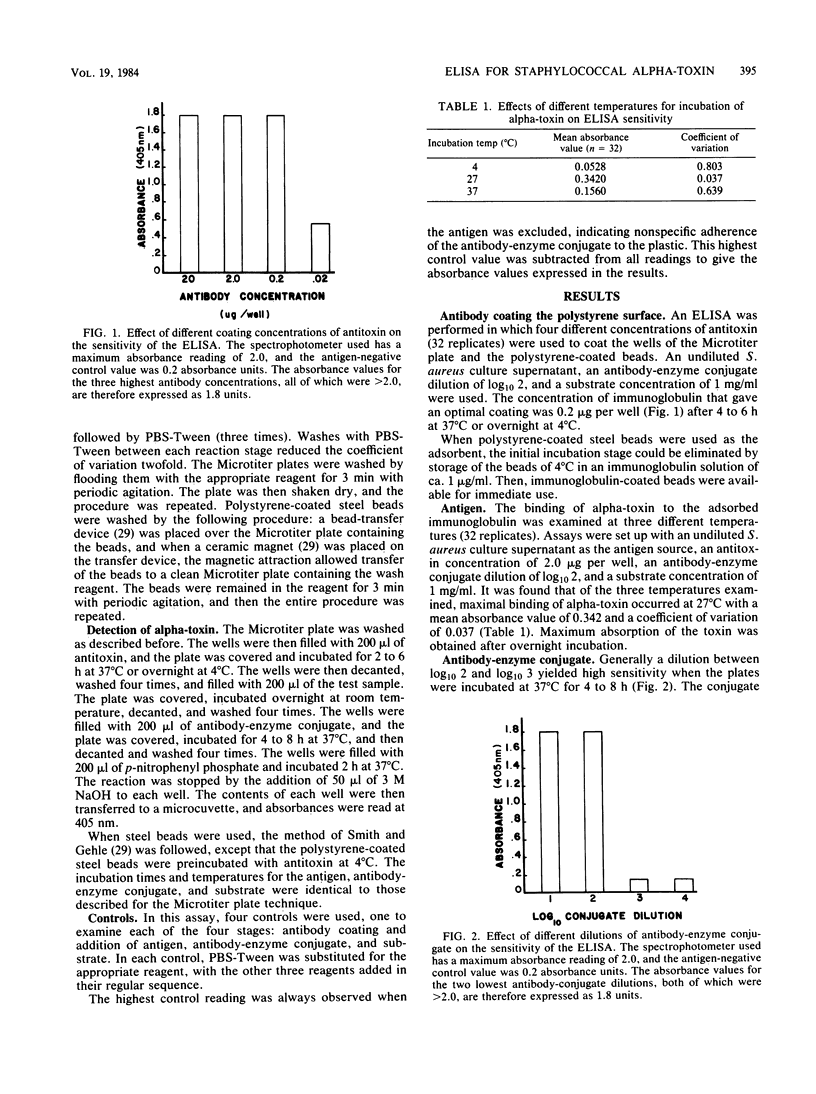
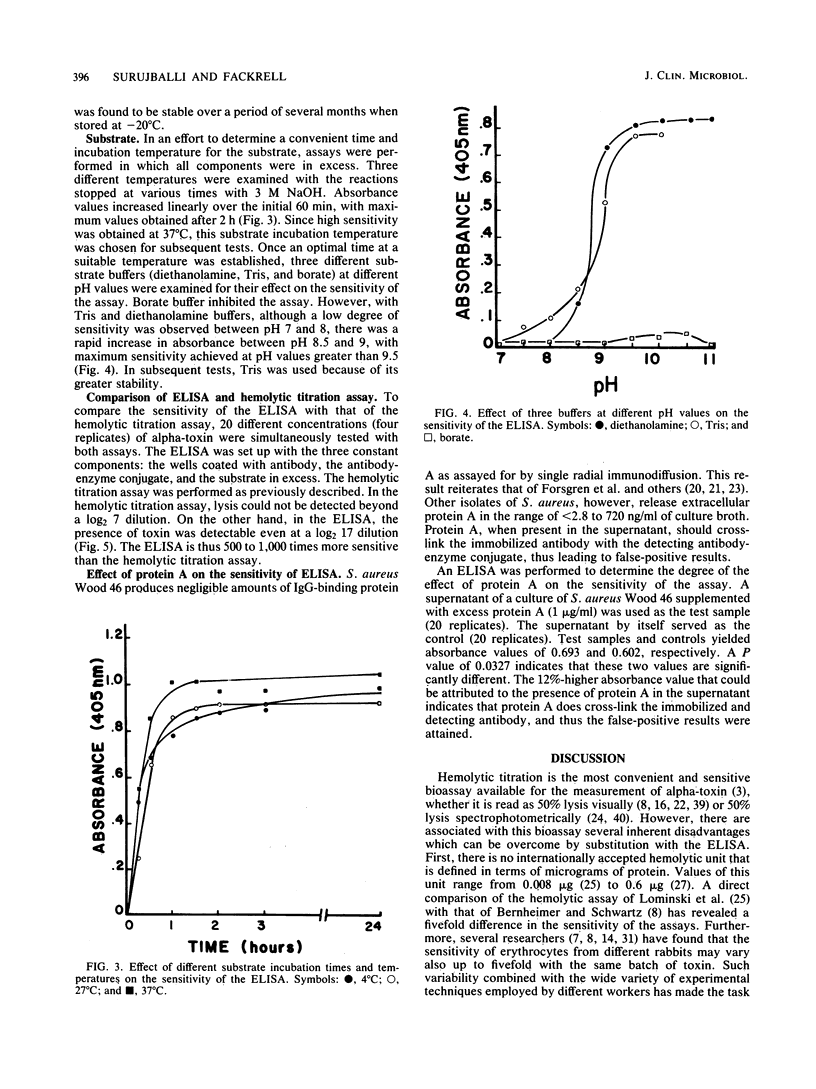
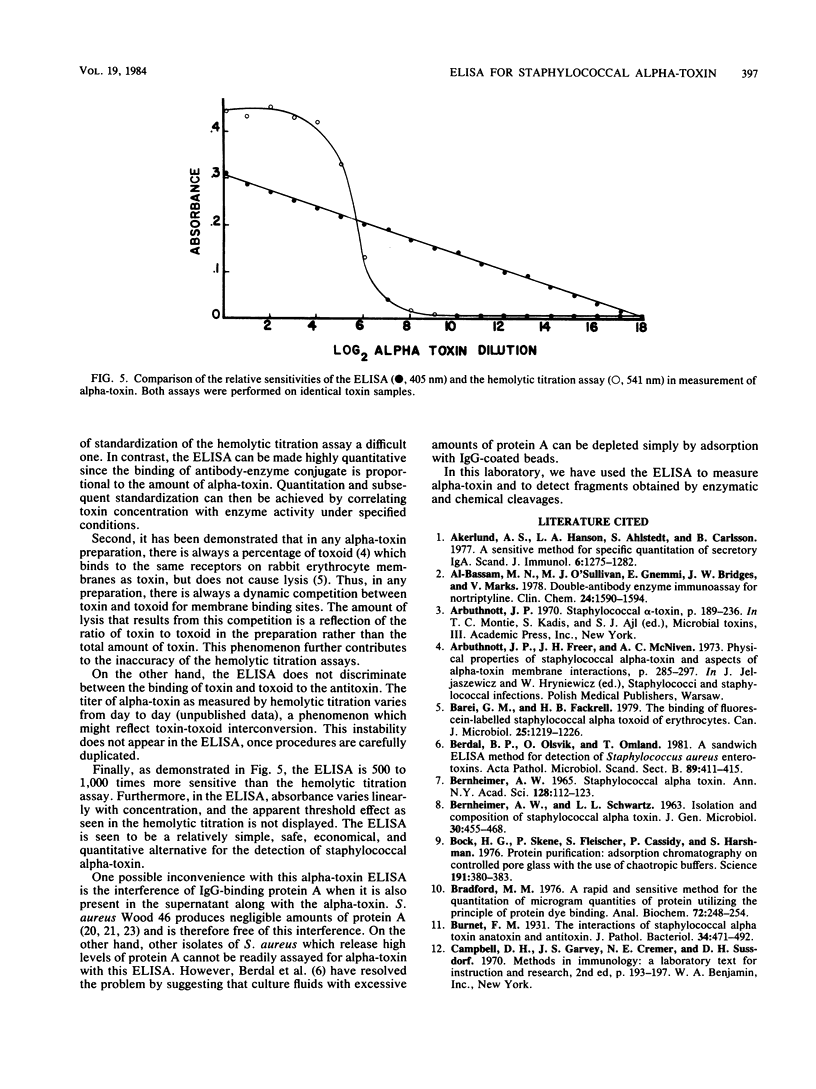
A sandwich enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay was developed for measuring Staphylococcus aureus alpha-toxin. This assay was 500 to 1,000 times more sensitive than the commonly used hemolytic titration assay and was less variable. The binding of alpha-toxin to the adsorbed antibody was most effective after an overnight incubation at 27 degrees C. The toxin was detectable even at a log2 17 dilution of an S. aureus culture supernatant.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akerlund A. S., Hanson L. A., Ahlstedt S., Carlsson B. A sensitive method for specific quantitation of secretory IgA. Scand J Immunol. 1977;6(12):1275–1282. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1977.tb00366.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Al-Bassam M. N., O'Sullivan M. J., Gnemmi E., Bridges J. W., Marks V. Double-antibody enzyme immunoassay for nortriptyline. Clin Chem. 1978 Sep;24(9):1590–1594. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arbuthnott J. P., Freer J. H., McNiven A. C. Physical properties of staphylococcal alpha-toxin and aspects of alpha-toxin membrane interactions. Contrib Microbiol Immunol. 1973;1:285–297. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BERNHEIMER A. W., SCHWARTZ L. L. Isolation and composition of staphylococcal alpha toxin. J Gen Microbiol. 1963 Mar;30:455–468. doi: 10.1099/00221287-30-3-455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barei G. M., Fackrell H. B. The binding of fluorescein-labelled stapbylococcal alpha toxoid to erythrocytes. Can J Microbiol. 1979 Nov;25(11):1219–1226. doi: 10.1139/m79-192. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berdal B. P., Olsvik O., Omland T. A sandwich ELISA method for detection of Staphylococcus aureus enterotoxins. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B. 1981 Dec;89(6):411–415. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernheimer A. W. Staphylococcal alpha toxin. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1965 Jul 23;128(1):112–123. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1965.tb11633.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bock H. G., Skene P., Fleischer S., Cassidy P., Harshman S. Protein purification: adsorption chromatography on controlled pore glass with the use of chaotropic buffers. Science. 1976 Jan 30;191(4225):380–383. doi: 10.1126/science.1859. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark M. F., Adams A. N. Characteristics of the microplate method of enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for the detection of plant viruses. J Gen Virol. 1977 Mar;34(3):475–483. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-34-3-475. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper L. Z., Madoff M. A., Weinstein L. Heat stability and species range of purified staphylococcal alpha-toxin. J Bacteriol. 1966 May;91(5):1686–1692. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.5.1686-1692.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crosson F. J., Jr, Winkelstein J. A., Moxon E. R. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for detection and quantitation of capsular antigen of Haemophilus influenzae type b. Infect Immun. 1978 Nov;22(2):617–619. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.2.617-619.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalen A. B. Spontaneous alpha-toxin mutants of Staphylococcus aureus. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B. 1976 Dec;84B(6):333–338. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1976.tb01949.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engvall E., Perlmann P. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Quantitative assay of immunoglobulin G. Immunochemistry. 1971 Sep;8(9):871–874. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(71)90454-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engvall E., Perlmann P. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, Elisa. 3. Quantitation of specific antibodies by enzyme-labeled anti-immunoglobulin in antigen-coated tubes. J Immunol. 1972 Jul;109(1):129–135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsgren A. Significance of protein a production by staphylococci. Infect Immun. 1970 Nov;2(5):672–673. doi: 10.1128/iai.2.5.672-673.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Füssle R., Bhakdi S., Sziegoleit A., Tranum-Jensen J., Kranz T., Wellensiek H. J. On the mechanism of membrane damage by Staphylococcus aureus alpha-toxin. J Cell Biol. 1981 Oct;91(1):83–94. doi: 10.1083/jcb.91.1.83. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lo C. Y., Fackrell H. B. Immunologic evidence that staphylococcal alpha toxin is oriented on membranes. Can J Microbiol. 1979 Jun;25(6):686–692. doi: 10.1139/m79-099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Sullivan M. J., Bridges J. W., Marks V. Enzyme immunoassay: a review. Ann Clin Biochem. 1979 Sep;16(5):221–240. doi: 10.1177/000456327901600162. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith K. O., Gehle W. D. Semiautomation of Immunoassays by use of magnetic transfer devices. Methods Enzymol. 1980;70(A):388–416. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)70066-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Weemen B. K., Schuurs A. H.W.M. Immunoassay using antigen-enzyme conjugates. FEBS Lett. 1971 Jun 24;15(3):232–236. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(71)80319-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voller A., Bidwell D. E., Bartlett A. Enzyme immunoassays in diagnostic medicine. Theory and practice. Bull World Health Organ. 1976;53(1):55–65. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walls K. W., Bullock S. L., English D. K. Use of the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and its microadaptation for the serodiagnosis of toxoplasmosis. J Clin Microbiol. 1977 Mar;5(3):273–277. doi: 10.1128/jcm.5.3.273-277.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wisdom G. B. Enzyme-immunoassay. Clin Chem. 1976 Aug;22(8):1243–1255. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiseman G. M., Caird J. D. Further observations on the mode of action of the alpha toxin of Staphylococcus aureus "Wood-46". Can J Microbiol. 1972 Jul;18(7):987–992. doi: 10.1139/m72-153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiseman G. M., Caird J. D. Mode of action of the alpha toxin of Staphylococcus aureus. Can J Microbiol. 1970 Jan;16(1):47–50. doi: 10.1139/m70-008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yolken R. H., Greenberg H. B., Merson M. H., Sack R. B., Kapikian A. Z. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for detection of Escherichia coli heat-labile enterotoxin. J Clin Microbiol. 1977 Nov;6(5):439–444. doi: 10.1128/jcm.6.5.439-444.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Knapen F., Panggabean S. O. Detection of circulating antigen during acute infections with Toxoplasma gondii by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. J Clin Microbiol. 1977 Dec;6(6):545–547. doi: 10.1128/jcm.6.6.545-547.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Weemen B. K., Schuurs A. H. Immunoassay using hapten--enzyme conjugates. FEBS Lett. 1972 Jul 15;24(1):77–81. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(72)80830-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


